目录
4.2.5、@SessionAttributes和@SessionAttribute
一、介绍
spring mvc源于mvc设计理念,通过将web应用分为模型层(M)、视图层(V)和控制层(C),实现了视图(比如jsp)和java Bean的解耦合、java和html的解耦合。mvc的根本好处在于前后台得到了一定的分离,大量的java代码得到了复用。现在前后端都采用了JSON数据交互,使得前后端的耦合度大大降低了。
二、初始化和流程
学习spring mvc,必须要了解它的初始化和流程。下面是我根据自己的理解描述的流程图,可能会有不对的地方,但大致如此。
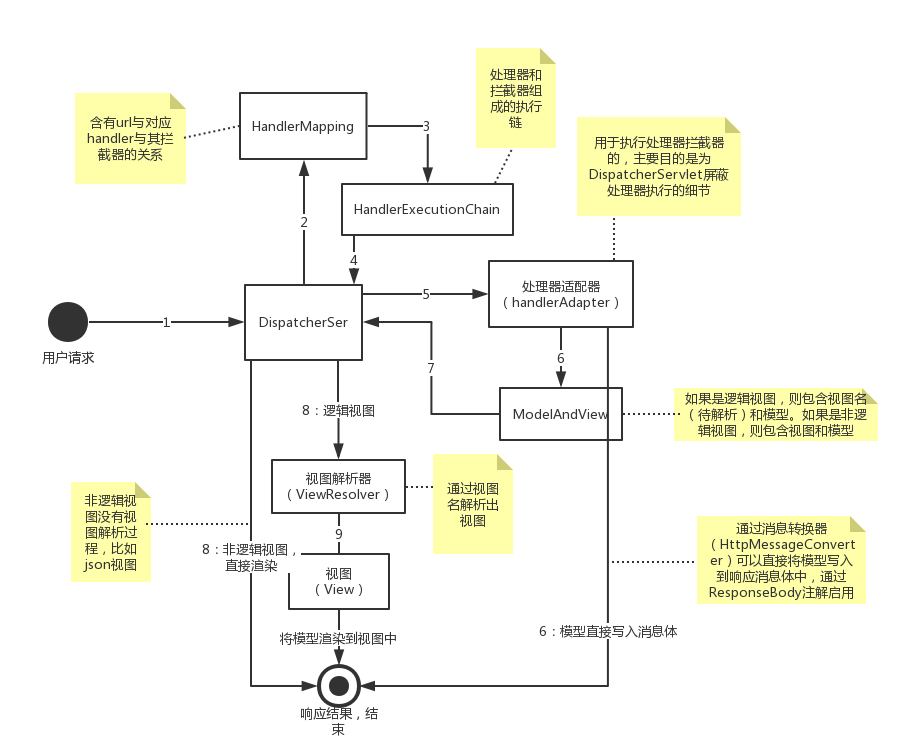
spring mvc框架的主要是由DispatcherServlet来完成请求的响应。DispatcherServlet是一个调度器,负责将请求分配给控制器处理,然后将控制器处理的模型渲染到视图中,最后返回给客户端。貌似很简单,但是它确实很复杂的,因为它实现了mvc分层与解耦,下面详细介绍。
DispatcherServlet是一个servlet,需要在web应用中配置它的映射URL(通常为“/”、“/*”,“*.do”、“/app/*”),当DispatcherServlet收到一个请求时,它会查询HandlerMapping,找出与url对应的处理器执行链(HandlerExecutionChain)。DispatcherServlet然后找到处理适配器来执行这个执行链。执行的结果是返回一个ModelAndView,或者执行在执行处理器时便通过HttpMessageConverter将模型转化为响应的消息体了。如果返回的是ModelAndView,又有两种情况:一、如果视图是逻辑视图,则存在视图解析的过程,通过视图名找到对应的视图,最后将模型渲染到视图中并返回响应;二、如果视图是非逻辑视图,则不存在视图解析的过程,而是直接将模型渲染到视图中并返回响应。
上面一段话基本描述到了spring mvc的各个组件和执行的流程。下面简略简洁它的各个组件。
DispatcherServlet在初始化时,会扫出描控制器,从控制器上的注解(比如@RequestMapping)找出url与控制器方法的对应关系,再从springmvc配置文件中找出拦截器和url的对应关系,由控制器经过包装而成的处理器和拦截器组成处理器执行链。而HandlerMapping则包含url和HandlerExecutionChain的关系,因此DispatcherServlet可以找到执行链,然后交由HandlerAdapter来执行,HandlerAdapter的主要目的是为DispatcherServlet屏蔽处理器执行的细节。
这里要说说处理器和控制器的关系了,处理器是控制器的一层包装,对请求参数进行简单的处理,然后将参数传给控制器。在创建控制器时,方法参数只要遵守一定的规则,springmvc都可以将控制器想要的参数传进来。这就是通过处理器来实现的,处理器先检查控制器的参数,然后通过一定方法将请求参数、某个作用域中的属性或者http相关类传递给控制器。因此控制器可以实现的非常灵活,可以不嵌入servlet相关类代码,可以单独进行单元测试。处理器在将参数传给控制器时会涉及到HttpMessageConverter、Converter、Formatter这些类的处理。HttpMessageConverter配合@RequestBody可以将请求的消息体转化为请求参数,配合@ResponseBody可以模型转化为响应消息体。如果使用注解@ResponseBody和HttpMessageConverter,则处理器返回的ModelAndView为null,也就没有视图渲染的过程了,因为响应结果已经生成好了。
