目录
2.2)创建一个空的maven工程,然后导入springboot相关的jar包
2.3)通过sts/idea创建 一个springboot项目
为啥我只要引入 spring-boot-starter-parent 和 spring-boot-starter-web就可以快速开发mvc的项目
3.2) 我们来分析看下 spring-boot-starter-web(场景启动器)为我项目中导入 web开发需要的jar包依赖
6.1)什么是webJar:以jar包的形式来引入前端资源,比如jquery 或者是BootStraphttps://www.webjars.org/
6.2)springboot是如何整合springmvc功能的(WebMvcAutoConfiguration)
7)如何全面接管springboot的mvc配置(让springboot给我们自动配置的功能失效,自己像如何整合ssm一样的整合springmvc,不推荐)
8.1)我们来看springboot为我们自动配置的异常处理的一些bean
第一节:springboot快速开始
一:springboot 微服务开发利器
1.1)什么是微服务,微服务和微服务架构的区别?
目前而已,对于微服务业界没有一个统一的标准定义,但是通常而言提倡把一个单一的应用程序划分为一组小
的服务,
每个小的服务都会运行在自己的进程中,服务之间通过轻量级的通信机制(http的rest api)进行通信,那么
一个个的
小服务就是微服务。
①:单体架构与微服务架构图示

传统的的单一电商应用来说,订单,支付,用户,商品,库存等模块都在一个项目中,若某一个模块出
现线上bug,会导致整个版本发布回退.
若把单一应用拆分为一个一微服务,比如订单微服务,用户微服务,商品微服务,积分微服务等,若某
一个微服务出错不会导致整个版本回退。
1.2)什么是微服务架构
微服务架构是一种架构模式(用于服务管理微服务的),它把一组小的服务互相协调、互相配合,并且
完成功能。每个服务运行在其独立的进程中,服务与服务间采用轻量级的通信机制互相协作(通常是基
于HTTP 协议的RESTfulAPI )。每个服务都围绕着具体业务进行构建,并且能够被独立的部署到生产环
境、类生产环境等。另外,应当尽量避免统一的、集中式的服务管理机制,对具体的一个服务而言,应
根据业务上下文,选择合适的语言、工具对其进行构建。

1.3微服务的优缺点:
优点:
①:优点每个服务足够内聚,足够小,代码容易理解这样能聚焦一个指定的业务功能或业务需求(职责单
一)
②:开发简单、开发效率提高,一个服务可能就是专一的只干一件事,微服务能够被小团队单独开发,这
个小团队是 2 到 5 人的开发人员组成。
③:微服务能使用不同的语言开发。
④:易于和第三方集成,微服务允许容易且灵活的方式集成自动部署,通过持续集成工具,如
Jenkins,Hudson,bamboo。
⑤:微服务只是业务逻辑的代码,不会和 HTML,CSS或其他界面组件混合。
⑥:每个微服务都有自己的存储能力,可以有自己的数据库。也可以有统一数据库。
.........................................
.........................................
缺点:
开发人员要处理分布式系统的复杂性(分布式事务)
多服务运维难度,随着服务的增加,运维的压力也在增大
系统部署依赖
服务间通信成本
数据一致性
.................................................
.................................................
二:springboot快速开始
2.1)(基于maven版本构建)
2.1)先把maven的配置文件设置为如下配置
<profile>
<id>jdk‐1.8</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
<jdk>1.8</jdk>
</activation>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8</maven.compiler.compilerVersion>
</properties>
</profile>
2.1)配置IDE的环境(maven配置)


2.2)创建一个空的maven工程,然后导入springboot相关的jar包
//父工程依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.8.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
spring mvc-web的依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!-- 引入一个spring boot插件,可以支持我们将web应用程序打成可运行jar包 -->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>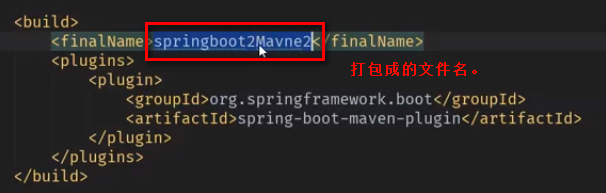
①:编写主入口程序
/**
* Created by smlz on 2019/3/18.
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class TulingStartMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(TulingStartMain.class,args);
}
}
②:其他业务组件 比如controller service repository compent注解标示的组件
********** 自己写的组件必须放在主启动类(TulingStartMain)在所包的及其子包下???????? 将源码分
析时候探究原理
/**
* Created by smlz on 2019/3/18.
*/
@RestController
public class TulingController {
@RequestMapping("/tuling")
public String tulingHelloWorld() {
return "tuling,hello";
}
}
③:运行main函数启动程序,访问http://localhost:8080/tuling,或者执行mvn package将项目打成
jar包,用java -jar XXX.jar直接运行

