在Spring中,每个bean都有相应的生命周期。而且Spring为bean提供了丰富的和生命周
期有关的方法对bean进行处理。我们可以通过这些方法对bean进行细致地处理。大体来说,
Spring中Bean的生命周期可以分为两个阶段:第一个是实例化Bean时所经历的一系列阶段;
第二个是Bean的作用范围。
依赖关系注入之后的行为
Spring提供了两种方式在Bean全部属性设置成功后执行特定的行为:
第一,使用配置文件的init-method属性;
第二,实现InitializingBean接口。
这两种方式都是在Bean属性注入成功后执行。如果两个都有,那么先执行InitializingBean接
口中定义的方法,然后执行init-method属性指定的方法。该属性指定的方法名可以是任意的名称。
两种方式达到的效果一样,因此没有必要两种方式都用。推荐使用init-method属性指定这种方法,
这样的话,自己定义的Bean可以不和Spring API耦合在一起,依然是个POJO对象
Bean销毁之前的行为
Spring提供了两种方法定制Bean实例销毁之前的行为:第一,使用destroy-method属性;
第二,实现DisposableBean接口。
如果两种方式都指定了,那么先执行DisposableBean接口中定义的方法,再执行
destroy-method属性指定的方法。该方法可以是任何名字,没有特殊要求。因为两种方式完
成的功能相同,没有必要两种都用。推荐使用destroy-method属性指定方法,这样可以不和
Spring API耦合,减少代码污染。
实现BeanNameAware接口,可以在Bean实例中获得Bean在配置文件中指定的id名称
实现BeanFactoryAware接口,可以在Bean实例中获得BeanFactory实例
实现ApplicationContextAware接口,可以在Bean实例中获得该Bean所在的Spring容器
后处理器
Bean后处理器BeanPostProcessor,会在Bean实例创建成功后,对Bean实例进行处理。
该接口的postProcessBeforeInitial方法会在调用init-method指定的方法和InitializingBean接口
的方法之前调用,对Bean进行处理,postProcessAfterInitialization会在init-method属性指定
的方法和InitializingBean接口的方法之后调用
Bean后处理器InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor是BeanPostProcessor后处理器的
子接口。该接口会在实例化一个Bean之前调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法处理,实例
化Bean后依次调用postProcessAfterInstantiation方法和postProcessPropertyValues方法处理。
容器后处理器BeanFactoryPostProcessor在容器启动后执行一次。Spring中还提供了其他
的容器后处理器,这些后处理器都是在容器启动时执行一次。完成一些整个过程只需执行一次
的行为为
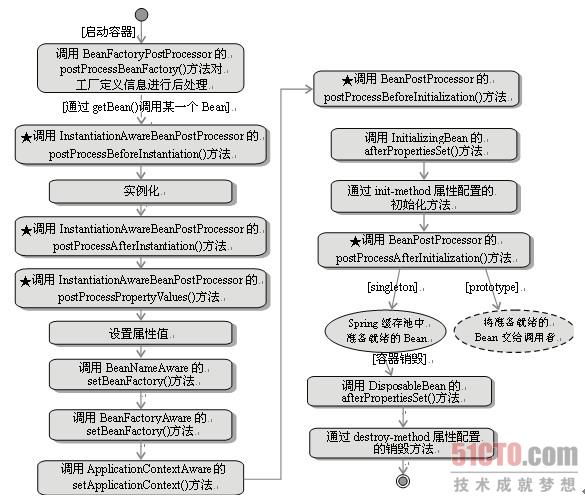
上面是和Bean的生命相关的一些知识的简要介绍,下面是Bean在ApplicationContext中的完整
生命周期图:
之后一个完整的测试例子。在这里作者先给出作者的运行结果,和上图的流程一模一样
调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory().
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInstantiation
调用Car()构造函数......
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInstantiation
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessPropertyValues
调用setBrand()设置属性......
调用setMaxSpeed()设置属性......
调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName()
调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()
调用ApplicationContextAware.setApplicationContext()
BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization
调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()。
调用init-method所指定的myInit(),将maxSpeed设置为240.
BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization
brand: hongqi; color: null; maxSpeed: 240
调用DisposableBean.destroy()。
调用destroy-method所指定的myDestroy().
下面是完整的实例。读者可以试一试,也可以改一改。像上图所示,Bean是singleton还是
prototype,应用程序是否获取Bean,都有不同的结果。这样可以加深印象。
主测试类
package lee;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.baobaotao.Car;
public class SpringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Car c = (Car)ctx.getBean("car");
c.introduce();
((AbstractApplicationContext)ctx).registerShutdownHook();
}
}实现接口的Bean类
package com.baobaotao;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
public class Car implements BeanNameAware, ApplicationContextAware, BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private String brand;
private String color;
private int maxSpeed;
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
private String beanName;
private ApplicationContext context;
public Car() {
System.out.println("调用Car()构造函数......");
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
System.out.println("调用setColor()设置属性......");
this.color = color;
}
public int getMaxSpeed() {
return maxSpeed;
}
public void setMaxSpeed(int maxSpeed) {
System.out.println("调用setMaxSpeed()设置属性......");
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
System.out.println("调用setBrand()设置属性......");
this.brand = brand;
}
public void introduce() {
System.out.println("brand: "+ brand +"; color: "+ color +"; maxSpeed: " + maxSpeed);
}
public void setBeanName(String beanName) {
System.out.println("调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName()");
this.beanName = beanName;
}
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()");
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("调用ApplicationContextAware.setApplicationContext()");
this.context = context;
}
public void myInit() {
System.out.println("调用init-method所指定的myInit(),将maxSpeed设置为240.");
this.maxSpeed = 240;
}
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()。");
}
public void myDestroy() {
System.out.println("调用destroy-method所指定的myDestroy().");
}
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("调用DisposableBean.destroy()。");
}
}
BeanPostProcessor实现类
package com.baobaotao.beanfactory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object arg0, String arg1) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization");
return arg0;
}
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object arg0, String arg1) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization");
return arg0;
}
}
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor实现类
package com.baobaotao.beanfactory;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object arg0, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInstantiation");
return true;
}
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> arg0, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInstantiation");
return null;
}
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] arg1, Object arg2, String arg3) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessPropertyValues");
return pvs;
}
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object arg0, String arg1) throws BeansException {
return arg0;
}
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object arg0, String arg1) throws BeansException {
return arg0;
}
}
BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现类
package com.baobaotao.beanfactory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory bf) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory().");
}
}
Spring配置文件中的配置的内容
<bean id="car" class="com.baobaotao.Car" init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestroy">
<property name="brand" value="hongqi"></property>
<property name="maxSpeed" value="200"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="myInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor" class="com.baobaotao.beanfactory.MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor"></bean>
<bean id="myBeanPostProcessor" class="com.baobaotao.beanfactory.MyBeanPostProcessor"></bean>
<bean id="myBeanFactoryPostProcessor" class="com.baobaotao.beanfactory.MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor"></bean>





















 373
373

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








