0 引出
需求:给定数列 (7, 3, 10, 12, 5, 1, 9),要求能够高效的完成对数据的查询和添加
方案:
- 数组未排序:如果不对数组排序,添加元素只需扩容并放到最后,速度快,但是查找慢
- 数组排序:有序数组使用查找算法,找起来是快,但是每次添加元素需要查找并整体移动数据,即添加慢
- 链表:不管链表是否有序,查找速度都慢,添加数据速度比数组快,不需要数据整体移动。
- 二叉排序树,BST: (Binary Sort(Search) Tree),将数列值作为权值创建节点,构建二叉排序树
1 二叉排序树的创建
- 所谓创建二叉树,其实就是从一颗没有节点的空树开始,不断添加节点,树从无到有根节点,到最后一个节点的添加,最终完成树的创建,因此我们需要编写添加节点的方法,实现自动创建树,而非手动改变每个节点的指向
- 保证添加每一个节点都满足二叉排序树的硬要求:左子节点的值比当前节点的值小,右子节点的值比当前节点的值大
- add方法内容:不断比较待添加节点和当前节点的权值,比当前节点小则判断是否有左子节点,没有则可以作为左子节点添加了,有左子节点则对左子节点递归调用add方法,对于待添加节点权值比当前节点的权值大的情况,和前面的处理同理
//添加节点
public void add(Nd nd) {
if (nd == null) {
return;
}
if (nd.value < this.value) {
if (this.left == null) {
this.left = nd;
} else {
this.left.add(nd);
}
} else {
if (this.right == null) {
this.right = nd;
} else {
this.right.add(nd);
}
}
}
2 二叉排序树的删除
- 相比创建时的简单添加节点,删除操作就需要考虑很多了,毕竟需要考虑放置删除节点的左右子树
- 先不谈删除root节点的特殊情况,删除节点的类型分为三种:叶子节点、有单子树、有双子树
- 删叶子节点:比如2,找到2和父节点1,看2是1的左子节点还是右子节点,然后将1的右指针置空,完成删除
- 删有单子树节点:比如1,找到1和父节点3,1是3的左子节点,2是1的右子节点,直接更新3的左子节点为2,完成删除
- 删有单子树节点:比如10,找到10和父节点7,两种删法:要么将10改为10的左子树中最大值9然后删除原来的9节点(叶子节点),要么将10改为10的右子树中最小值11然后删除原来的11节点(叶子节点),完成删除
- 对于root节点的删除,只需模仿上面345加以判断即可
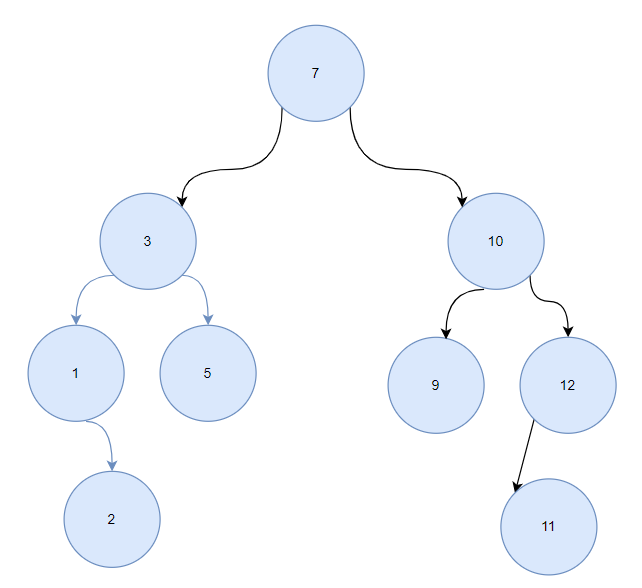
//二叉排序树
public class App04_BinarySortTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {7, 3, 10, 12, 5, 1, 9,2,11};
BinarySortTree tree = new BinarySortTree();
for (int i : arr) {
tree.add(new Nd(i));
}
tree.infixOrder();
System.out.println("-------删除前------");
tree.delNode(11);
tree.delNode(2);
tree.delNode(9);
tree.delNode(5);
tree.delNode(1);
tree.delNode(12);
tree.delNode(3);
tree.delNode(10);
tree.delNode(7);
tree.infixOrder();
}
}
class BinarySortTree {
private Nd root;
public Nd getRoot() {
return root;
}
//中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (root != null) {
root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("树为空!!!");
}
}
//添加节点
public void add(Nd nd) {
if (root == null) {
root = nd;
} else {
root.add(nd);
}
}
//找到删除节点及其父节点
public Nd search(int value) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
} else {
return root.search(value);
}
}
public Nd searchParent(int value) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
} else {
if (root.getLeft() == null && root.getRight() == null) {
return null;
} else {
return root.searchParent(value);
}
}
}
//删除节点
public void delNode(int value) {
if (root == null) {
return;
} else {
Nd target = search(value);
Nd parent = searchParent(value);//为空则只能是删根节点
//有的删才行
if (target != null) {
if (parent != null) {
//删叶子节点
if (target.getLeft() == null && target.getRight() == null) {
if (parent.getLeft()!=null&&parent.getLeft().getValue() == value) {
parent.setLeft(null);
} else {
parent.setRight(null);
}
//删有双子树的节点
} else if (target.getLeft() != null && target.getRight() != null) {
//target为左子树
if (parent.getLeft().getValue() == value) {
int max = delLeftTreeMax(target);
target.setValue(max);
//target为右子树
} else {
int min = delRightTreeMin(target);
target.setValue(min);