2.3)通过sts/idea创建 一个springboot项目


编写自己的业务代码就maven构建springboot工程版本的一样 这里就不做累赘讲诉.
三:helloworld的探究,
为啥我只要引入 spring-boot-starter-parent 和 spring-boot-starter-web就可以快速开发mvc的项目
3.1)pom分析
SpringBoot项目的父项目是spring-boot-starter-parent,而spring-boot-starter-parent项目的父项目是spring-boot-dependencies,spring-boot-dependencies项目是个依赖版本管理项目。
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.8.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
真正的版本管理仲裁中心 来决定应用的版本
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.0.8.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath>../../spring-boot-dependencies</relativePath>
</parent>
以后我们导入依赖默认是不需要写版本;(没有在dependencies里面管理的依赖自然需要声明版本号)
3.2) 我们来分析看下 spring-boot-starter-web(场景启动器)为我项目中导入 web开发需要的jar包依赖

4)多profile切换
我们在开发应用时,通常一个项目会被部署到不同的环境中,比如:开发、测试、生产等。其中每个环
境的数据库地址、服务器端口等等配置都会不同,对于多环境的配置,大部分构建工具或是框架解决的
基本思路是一致的,通过配置多份不同环境的配置文件,再通过打包命令指定需要打包的内容之后进行
区分打包
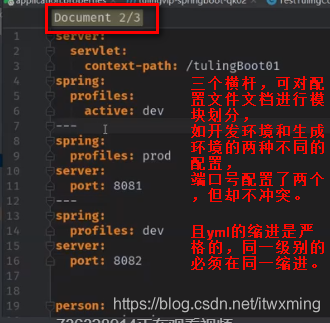
4.1)yml支持多模块文档块
server:
port: 8081
servlet:
context-path: /tuling01
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
---
开发环境配置
spring:
profiles: dev
server:
port: 8082
---
生产环境配置
spring:
profiles: prod
server:
port: 8083
从上图看出,我们激活的配置是开发环境的配置,但是现在 我们还看到了 servlet:context-path的配置形成互补配置
4.1.1)将配置文件中的部分内容直接加载到一个类中。



4.2) 多yml|properties文件的环境切换
application.yml (用于激活不同环境的配置文件)
spring:
profiles:
active: devapplication-dev.yml
server:
port: 8081
servlet:
context-path: /tl_devapplication-prod.yml
server:
port: 8082
servlet:
context-path: /tl_prod
4.3)激活指定环境配置的方法
①:直接在application.yml的配置文件中使用 spring.profiles.active=dev|prod|test
②:设置虚拟机参数 -Dspring.profiles.active=dev|prod|test
③:命令行参数启动(打成Jar包时候) java -jar tuling-vip-springboot-02-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.profiles.active=prod
4.4)设置jvm参数 然后我们看是否设置成功
java -Xms128m -Xmx128m -jar tuling-vip-springboot-02-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8888
第一步:在cmd窗口中使用jps来看我们主进程的


第二步:使用jinfo命令 +进程号来查看具体信息

4.5) springboot关于打包问题总结
4.5.1):打成指定的jar名称的
<build>
指定打包的文件名称
<finalName>tulingVipSpringboot</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>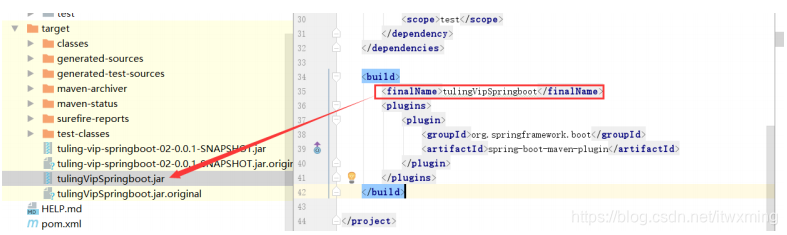
4.5.2)若出现工程中出现多个mainclass的时候需要指定主启动类
<build>
<finalName>tulingVipSpringboot</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<mainClass>com.tuling.TulingVipSpringboot02Application</mainClass>
</configuration>
<goals>
<goal>repackage</goal>
</goals>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>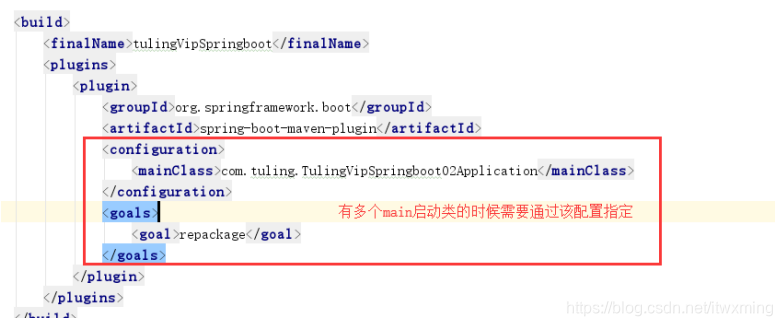
4.5.3)如何打出一个war包
第一步:指定springboot pom中的打包方式 由jar改为war

