CFSSL is the result of real-world expertise about how the TLS ecosystem on the Web works that you can gain by working at CloudFlare's scale. These are hard-won lessons, applied in code. The rest of this blog post serves as an under-the-hood look at how and why CFSSL works, and how you can use it as a certificate bundler or as a lightweight CA.
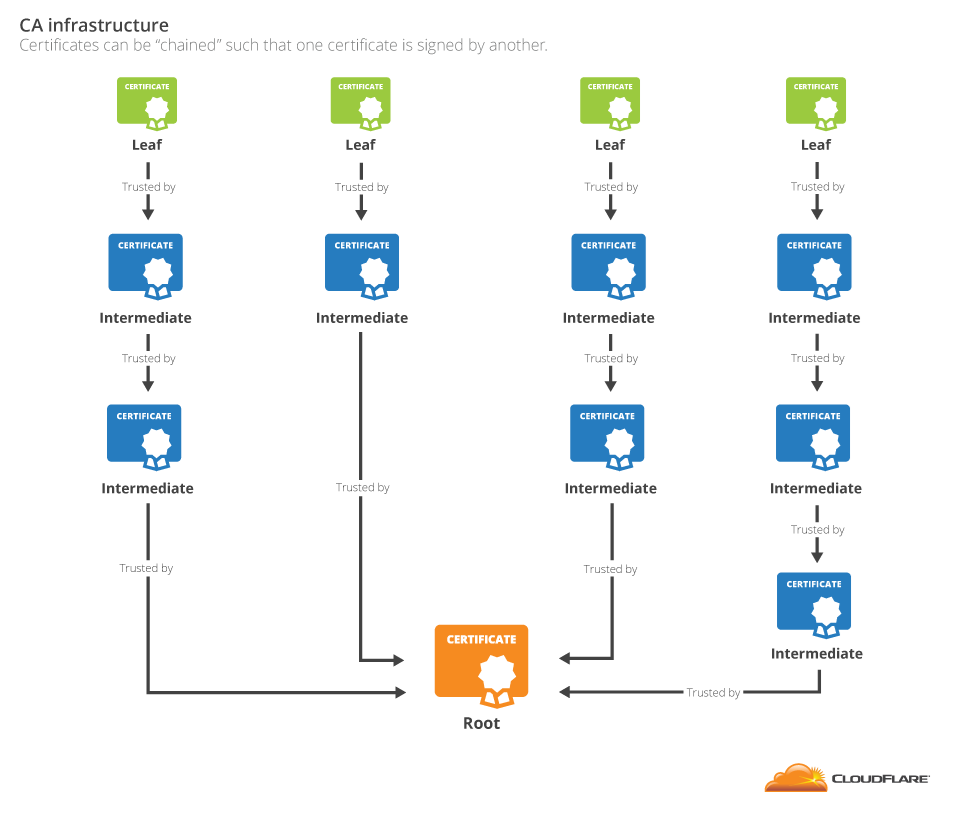
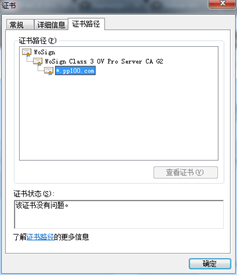
As you can see in the above image, the key is owned by CloudFlare, Inc., and the issuer is GlobalSign (a well-known CA). GlobalSign has issued a certificate named "GlobalSign Extended Validation CA - SHA256 - G2"; this G2 certificate is signed by another certificate called "GlobalSign Root CA - R2". Note that the root certificate does not have an issuer—it is signed by its own private key. In other words, the root vouches for itself.
The reason your browser trusts a root certificate is because browsers have a list of root certificates that they implicitly trust, and when a site is trusted it will show the lock icon to the left of the web address (see image below). Certain certificates are on the list typically because they have been around for some time, and they belong to certificate authorities that have gone through a rigorous security audit. GlobalSign is one of these trusted authorities; therefore, its root certificate is in the list of trusted root certificates for nearly every browser.
What Are SSL Certificates?
SSL certificates form the core of trust on the web by assuring the identity of websites. This trust is built by digitally binding a cryptographic key to an organization's identity. An SSL certificate will bind domain names to server names, and company names to locations. This ensures that if you go to your bank's web site, for example, you know for sure it is your bank, and you are not giving out your information to a phishing scam.