}
//删有单子树的节点
} else {
//4种可能,左左,左右,右左,右右
if (parent.getLeft()!=null&& parent.getLeft().getValue() == value && target.getLeft() != null) {
parent.setLeft(target.getLeft());
} else if (parent.getLeft() != null && parent.getLeft().getValue() == value && target.getRight() != null) {
parent.setLeft(target.getRight());
} else if (parent.getRight().getValue() == value && target.getLeft() != null) {
parent.setRight(target.getLeft());
} else {
parent.setRight(target.getRight());
}
}
} else {//没有父节点,说明就是删root,因为删除的节点存在
//叶子
if (root.getLeft() == null && root.getRight() == null) {
root = null;
//有双子树
} else if (root.getLeft() != null && root.getRight() != null) {
//用左子树最大或右子树最小都可以
root.setValue(delLeftTreeMax(root.getLeft()));
//有单子树
} else {
if (root.getRight() != null) {
root = root.getRight();
} else {
root = root.getLeft();
}
}
}
} else {
System.out.println("删除的节点不存在!!!");
}
}
}
//删左子树,最大值
public int delLeftTreeMax(Nd nd) {
Nd temp = nd;
while (true) {
if (temp.getRight() == null) {
break;
}
temp = temp.getRight();
}
delNode(temp.getValue());
return temp.getValue();
}
//删右子树,最小值
public int delRightTreeMin(Nd nd) {
Nd temp = nd;
while (true) {
if (temp.getLeft() == null) {
break;
}
temp = temp.getLeft();
}
delNode(temp.getValue());
return temp.getValue();
}
}
class Nd {
private int value;
private Nd left;
private Nd right;
public Nd(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Nd getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(Nd left) {
this.left = left;
}
public Nd getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(Nd right) {
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Nd [value=" + value + "]";
}
//中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
System.out.println(this);
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
//添加节点
public void add(Nd nd) {
if (nd == null) {
return;
}
if (nd.value < this.value) {
if (this.left == null) {
this.left = nd;
} else {
this.left.add(nd);
}
} else {
if (this.right == null) {
this.right = nd;
} else {
this.right.add(nd);
}
}
}
//查找要删除节点
public Nd search(int value) {
if (this.value == value) {
return this;
} else if (value < this.value) {//这里对于==的处理与add方法保持一致
if (this.left != null) {
return this.left.search(value);
}
} else {
if (this.right != null) {
return this.right.search(value);
}
}
return null;
}
//查找要删除的节点的父节点
public Nd searchParent(int value) {
if ((this.left != null && this.left.value == value) ||
this.right != null && this.right.value == value) {
return this;
} else {
if (value < this.value && this.left != null) {
return this.left.searchParent(value);
} else if (value >= this.value && this.right != null) {
return this.right.searchParent(value);
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
}
3 总结
- 对于二叉排序树,中序遍历结果就是原数列升序排序后的结果
- 为什么说二叉排序树结合数组+链表的优点? 它的查找速度其实等价于有序数组的二分查找速度,而它的添加速度基于二分查找在找到位置后等于链表的链尾追加操作(改变空指针的指向),因此得名






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