第二步:在spring-boot-starter-web模块打包比依赖与 tomcat(即要打成war包的那个模块加此tomcat依赖,并设置provided。只在要打成war包给tomcat使用的时候才加此依赖,否则不要。)(是为了排除掉tomcat。springboot程序是jar的方式,是通过IOC容器启动,带动了tomcat的启动。打成war的时候,是tomcat启动带动IOC容器的启动)

第三步:主启动类上 实现SpringBootServletInitializer 从写confiure方法(原理第三节课节讲)
@SpringBootApplication
public class TulingVipSpringboot03Application extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(TulingVipSpringboot03Application.class, args);
}
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(TulingVipSpringboot03Application.class);
}
}第四步:打成war包 放在tomcat上运行.
6)springboot 的web开发()
6.1)什么是webJar:以jar包的形式来引入前端资源,比如jquery 或者是BootStrap
https://www.webjars.org/
6.1.1)引入对应的jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>jquery</artifactId>
<version>3.3.1-2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>bootstrap</artifactId>
<version>4.3.1</version>
</dependency>
6.1.2)映射规则 /webjars/** 都会被映射到classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/ 目录下去处理

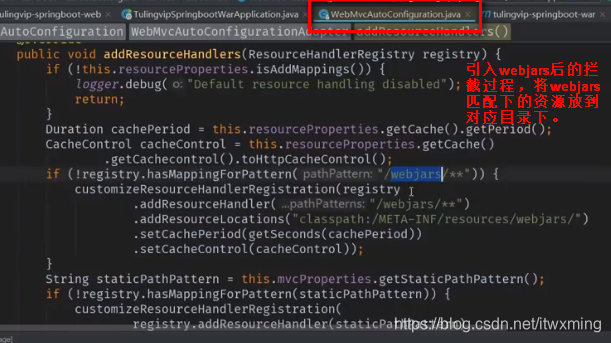
6.1.3)前端资源映射规则 核心源代码:
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if(!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
} else {
Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
CacheControl cacheControl = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();
//处理映射webjar 的请求的
if(!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{"/webjars/**"}).addResourceLocations(new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/"}).setCachePeriod(this.getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
//处理静态资源文件的
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
if(!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{staticPathPattern}).addResourceLocations(getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations())).setCachePeriod(this.getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
}
}源码里的原文
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
return;
}
Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
CacheControl cacheControl = this.resourceProperties.getCache()
.getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry
.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**")
.addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/")
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod))
.setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(
registry.addResourceHandler(staticPathPattern)
.addResourceLocations(getResourceLocations(
this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()))
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod))
.setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
}6.1.4)http://localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.3.1-2/jquery.js 请求如何拦截处理请求的
①根据日志打印,我们发现如下突破口

②:第二步:
org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.ResourceHttpRequestHandler#handleRequest方法
>org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.ResourceHttpRequestHandler#getResource
>org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.ResourceResolverChain#resolveResource
>org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.PathResourceResolver#resolveResourceInternal
>org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.PathResourceResolver#getResource(真正的资源映射
处理逻辑)
private Resource getResource(String resourcePath, @Nullable HttpServletRequest request,List<? extends Resource> locations) {
for (Resource location : locations) {
try {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Checking location: " + location);
}
String pathToUse = encodeIfNecessary(resourcePath, request, location);
//真正的处理逻辑 把jquery/3.3.1-2/jquery.js 映射到
Resource resource = getResource(pathToUse, location);
if (resource != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found match: " + resource);
}
return resource;
}
else if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No match for location: " + location);
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
logger.trace("Failure checking for relative resource - trying next location", ex);
}
}
return null;
}
6.1.5)访问静态html页面 我们直接把静态页面放在static的目录下,直接可以在路径直接访问

