BeanFactory
spring容器的底层接口,可以根据bean定义的信息,返回对应的实例对象。提供了最简单的容器获取和实例化对象的功能。
ApplicationContext
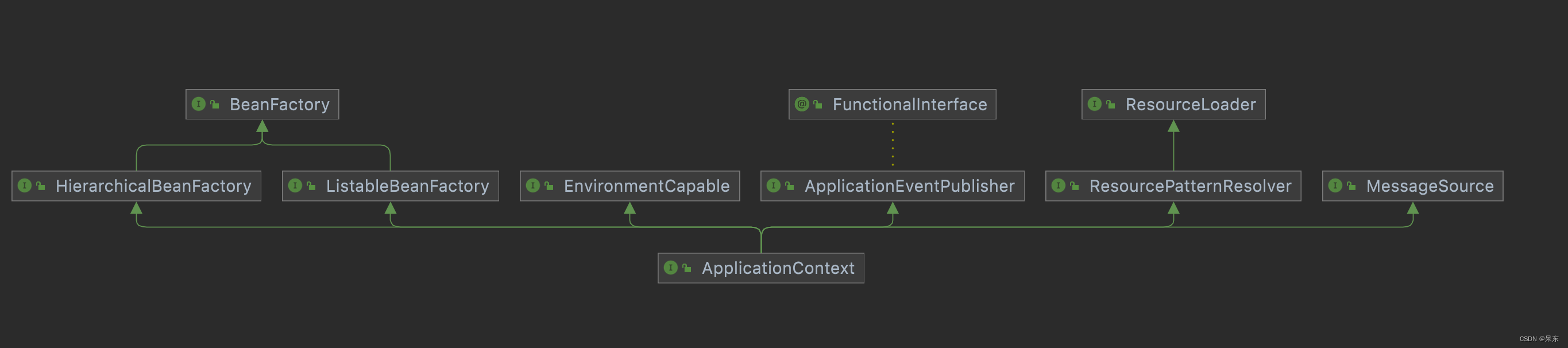
我们从继承图上可以看到ApplicationContext继承自BeanFactory,所以BeanFactory有的功能,都包含其中,并且对于比BeanFactory,提供了更加丰富的功能。增加那些具体的实现了我们可以总ApplicationContext的描述中看到
/* <p>An ApplicationContext provides:
* <ul>
* <li>Bean factory methods for accessing application components.
* Inherited from {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory}.
* <li>The ability to load file resources in a generic fashion.
* Inherited from the {@link org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader} interface.
* <li>The ability to publish events to registered listeners.
* Inherited from the {@link ApplicationEventPublisher} interface.
* <li>The ability to resolve messages, supporting internationalization.
* Inherited from the {@link MessageSource} interface.
* <li>Inheritance from a parent context. Definitions in a descendant context
* will always take priority. This means, for example, that a single parent
* context can be used by an entire web application, while each servlet has
* its own child context that is independent of that of any other servlet.
* </ul>
* /
// ResourceLoader - 提供了文件加载的能力
// ApplicationEventPublisher - 提供了基于事件的发布订阅机制
// MessageSource —— 支持国际化能力
对比代码实现
已BeanFactory的实现类XmlBeanFactory和ApplicationContext的实现类ClassPathXmlApplicationContext来看下两者的具体区别
XmlBeanFactory的构造方法
XmlBeanFactory xmlBeanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("beanFactory.xml")); XmlBeanFactory xmlBeanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("beanFactory.xml"));
// 首先看下创建对象时做了哪些实现,最后具体的调用实现方法如下
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
super(parentBeanFactory);
// 只做了一个事情,就是解析xml文件,转化为BeanDefinition,但是并没有进行实例化,只有在getBean的时候才会具体的实例化,也就是只能进行懒加载处理。
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的构造方法
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beanFactory.xml");
// 最终调用的构造方法
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
// refresh方法
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 类似于BeanFactory的构造方法中做的事情,也就是加载配置文件,构建对应的BeanDefinition
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. // 注册对应的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,其中对于注解的处理,就在此处进行扩展实现,其中一个主要的类就是ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 看方法名就知道对应的就是实现了MessageSource接口,提供了国家化的支持
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 注册对应的多播器,用于后续的事件发布实现
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 可以注册对应的监听器,用于扩展实现
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 支持了非延迟加载bean的实例化操作
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
// 省略部分方法。。。
}
总结
从两个类的构造方法中,我们总结如下
- ApplicationContext提供了即时加载的能力,也就是将未配置为懒加载的bean,在构造方法中,就进行了创建实例化功能,而BeanFactory只做了将bean转化为BeanDefinition,只提供了懒加载的能力。
- ApplicationContext提供了基于事件的发布订阅实现,可以用来实现相关扩展,如SpringMVC中的九大组件的初始化工作,就是基于事件来进行扩展的
- ApplicationContext提供了注解的支持,也就是在invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法中,通过实现了BeanFactroyPostProcessor的ConfigurationClassPostProcessor来支持注解
- ApplicationContext通过initMessageSource来支持国家化操作
- ApplicationnContext支持自己创建和管理BeanPostProcessor通过registerBeanPostProcessors,而BeanFactory需要手动添加BeanPostProcessor






















 384
384











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








