对于一个文件描述符,默认都是阻塞IO
非阻塞IO
fcntl函数原型
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ..../* arg */ );
传入的cmd的值不同, 后⾯面追加的参数也不相同.
fcntl函数有5种功能:
- 复制一个现有的描述符(cmd=F_DUPFD).
- 获得/设置文件描述符标记(cmd=FGETFD 或 FSETFD).
- 获得/设置文件状态标记(cmd=FGETFL 或 FSETFL).
- 获得/设置异步I/O所有权(cmd=FGETOWN 或 FSETOWN).
- 获得/设置记录锁(cmd=FGETLK,FSETLK或F_SETLKW).
这里我们只是用第三种功能,获取/设置文件状态标记,就可以将一个文件描述符设置为非阻塞
该段代码是使用轮询方式读取标准输入
3 #include <fcntl.h>
4 #include <unistd.h>
5 #include <stdio.h>
6
7 void SetNonBlock(int fd)
8 {
9 int fl = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL);
10 if( fl < 0 ){
11 perror("fcntl");
12 return;
13 }
14 fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, fl | O_NONBLOCK);
15 }
16
17 int main()
18 {
19 SetNonBlock(0); //将标准输入文件描述符设置为非阻塞
20 while(1){ //循环读取,即轮询
21 char buf[1024];
22 ssize_t read_size = read(0, buf, sizeof(buf)-1);
23 if( read_size < 0 ){
24 perror("read");
25 sleep(1);
26 continue;
27 }
28 printf("input:%s\n", buf);
29 }
30 return 0;
31 }
那么此处我们可以引出一个概念,重定向
重定向
1.dup/dup2系统调用
函数原型
#include <unistd.h>
int dup(int oldfd);
int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
使用·dup将标准输出重定向到文件中
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <unistd.h>
3 #include <fcntl.h>
4
5 int main()
6 {
7 int fd = open("./log", O_CREAT | O_RDWR);
8 if( fd < 0 ){
9 perror("open");
10 return 1;
11 }
12 close(1);
13 int new_fd = dup(fd);
14 if( new_fd != 1 ){
15 perror("dup");
16 return 2;
17 }
18 printf("new_fd: %d\n", new_fd);
19 close(fd);
20
21 for(;;){
22 char buf[1024] = {0};
23 ssize_t read_size = read(0, buf, sizeof(buf)-1);
24 if(read_size < 0){
25 perror("read");
26 continue;
27 }
28 printf("%s", buf);
29 fflush(stdout);
30 }
31 close(new_fd);
32 return 0;
33 }
运行结果如下:
使用dup2将标准输出重定向到文件中
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main()
{
int fd = open("./log", O_CREAT | O_RDWR);
if( fd < 0 ){
perror("open");
return 1;
}
close(1);
dup2(fd, 1); //newfd为1,是fd的拷贝,所以1里面存放的是fd的内容
for(;;){
char buf[1024];
ssize_t read_size = read(0, buf, sizeof(buf));
if( read_size < 0 ){
perror("read");
break;
}
printf("%s", buf);
fflush(stdout);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
IO多路转接之select
首先我们要明确一点,无论它怎么工作,以何种方式工作,它的目的只有一个那就是等(等多个文件描述符),即它最根本的工作机制就是等待内核将数据准备好,直到被监视的多个文件描述符中的一个或者多个状态发生了改变
函数原型:
#include <sys/select.h>
int select(int nfds, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds, fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *timeout);
参数解释:
- 参数nfds是需要监视的最大的⽂文件描述符值+1;
- rdset,wrset,exset分别对应于需要检测的可读文件描述符的集合,可写文件描述符的集 合及异常文件描述符的集合;
关于fd_set
其实这个结构就是一个整数数组, 更严格的说, 是一个 "位图". 使用位图中对应的位来表示要监视的文件描述 符. 提供了一组操作fd_set的接口, 来比较方便的操作位图
void FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set *set); // 用来清除描述词组set中相关fd 的位
int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *set); // 用来测试描述词组set中相关fd 的位是否为真
void FD_SET(int fd, fd_set *set); // 用来设置描述词组set中相关fd的位
void FD_ZERO(fd_set *set); // 用来清除描述词组set的全部位
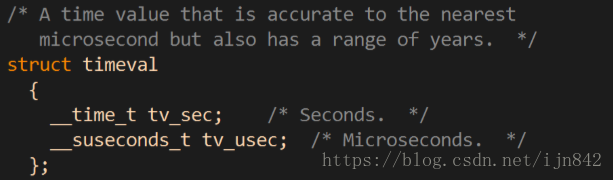
- 参数timeout为结构timeval,用来设置select()的等待时间
timeval结构用于描述一段时间长度,如果在这个时间内,需要监视的描述符没有事件发生则函数返回,返回值为0。
- 执行成功则返回文件描述词状态已改变的个数
- 如果返回0代表在描述词状态改变前已超过timeout时间,没有返回
- 当有错误发生时则返回-1,错误原因存于errno,此时参数readfds,writefds, exceptfds和timeout 的值变成不可预测。
select使用实例1:检测标准输入
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>











 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章














 1146
1146











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