6.1.6)映射原理 /**请求都会被映射到
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = {
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/",
"classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/" };public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
.....
......
......
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(
registry.addResourceHandler(staticPathPattern)
.addResourceLocations(getResourceLocations(
this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()))
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod))
.setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
}6.1.7)欢迎页; 静态资源文件夹下的所有index.html页面;被"/**"映射;
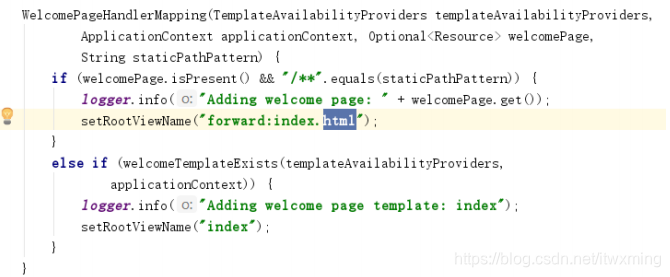
6.1.8) 使用webjar的方式修前端页面修改引用路径


6.2)springboot是如何整合springmvc功能的(WebMvcAutoConfiguration)
6.2.1)自动装配的组件
①:ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 和 BeanNameViewResolver 视图解析器
视图解析器的作用:根据方法的值找到对应的视图
②:Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars 支持静态资源和webJars
③:Converter ,日期格式化器 Formatter
④:消息装换器: HttpMessageConverters
⑤:首页设置index.html
⑥:图标支持 Favicon
6.2.2)如何扩展springmvc的配置(springboot提我们自己配置的springmvc的功能不丢失的情况
下) 比如我需要使用自己定义的拦截器
我们需要自己写一个配置类 继承 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter 需要什么组件 就注册什么组件
A:如何往容器中添加一个拦截器
第一步:创建一个拦截器
@Component
public class TulingInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)throws Exception {
System.out.println("我是TulingInterceptor的preHandle方法");
return true;
}
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler,@Nullable ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("我是TulingInterceptor的postHandle方法");
}
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler,@Nullable Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("我是TulingInterceptor的afterCompletion方法");
}
}第二步:注册拦截器
@Configuration
public class TulingConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private TulingInterceptor tulingInterceptor;
/**
* 注册拦截器
* @param registry
*/
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(tulingInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/**").excludePathPatterns("/index.html","/");
}
}B:往容器中增加一个过滤器
public class TulingFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("TulingFilter的doFilter方法");
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}/**
* 注册一个filter
* @return
*/
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean tulingFilter(){
FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
filterRegistrationBean.setFilter(new TulingFilter());
filterRegistrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/*");
return filterRegistrationBean;
}C:往容器中增加一个servlet
public class TulingServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.getWriter().write("hello......");
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req,resp);
}
}public class TulingServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.getWriter().write("hello......");
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req,resp);
}
}7)如何全面接管springboot的mvc配置(让springboot给我们自动配置的功能失效,自己像如
何整合ssm一样的整合springmvc,不推荐)
官网原话:
If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features and you want to add additional MVC
configuration (interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your
own @Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc . If you wish to provide
custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping , RequestMappingHandlerAdapter ,
or ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver , you can declare a WebMvcRegistrationsAdapter instance to provide such
components.

大概意思说,在配置文件中使用一个@EnableWebMvc来标识到配置类上,就会导致配置失效 why?为什么会失
效?????????????????
原理: @EnableWebMvc 为容器中导入了DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration的组件
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableWebMvc {
}1)我们来分析一下DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration是一个什么东西?????
我们发现DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration是WebMvcConfiurationSupport(只保证了springmvc的基本功能)类
型的
@Configuration
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport2)我们来看下WebMvcAutoConfiguration上的注解
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
//容器中 没有WebMvcConfigurationSupport 该配置文件才生生效,但是我们使用了 @EnableWebMvc 导入了WebMvcConfiurationSupport的配置,所以导致该配置类失效,
//只保存了springmvc的最基本的功能
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration3)我们的webJar 欢迎页 等全部失效


8)springboot错误处理机制?如何定制错误页面?
案例:浏览器模拟发送的错误请求 http://localhost:8080/aaaaaaaaaaaaaa