处理器产生了ModelAndView后,就有了视图解析、渲染的过程了。视图分为两种:逻辑视图,非逻辑视图。如果是逻辑视图,那么ModelAndView包含的有视图名,而视图解析器的作用就是通过视图名找到视图,比如视图名“index”找到视图“/WEB-INF/jsp/index.jsp”。如果是非逻辑视图,那么ModelAndView中含有View,然后可以直接将模型渲染到视图中,比如json视图。
这里再谈谈Converter和Formatter,一般请求到来时,参数会先经过HttpMessageConverter的处理,在处理器对控制器方法进行传参时,如果不是字符串类型的,会涉及到类型转化的过程,由Converter和Formatter完成,而Formatter内部又由Converter完成。spring mvc已经提供了很多converter来满足一般的使用,但是也可以自定义。如果有@ResponseBody注解的话,控制器返回的对象会直接被HttpMessageConverter转化为响应消息体,这样便没有接下来视图解析、渲染的过程了。
三、配置
要配置spring mvc的环境,首先需要配置所需的jar包,关于jar包会在另一篇博客中谈到。spring mvc的关键类为DispatcherServlet,它是一个Servlet,需要在web.xml的配置文件中配置(尽管从servlet3.0开始,可以使用注解配置web.xml的内容,但是这里不谈及)。一般spring mvc应用会存在上下文层次结构(Context Hierarchy),即存在一个顶层容器和servlet容器。顶层容器一般含有服务层服务、数据访问层对象等,servlet容器含有控制层控制器、视图解析器、处理器映射器等。也就是说存在spring ioc的容器和spring mvc的容器,不过两个容器都是WebApplicationContext的实例。当然可以只存在spring mvc的容器,只需要不配置spring ioc。
3.1、web.xml配置
和spring ioc配置相关的类为ContextLoaderListener,是一个servlet的上下文的监听器;和spring mvc配置相关的类为DispatcherServlet,是一个servlet。都是在web.xml中配置的,下面给出配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd"
version="3.0">
<!-- 配置加载Spring文件的监听器-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
</listener-class>
</listener>
<!-- 配置Spring MVC前端核心控制器 -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc-config.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<!-- 配置服务器启动后立即加载Spring MVC配置文件 -->
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
这里配置了spring ioc容器和spring mvc容器,它们的配置文件通过contextConfigLocation参数值指定(不过两者都有默认值,这里不谈及了),路径可以相对于classpath路径或者web应用中WEB-INF目录,如下所示,给出了多个配置文件的路径:
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
/WEB-INF/spitter-security.xml
classpath:service-context.xml
...