A certificate is a file that contains a public key which is bound to a record of its owner. The mechanism that makes this binding trustworthy is called the Public Key Infrastructure and public-key cryptography is the glue that makes this possible.
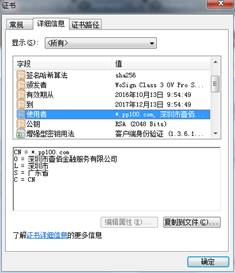
A certificate is associated with a private key that corresponds to the certificate's public key, which is stored separately. The certificate comes with a digital signature from a trusted third-party called a certificate authority or CA. Let's examine the cloudflare.com certificate.
The length of intermediate certificates in a chain can vary, but chains will always have one leaf and one root.
Unfortunately, there is a catch for the owner of the leaf certificate: presenting only the leaf certificate to the browser is usually not enough. The intermediate certificates are not always known to the browser, requiring the website to include them with the leaf certificate. The list of certificates that the browser needs to validate a certificate is called a certificate bundle. It should contain all the certificates in the chain up to the first certificate known to the browser. In the case of the CloudFlare website, this bundle contains both the cloudflare.com certificate and the GlobalSign G2 intermediate.
CFSSL was written to make certificate bundling easier.
之前没接触过证书加密的话,对证书相关的这些概念真是感觉挺棘手的,因为一下子来了一大堆新名词,看起来像是另一个领域的东西,而不是我们所熟悉的编程领域的那些东西,起码我个人感觉如此,且很长时间都没怎么搞懂.写这篇文章的目的就是为了理理清这些概念,搞清楚它们的含义及关联,还有一些基本操作.
SSL
SSL - Secure Sockets Layer,现在应该叫"TLS",但由于习惯问题,我们还是叫"SSL"比较多.http协议默认情况下是不加密内容的,这样就很可能在内容传播的时候被别人监听到,对于安全性要求较高的场合,必须要加密,https就是带加密的http协议,而https的加密是基于SSL的,它执行的是一个比较下层的加密,也就是说,在加密前,你的服务器程序在干嘛,加密后也一样在干嘛,不用动,这个加密对用户和开发者来说都是透明的.More:[维基百科]
OpenSSL - 简单地说,OpenSSL是SSL的一个实现,SSL只是一种规范.理论上来说,SSL这种规范是安全的,目前的技术水平很难破解,但SSL的实现就可能有些漏洞,如著名的"心脏出血".OpenSSL还提供了一大堆强大的工具软件,强大到90%我们都用不到.
证书标准
X.509 - 这是一种证书标准,主要定义了证书中应该包含哪些内容.其详情可以参考RFC5280,SSL使用的就是这种证书标准.
编码格式
同样的X.509证书,可能有不同的编码格式,目前有以下两种编码格式.
PEM - Privacy Enhanced Mail,打开看文本格式,以"-----BEGIN..."开头, "-----END..."结尾,内容是BASE64编码.
查看PEM格式证书的信息:openssl x509 -in certificate.pem -text -noout
Apache和*NIX服务器偏向于使用这种编码格式.
DER - Distinguished Encoding Rules,打开看是二进制格式,不可读.
查看DER格式证书的信息:openssl x509 -in certificate.der -inform der -text -noout
Java和Windows服务器偏向于使用这种编码格式.
相关的文件扩展名
这是比较误导人的地方,虽然我们已经知道有PEM和DER这两种编码格式,但文件扩展名并不一定就叫"PEM"或者"DER",常见的扩展名除了PEM和DER还有以下这些,它们除了编码格式可能不同之外,内容也有差别,但大多数都能相互转换编码格式.
CRT - CRT应该是certificate的三个字母,其实还是证书的意思,常见于*NIX系统,有可能是PEM编码,也有可能是DER编码,大多数应该是PEM编码,相信你已经知道怎么辨别.
CER - 还是certificate,还是证书,常见于Windows系统,同样的,可能是PEM编码,也可能是DER编码,大多数应该是DER编码.
KEY - 通常用来存放一个公钥或者私钥,并非X.509证书,编码同样的,可能是PEM,也可能是DER.
查看KEY的办法:openssl rsa -in mykey.key -text -noout
如果是DER格式的话,同理应该这样了:openssl rsa -in mykey.key -text -noout -inform der
CSR - Certificate Signing Request,即证书签名请求,这个并不是证书,而是向权威证书颁发机构获得签名证书的申请,其核心内容是一个公钥(当然还附带了一些别的信息),在生成这个申请的时候,同时也会生成一个私钥,私钥要自己保管好.做过iOS APP的朋友都应该知道是怎么向苹果申请开发者证书的吧.