案例2:通过postman 或者restlet 发送的请求 http://localhost:8080/testTuling/dddd

我们可以看出 不同的终端发送的请求 会返回不同的错误异常类容 是根据什么原理?
原理: 是根据不同客户端发送的请求的请求头来区分是 返回页面还是json数据

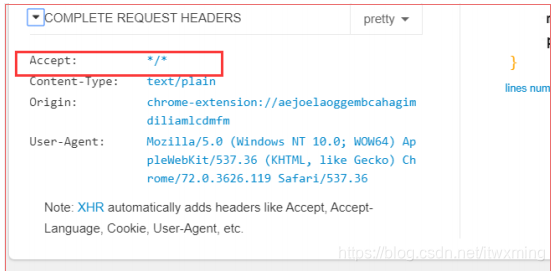
8.1)我们来看springboot为我们自动配置的异常处理的一些bean
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorAttributes.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() {
return new DefaultErrorAttributes(this.serverProperties.getError().isIncludeException());
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorController.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public BasicErrorController basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes) {
return new BasicErrorController(errorAttributes, this.serverProperties.getError(),this.errorViewResolvers);
}
@Bean
public ErrorPageCustomizer errorPageCustomizer() {
return new ErrorPageCustomizer(this.serverProperties, this.dispatcherServletPath);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(DispatcherServlet.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public DefaultErrorViewResolver conventionErrorViewResolver() {
return new DefaultErrorViewResolver(this.applicationContext,this.resourceProperties);
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "server.error.whitelabel", name = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
@Conditional(ErrorTemplateMissingCondition.class)
protected static class WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration {
private final SpelView defaultErrorView = new SpelView(
"<html><body><h1>Whitelabel Error Page</h1>"
+ "<p>This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.</p>"
+ "<div id='created'>${timestamp}</div>"
+ "<div>There was an unexpected error (type=${error}, status=${status}).</div>"
+ "<div>${message}</div></body></html>");
@Bean(name = "error")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "error")
public View defaultErrorView() {
return this.defaultErrorView;
}我们具体来分析上诉源代码的组件
A:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.ErrorPageCustomizer(错
误页面定制器)
作用:系统出现错误以后来到/error请求进行处理;
/**
* Path of the error controller.
*/
@Value("${error.path:/error}")
private String path = "/error";那么当我们 发生错误,需要/error 的请求映射来请求 接下来就会引出另外一个组件 来处理/error请求
B:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.BasicErrorController (基础错误控制器)
@Controller
@RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}")
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
//处理浏览器页面异常
@RequestMapping(produces = "text/html")
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
//处理postman 请求的Json数据异常错误
@RequestMapping
@ResponseBody
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request,isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL));
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status);
}
}B1:我们来看下浏览器的响应过程怎么来处理请求异常信息的?
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) {
//获取状态码
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
//获取页面的模型数据
Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
//解析错误视图
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
protected ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {
//获取容器中的所有错误视图解析器 DefaultErrorViewResolver
for (ErrorViewResolver resolver : this.errorViewResolvers) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolver.resolveErrorView(request, status, model);
if (modelAndView != null) {
return modelAndView;
}
}
return null;
}B2:我们接着分析
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.DefaultErrorViewResolver#DefaultErrorViewResolver
错误视图解析器
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status,Map<String, Object> model) {
//解析视图
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status), model);
//没有对应的解析精确匹配的状态码 使用模糊匹配比如4XX 5XX
if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {
//返回4XX 5XX的页面
modelAndView = resolve(SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model);
}
return modelAndView;
}
private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
// error/404
String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName;
//视图是否有模版引擎解析
TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider(errorViewName, this.applicationContext);
//有模版引擎解析直接返回
if (provider != null) {
return new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model);
}
//静态html的页面解析
return resolveResource(errorViewName, model);
}
private ModelAndView resolveResource(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
for (String location : this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()) {
try {
//在static模版下需要创建一个error/404.html
Resource resource = this.applicationContext.getResource(location);
resource = resource.createRelative(viewName + ".html");
//存在该页面 直接返回
if (resource.exists()) {
return new ModelAndView(new HtmlResourceView(resource), model);
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
}
}
return null;
}浏览器模拟发送异常请求的流程 视图解析过程
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.AbstractErrorController#resolveErrorView
开始解析视图,获取所有的异常错误视图解析器
>org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.DefaultErrorViewResolver#resolveErrorView
默认错误视图解析器解析视图
>org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.DefaultErrorViewResolver#resolve
响应码精准匹配视图
1)判断模版引擎是否能够处理错误视图,能处理就处理,不能处理交给静态页面解析处理
>org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.DefaultErrorViewResolver#resolveResource
html资源视图
>若不能精准匹配,那么就进行4XX 5XX模糊匹配
>若不能精准匹配(error/状态码.html)的错误页面,也没有(error/状态码开头xx.html错误页面那
就使用默认的错误空白页面)
private final SpelView defaultErrorView = new SpelView(
"<html><body><h1>Whitelabel Error Page</h1>"
+ "<p>This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.</p>"
+ "<div id='created'>${timestamp}</div>"
+ "<div>There was an unexpected error (type=${error}, status=${status}).</div>"
+ "<div>${message}</div></body></html>");
@Bean(name = "error")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "error")
public View defaultErrorView() {
return this.defaultErrorView;
}我们怎么包含一个自己的错误异常信息的 自适应的效果
浏览器效果:(需要返回自己定义的错误页面 包含了自定义的错误异常信息)
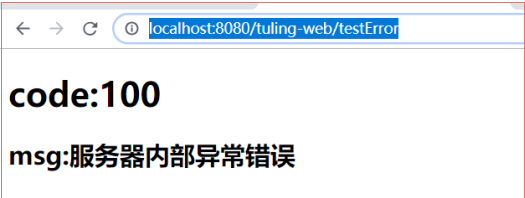

