对话框大合集
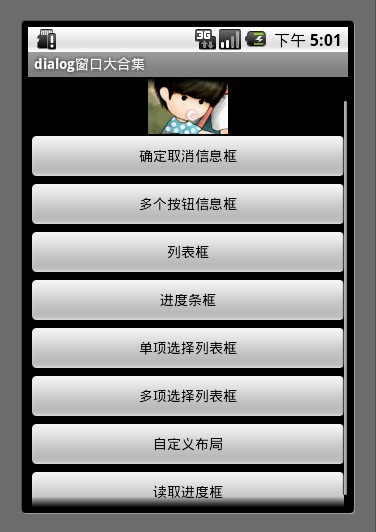
1.确定取消对话框
对话框中有2个按钮 通过调用 setPositiveButton 方法 和 setNegativeButton 方法 可以设置按钮的显示内容以及按钮的监听事件。
雨松MOMO原创文章如转载,请注明:转载自雨松MOMO的博客原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/xys289187120/article/details/6601613
雨松MOMO带大家盘点Android 中的对话框
今天我用自己写的一个Demo 和大家详细介绍一个Android中的对话框的使用技巧。
今天我用自己写的一个Demo 和大家详细介绍一个Android中的对话框的使用技巧。

1.确定取消对话框
对话框中有2个按钮 通过调用 setPositiveButton 方法 和 setNegativeButton 方法 可以设置按钮的显示内容以及按钮的监听事件。

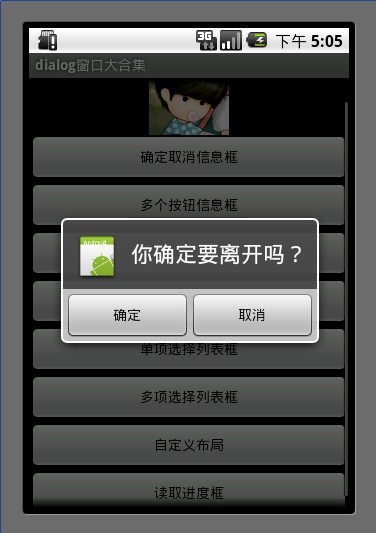
我们使用AlerDialog 创建对话框
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this);
使用builder设置对话框的title button icon 等等
builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon); builder.setTitle("你确定要离开吗?"); builder.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { //这里添加点击确定后的逻辑 showDialog("你选择了确定"); } }); builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { //这里添加点击确定后的逻辑 showDialog("你选择了取消"); } }); builder.create().show();
这个dialog用于现实onClick后监听的内容信息
private void showDialog(String str) { new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this) .setMessage(str) .show(); }
2.多个按钮信息框

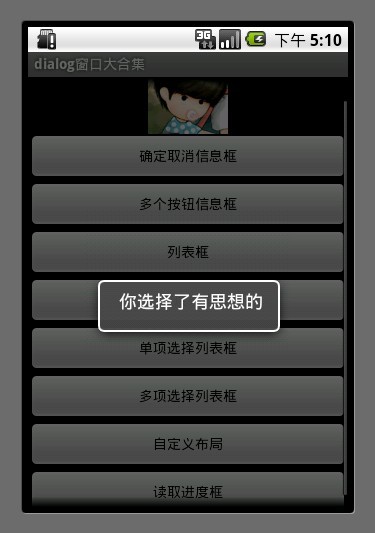
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this); builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon); builder.setTitle("投票"); builder.setMessage("您认为什么样的内容能吸引您?"); builder.setPositiveButton("有趣味的", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { showDialog("你选择了有趣味的"); } }); builder.setNeutralButton("有思想的", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { showDialog("你选择了有思想的"); } }); builder.setNegativeButton("主题强的", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { showDialog("你选择了主题强的"); } }); builder.create().show();
3.列表框

