Floyd算法是解决所有结点对的最短路径问题。算法运行时间为θ(V^3)。
算法分析:
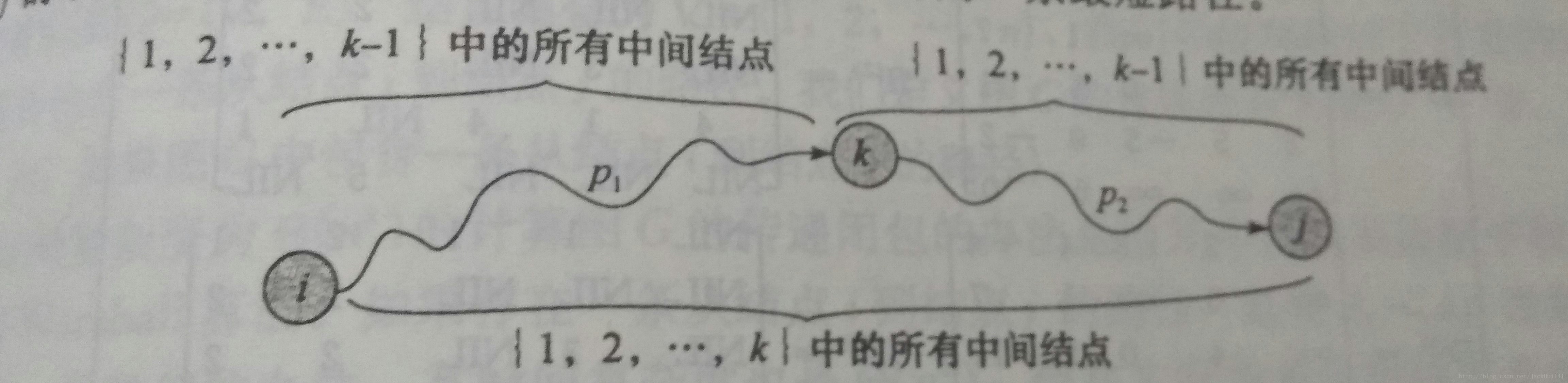
Floyd算法考虑的是一条最短路径的中间节点,即简单路径p={v1,v2,…,vn}上除v1和vn的任意节点。
设k是p的一个中间节点,那么从i到j的最短路径p就被分成i到k和k到j的两段最短路径p1,p2。p1是从i到k且中间节点属于{1,2,…,k-1}取得的一条最短路径。p2是从k到j且中间节点属于{1,2,…,k-1}取得的一条最短路径。
由此可以写递归式:
当k=0时,就是i和j之间没有节点,最短路径就是i到j的权值
当k>=1时,下面图中路径选最短
递归式:
代码实现
a.伪代码
FLOYD-WARSHALL(W)
n=W.rows
D=W
for k=1 to n
for i=1 to n
for j=1 to n
d(ij)=min(d(ij)+d(ji))
return Db.(学校上机题)
All-pairs shortest paths. The adjacency matrix is as same as that of problem 3.
A->B -1 A->C 3
B->C 3 B->D 2 B->E 2
D->B 1 D->C 5
E->D -3
package 算法导论上机;
public class Allpairs {
public static void FLOYD(int [][] w,int n){
int [][] p=new int[n][n];
int [][] m=new int[n][n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(w[i][j]<Integer.MAX_VALUE){
m[i][j]=j;
}else{
m[i][j]=-1;
}
p[i][j]=w[i][j];
}
}
for(int a=0;a<n;a++){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(p[i][j]>p[i][a]+p[a][j]){
p[i][j]=p[i][a]+p[a][j];
m[i][j]=m[i][a];
}
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
System.out.print(m[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
System.out.println(i+"到"+j+"的最短路径:");
if(m[i][j]==-1){
System.out.println("no");
}else{
System.out.println(m[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String [] args){
int [][] w={{Integer.MAX_VALUE,-1,3,Integer.MAX_VALUE,Integer.MAX_VALUE},
{Integer.MAX_VALUE,Integer.MAX_VALUE,3,2,2},
{Integer.MAX_VALUE,Integer.MAX_VALUE,Integer.MAX_VALUE,Integer.MAX_VALUE,Integer.MAX_VALUE},
{Integer.MAX_VALUE,1,5,Integer.MAX_VALUE,Integer.MAX_VALUE},
{Integer.MAX_VALUE,Integer.MAX_VALUE,Integer.MAX_VALUE,-3,Integer.MAX_VALUE}
};
Allpairs.FLOYD(w, 5);
}
}








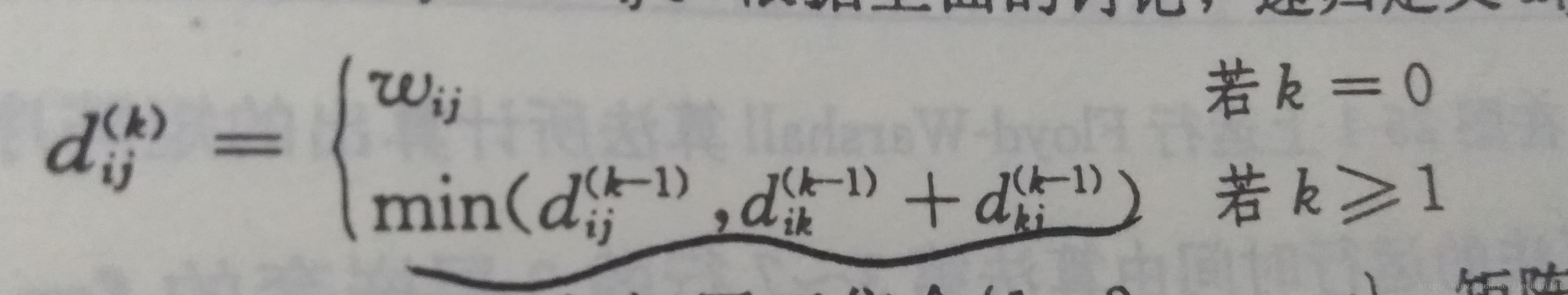














 1076
1076

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