查看的办法:openssl req -noout -text -in my.csr (如果是DER格式的话照旧加上-inform der,这里不写了)
PFX/P12 - predecessor of PKCS#12,对*nix服务器来说,一般CRT和KEY是分开存放在不同文件中的,但Windows的IIS则将它们存在一个PFX文件中,(因此这个文件包含了证书及私钥)这样会不会不安全?应该不会,PFX通常会有一个"提取密码",你想把里面的东西读取出来的话,它就要求你提供提取密码,PFX使用的时DER编码,如何把PFX转换为PEM编码?
openssl pkcs12 -in for-iis.pfx -out for-iis.pem -nodes
这个时候会提示你输入提取代码. for-iis.pem就是可读的文本.
生成pfx的命令类似这样:openssl pkcs12 -export -in certificate.crt -inkey privateKey.key -out certificate.pfx -certfile CACert.crt
其中CACert.crt是CA(权威证书颁发机构)的根证书,有的话也通过-certfile参数一起带进去.这么看来,PFX其实是个证书密钥库.
JKS - 即Java Key Storage,这是Java的专利,跟OpenSSL关系不大,利用Java的一个叫"keytool"的工具,可以将PFX转为JKS,当然了,keytool也能直接生成JKS,不过在此就不多表了.
证书编码的转换
PEM转为DER openssl x509 -in cert.crt -outform der -out cert.der
DER转为PEM openssl x509 -in cert.crt -inform der -outform pem -out cert.pem
(提示:要转换KEY文件也类似,只不过把x509换成rsa,要转CSR的话,把x509换成req...)
获得证书
向权威证书颁发机构申请证书
用这命令生成一个csr: openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -new -nodes -keyout my.key -out my.csr
把csr交给权威证书颁发机构,权威证书颁发机构对此进行签名,完成.保留好csr,当权威证书颁发机构颁发的证书过期的时候,你还可以用同样的csr来申请新的证书,key保持不变.
或者生成自签名的证书
openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -new -nodes -x509 -days 3650 -keyout key.pem -out cert.pem
在生成证书的过程中会要你填一堆的东西,其实真正要填的只有Common Name,通常填写你服务器的域名,如"yourcompany.com",或者你服务器的IP地址,其它都可以留空的.
生产环境中还是不要使用自签的证书,否则浏览器会不认,或者如果你是企业应用的话能够强制让用户的浏览器接受你的自签证书也行.向权威机构要证书通常是要钱的,但现在也有免费的,仅仅需要一个简单的域名验证即可.有兴趣的话查查"沃通数字证书".
根证书
证书信任
证书链
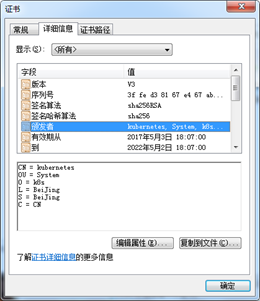
- "CN":Common Name,kube-apiserver 从证书中提取该字段作为请求的用户名 (User Name);浏览器使用该字段验证网站是否合法;
- "O":Organization,kube-apiserver 从证书中提取该字段作为请求用户所属的组 (Group);
[root@node85 ssl]# cat ca-csr.json
{
"CN": "kubernetes",
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size": 2048
},
"names": [
{
"C": "CN",
"ST": "BeiJing",
"L": "BeiJing",
"O": "k8s",
"OU": "System"
}
]
}
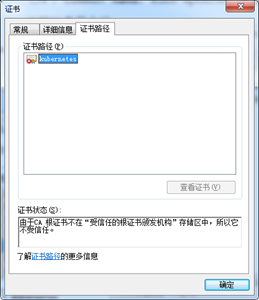
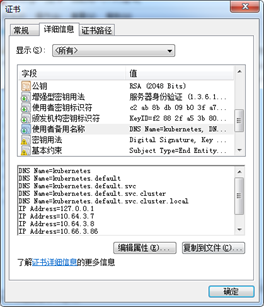
在开始运行中输入certmgr.msc,打开证书管理器























 775
775

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