这个数组用于列表选择
final String[] mItems = {"item0","item1","itme2","item3","itme4","item5","item6"};
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this); builder.setTitle("列表选择框"); builder.setItems(mItems, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { //点击后弹出窗口选择了第几项 showDialog("你选择的id为" + which + " , " + mItems[which]); } }); builder.create().show();
4.单项选择列表框
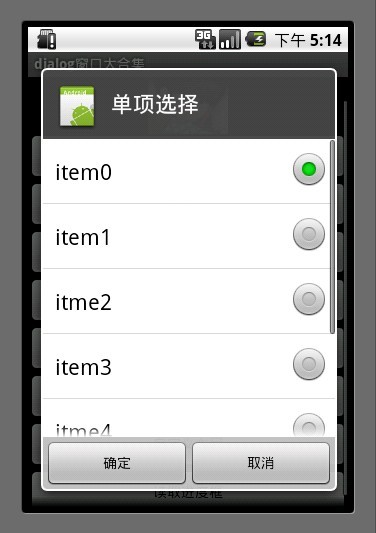
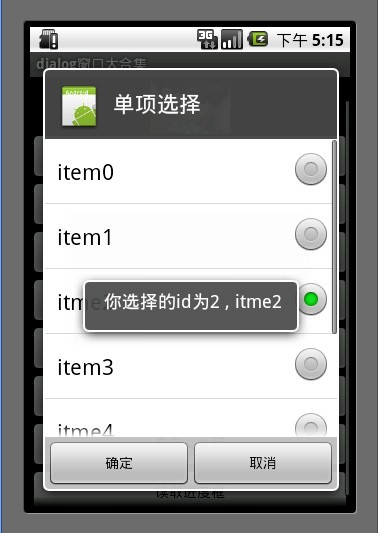
mSingleChoice 用于记录单选中的ID
int mSingleChoiceID = -1; AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this); mSingleChoiceID = -1; builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon); builder.setTitle("单项选择"); builder.setSingleChoiceItems(mItems, 0, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { mSingleChoiceID = whichButton; showDialog("你选择的id为" + whichButton + " , " + mItems[whichButton]); } }); builder.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { if(mSingleChoiceID > 0) { showDialog("你选择的是" + mSingleChoiceID); } } }); builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { } }); builder.create().show();
5.进度条框
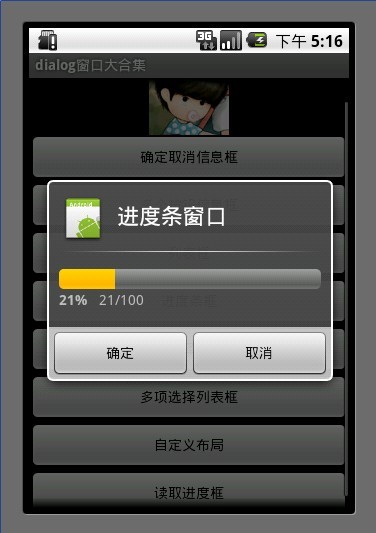
点击进度条框按钮后 开启一个线程计算读取的进度 假设读取结束为 100
Progress在小于100的时候一直在线程中做循环++ 只到读取结束后,停止线程。
mProgressDialog = new ProgressDialog(MainDialog.this); mProgressDialog.setIcon(R.drawable.icon); mProgressDialog.setTitle("进度条窗口"); mProgressDialog.setProgressStyle(ProgressDialog.STYLE_HORIZONTAL); mProgressDialog.setMax(MAX_PROGRESS); mProgressDialog.setButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { //这里添加点击后的逻辑 } }); mProgressDialog.setButton2("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { //这里添加点击后的逻辑 } }); mProgressDialog.show(); new Thread(this).start(); public void run() { int Progress = 0; while(Progress < MAX_PROGRESS) { try { Thread.sleep(100); Progress++; mProgressDialog.incrementProgressBy(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }
6.多项选择列表框
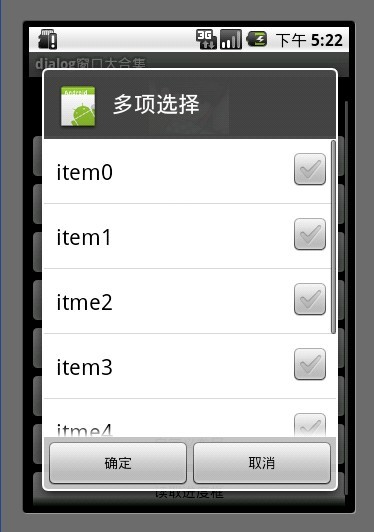
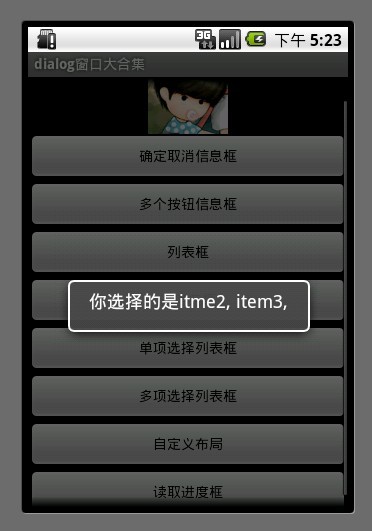
MultiChoiceID 用于记录多选选中的id号 存在ArrayList中
选中后 add 进ArrayList
取消选中后 remove 出ArrayList 。
ArrayList <Integer>MultiChoiceID = new ArrayList <Integer>();
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this); MultiChoiceID.clear(); builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon); builder.setTitle("多项选择"); builder.setMultiChoiceItems(mItems, new boolean[]{false, false, false, false, false, false, false}, new DialogInterface.OnMultiChoiceClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton, boolean isChecked) { if(isChecked) { MultiChoiceID.add(whichButton); showDialog("你选择的id为" + whichButton + " , " + mItems[whichButton]); }else { MultiChoiceID.remove(whichButton); } } }); builder.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { String str = ""; int size = MultiChoiceID.size(); for (int i = 0 ;i < size; i++) { str+= mItems[MultiChoiceID.get(i)] + ", "; } showDialog("你选择的是" + str); } }); builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { } }); builder.create().show();