其他客户端的效果:
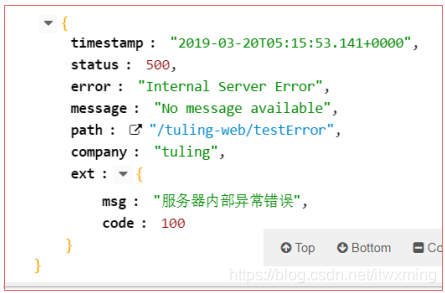
第一步:我们定义一个全局异常处理器,然后返回看执行效果
@ControllerAdvice
public class TulingExceptionHanlder {
/**
* 浏览器和其他客户端都返回了json 数组,不满足自适应
* @param e
* @param request
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value= TulingException.class)
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,Object> dealException(TulingException e, HttpServletRequest request){
Map<String,Object> retInfo = new HashMap<>();
retInfo.put("code",e.getCode());
retInfo.put("msg",e.getMsg());
return retInfo;
}
}效果: 浏览器不满足 自适应效果返回的是一个json字符串,而不是一个页面

其他客户端满足要求,返回自己定义的错误异常信息

第二步:在异常处理器中 进行重定向
根据第一步的效果来看 浏览器不能满足自适应效果 ,那么我们看下BasicErrorController的类
@Controller
@RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}")
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController他处理的请求是/error的请求,那么我们就想到 在全局异常处理器进行重定向
@ControllerAdvice
public class TulingExceptionHanlder {
@ExceptionHandler(value= TulingException.class)
public String dealException(TulingException e, HttpServletRequest request){
Map<String,Object> retInfo = new HashMap<>();
retInfo.put("code",e.getCode());
retInfo.put("msg",e.getMsg());
//重定向,把请求转发到BasicErrorController来处理 /error
return "forward:/error";
}执行效果:


分析过程
①:根据上述执行效果我们发现 进行转发后 他的http状态码变为200 那么错误异常处理就不能进行正常
流程的处理
②:那么我们需要分析 错误异常处理器 看下是如何获取异常状态码的.
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.AbstractErrorController#getStatus
很明显,BasicErrorController 的getStatus的过程中,都是从request中获取
javax.servlet.error.status_code属性
protected HttpStatus getStatus(HttpServletRequest request) {
Integer statusCode = (Integer) request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code");
if (statusCode == null) {
return HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
}
try {
return HttpStatus.valueOf(statusCode);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
return HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
}
}那么我们需要在我们的全局异常处理器中request中设置该属性

页面返回的属性字段是在哪里配置的???

那我们来着重分析一下
org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.DefaultErrorAttributes#getErrorAttributes

疑问:我们来看下这个类的自动装配原理,发现容器中有ErrorAttributes主键,那么就不进行自动装配,我
们可以来自己写一个类来继承他

@Component
public class TulingErrorAttribute extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) {
//获取父类的封装字段结果
Map<String, Object> retInfo = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest,includeStackTrace);
//获取全局异常自定义的结果
Map<String,Object> ext = (Map<String, Object>) webRequest.getAttribute("ext",0);
//封装自定义的错误信息
retInfo.put("company","tuling");
retInfo.put("ext",ext);
return retInfo;
}
}

























 426
426

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