7.自定义布局
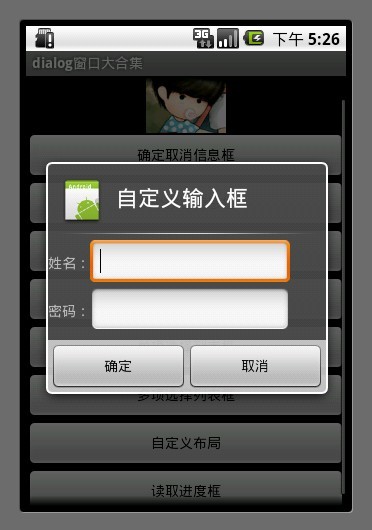
讲到自定义布局我就得多说一说了,为什么要多说一说呢?
其实自定义布局在Android的开发中非常重要 因为它能让开发者做出自己五彩缤纷的Activity 而不用去使用系统枯燥的界面。
自定义dialog有什么好处?
比如我们在开发过长当中 要通过介绍系统发送的一个广播弹出一个dialog . 但是dialog必需是基于activity才能呈现出来 如果没有activity 的话 程序就会崩溃。所以我们可以写一个自定义的 dialog 把它定义成一个activity
这样我们收到一条打开dialog的广播后 直接启动这个 activity 程序正常运行~~
这就是自定义dialog的好处。
注明:下面这个例子只是写了自定义dialog 没有把它单独的写在一个activity中 如果须要的话 可以自己改一下。
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this); LayoutInflater factory = LayoutInflater.from(this); final View textEntryView = factory.inflate(R.layout.test, null); builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon); builder.setTitle("自定义输入框"); builder.setView(textEntryView); builder.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { EditText userName = (EditText) textEntryView.findViewById(R.id.etUserName); EditText password = (EditText) textEntryView.findViewById(R.id.etPassWord); showDialog("姓名 :" + userName.getText().toString() + "密码:" + password.getText().toString() ); } }); builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { } }); builder.create().show();
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" android:id="@+id/dialog"> <LinearLayout android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" android:id="@+id/dialogname"> <TextView android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/tvUserName" android:text="姓名:" /> <EditText android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/etUserName" android:minWidth="200dip"/> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" android:id="@+id/dialognum" android:layout_below="@+id/dialogname" > <TextView android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/tvPassWord" android:text="密码:" /> <EditText android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/etPassWord" android:minWidth="200dip"/> </LinearLayout> </RelativeLayout>
8.读取进度框
显示一个正在转圈的进度条loading
mProgressDialog = new ProgressDialog(this); mProgressDialog.setTitle("读取ing"); mProgressDialog.setMessage("正在读取中请稍候"); mProgressDialog.setIndeterminate(true); mProgressDialog.setCancelable(true); mProgressDialog.show();
最后如果你还是觉得我写的不够详细 不要紧我把源代码的下载地址贴出来 欢迎大家一起讨论学习 雨松MOMO希望可以和大家一起进步。
下载地址 :http://download.csdn.net/source/3438085
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this);
使用builder设置对话框的title button icon 等等
builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon); builder.setTitle("你确定要离开吗?"); builder.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { //这里添加点击确定后的逻辑 showDialog("你选择了确定"); } }); builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { //这里添加点击确定后的逻辑 showDialog("你选择了取消"); } }); builder.create().show();
这个dialog用于现实onClick后监听的内容信息
private void showDialog(String str) { new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this) .setMessage(str) .show(); }
2.多个按钮信息框


AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this); builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon); builder.setTitle("投票"); builder.setMessage("您认为什么样的内容能吸引您?"); builder.setPositiveButton("有趣味的", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { showDialog("你选择了有趣味的"); } }); builder.setNeutralButton("有思想的", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { showDialog("你选择了有思想的"); } }); builder.setNegativeButton("主题强的", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { showDialog("你选择了主题强的"); } }); builder.create().show();
3.列表框

这个数组用于列表选择
final String[] mItems = {"item0","item1","itme2","item3","itme4","item5","item6"};
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this); builder.setTitle("列表选择框"); builder.setItems(mItems, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { //点击后弹出窗口选择了第几项 showDialog("你选择的id为" + which + " , " + mItems[which]); } }); builder.create().show();
4.单项选择列表框


mSingleChoice 用于记录单选中的ID
int mSingleChoiceID = -1; AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this); mSingleChoiceID = -1; builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon); builder.setTitle("单项选择"); builder.setSingleChoiceItems(mItems, 0, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { mSingleChoiceID = whichButton; showDialog("你选择的id为" + whichButton + " , " + mItems[whichButton]); } }); builder.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { if(mSingleChoiceID > 0) { showDialog("你选择的是" + mSingleChoiceID); } } }); builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { } }); builder.create().show();
5.进度条框

点击进度条框按钮后 开启一个线程计算读取的进度 假设读取结束为 100
Progress在小于100的时候一直在线程中做循环++ 只到读取结束后,停止线程。
mProgressDialog = new ProgressDialog(MainDialog.this); mProgressDialog.setIcon(R.drawable.icon); mProgressDialog.setTitle("进度条窗口"); mProgressDialog.setProgressStyle(ProgressDialog.STYLE_HORIZONTAL); mProgressDialog.setMax(MAX_PROGRESS); mProgressDialog.setButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { //这里添加点击后的逻辑 } }); mProgressDialog.setButton2("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { //这里添加点击后的逻辑 } }); mProgressDialog.show(); new Thread(this).start(); public void run() { int Progress = 0; while(Progress < MAX_PROGRESS) { try { Thread.sleep(100); Progress++; mProgressDialog.incrementProgressBy(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }
6.多项选择列表框


MultiChoiceID 用于记录多选选中的id号 存在ArrayList中
选中后 add 进ArrayList
取消选中后 remove 出ArrayList 。
ArrayList <Integer>MultiChoiceID = new ArrayList <Integer>();
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this); MultiChoiceID.clear(); builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon); builder.setTitle("多项选择"); builder.setMultiChoiceItems(mItems, new boolean[]{false, false, false, false, false, false, false}, new DialogInterface.OnMultiChoiceClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton, boolean isChecked) { if(isChecked) { MultiChoiceID.add(whichButton); showDialog("你选择的id为" + whichButton + " , " + mItems[whichButton]); }else { MultiChoiceID.remove(whichButton); } } }); builder.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { String str = ""; int size = MultiChoiceID.size(); for (int i = 0 ;i < size; i++) { str+= mItems[MultiChoiceID.get(i)] + ", "; } showDialog("你选择的是" + str); } }); builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { } }); builder.create().show();
7.自定义布局

讲到自定义布局我就得多说一说了,为什么要多说一说呢?
其实自定义布局在Android的开发中非常重要 因为它能让开发者做出自己五彩缤纷的Activity 而不用去使用系统枯燥的界面。
自定义dialog有什么好处?
比如我们在开发过长当中 要通过介绍系统发送的一个广播弹出一个dialog . 但是dialog必需是基于activity才能呈现出来 如果没有activity 的话 程序就会崩溃。所以我们可以写一个自定义的 dialog 把它定义成一个activity
这样我们收到一条打开dialog的广播后 直接启动这个 activity 程序正常运行~~
这就是自定义dialog的好处。
注明:下面这个例子只是写了自定义dialog 没有把它单独的写在一个activity中 如果须要的话 可以自己改一下。
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this); LayoutInflater factory = LayoutInflater.from(this); final View textEntryView = factory.inflate(R.layout.test, null); builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon); builder.setTitle("自定义输入框"); builder.setView(textEntryView); builder.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { EditText userName = (EditText) textEntryView.findViewById(R.id.etUserName); EditText password = (EditText) textEntryView.findViewById(R.id.etPassWord); showDialog("姓名 :" + userName.getText().toString() + "密码:" + password.getText().toString() ); } }); builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) { } }); builder.create().show();
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" android:id="@+id/dialog"> <LinearLayout android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" android:id="@+id/dialogname"> <TextView android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/tvUserName" android:text="姓名:" /> <EditText android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/etUserName" android:minWidth="200dip"/> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" android:id="@+id/dialognum" android:layout_below="@+id/dialogname" > <TextView android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/tvPassWord" android:text="密码:" /> <EditText android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/etPassWord" android:minWidth="200dip"/> </LinearLayout> </RelativeLayout>
8.读取进度框
显示一个正在转圈的进度条loading
mProgressDialog = new ProgressDialog(this); mProgressDialog.setTitle("读取ing"); mProgressDialog.setMessage("正在读取中请稍候"); mProgressDialog.setIndeterminate(true); mProgressDialog.setCancelable(true); mProgressDialog.show();
最后如果你还是觉得我写的不够详细 不要紧我把源代码的下载地址贴出来 欢迎大家一起讨论学习 雨松MOMO希望可以和大家一起进步。
下载地址 :http://download.csdn.net/source/3438085




















 494
494

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