</param-value>
</context-param>注意:web应用中的WEB-INF/classes和WEB-INF/lib是classpath路径,而WEB-INF不是。
如果只想使用spring mvc容器,那么不必配置ContextLoaderListener。
3.2、spring ioc配置
在web.xml中指定了spring ioc的配置文件为applicationContext.xml,这里暂不配置任何内容,ssm总配置会在另一篇博客中谈及。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
</beans>
3.3、spring mvc配置
在web.xml中指定了spring mvc的配置文件为springmvc-config.xml,基本内容如注解所示:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.3.xsd">
<!-- 配置扫描器 -->
<context:component-scan
base-package="com.luo.controller" />
<!-- 注解驱动:配置处理器映射器和适配器 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<!-- 允许静态资源访问 -->
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
<!-- 配置视图解释器ViewResolver -->
<bean id="jspViewResolver" class=
"org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</bean>
</beans>四、控制器开发
spring mvc简化了处理请求和响应结果的过程,开发者只需要在方法定义中声明自己所需的参数(参数类型有一定限制,不是想要什么就有什么),spring mvc就能根据参数类型正确的传入参数。方法返回时,开发者只需要放回ModelAndView,或者视图名,或者一个pojo对象,spring mvc都会正确的生成响应结果。关于控制器支持的参数类型和返回值类型,参考:https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/web.html#mvc-ann-arguments
上面谈到控制器和处理器的关系,这里我认为将处理器理解为控制器中方法的包装更为合适。
4.1、@RequestMapping
通过该注解,可以将url映射到某个控制器上(即方法)。可以指定请求路径、请求方法,然后其他的作为限定项,比如请求参数、请求头、请求类型(context-type)、结果类型(accept)。该注解可以声明到类和方法上,如果类和方法都声明,则方法对应的url为两个URL的合并。
@RequestMapping(value="index2",method=RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView index2(){
ModelAndView mv=new ModelAndview();
mv.setViewName("index");
return mv;
}假设项目名为web,那么/web/index2.do会访问index2方法。
注意,尽管注解中value没有显示指定index2.do的url,也会执行该方法,原因请参考:Pattern Comparision或4.1.1小节
但是@RequestMapping更适合注解在类上,方法上使用更具体的@RequestMapping的变种:
-
@GetMapping -
@PostMapping -
@PutMapping -
@DeleteMapping -
@PatchMapping
如:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/persons")
class PersonController {
//此时只能通过get方法访问此方法
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Person getPerson(@PathVariable Long id) {
// ...
}
@PostMapping
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public void add(@RequestBody Person person) {
// ...
}
}4.1.1、URL匹配模式
@RequestMapping注解使用了ant样式的路径模式(Ant-style path patterns),规则如下:
?matches one character*matches zero or more characters within a path segment**match zero or more path segments{spring:[a-z]+}matches the regexp[a-z]+as a path variable named "spring"
对于第四点,它可以匹配一个正则表达式并提取作为一个路径变量,下面是一个例子:
@GetMapping("/{name:[a-z-]+}-{version:\\d\\.\\d\\.\\d}{ext:\\.[a-z]+}")
public void handle(@PathVariable String version, @PathVariable String ext) {
// ...
}注意:请勿和web.xml中url pattern的*混淆
多个url模式可以同时匹配一个url,此时哪个控制器执行取决于模式的确定性。其中/**表示默认url模式,具有最低的确定性,最后匹配。
spring mvc会在url模式后默认添加 .* 后缀匹配,因此模式/person能够匹配/person.pdf ,/person.xml等等。后缀匹配没什么用,可以被关闭,如:
<!-- 注解驱动:配置处理器映射器和适配器 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<!-- 不使用后缀匹配 -->
<mvc:path-matching suffix-pattern="false"/>
</mvc:annotation-driven>4.2、方法参数
控制器的方法参数很灵活,可以声明自己需要的参数,spring mvc就会自动传入进来。不仅可以声明和servlet有关的参数,比如HttpSession,HttpServletRequest、请求参数等,还能声明和作用域范围(请求范围、会话范围)的属性、url中rest风格参数、请求头参数。下面的表格给出了所有控制器可以声明的参数类型(重要的会加粗、下划线):
注意,如果是注解的话,指的是被注解的参数
| Controller method argument | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Generic access to request parameters and request and session attributes, without direct use of the Servlet API. |
|
| Choose any specific request or response type — for example, |
|
| Enforces the presence of a session. As a consequence, such an argument is never |
|
| Servlet 4.0 push builder API for programmatic HTTP/2 resource pushes. Note that, per the Servlet specification, the injected |
|
| Currently authenticated user — possibly a specific |
|
| The HTTP method of the request. |
|
| The current request locale, determined by the most specific |
|
| The time zone associated with the current request, as determined by a |
|
| For access to the raw request body as exposed by the Servlet API. |
|
| For access to the raw response body as exposed by the Servlet API. |
|
| For access to URI template variables. See URI patterns. |
|
| For access to name-value pairs in URI path segments. See Matrix Variables. |
|
| For access to the Servlet request parameters, including multipart files. Parameter values are converted to the declared method argument type. See Note that use of |
|
| For access to request headers. Header values are converted to the declared method argument type. See |
|
| For access to cookies. Cookies values are converted to the declared method argument type. See |
|
| For access to the HTTP request body. Body content is converted to the declared method argument type by using |
|
| For access to request headers and body. The body is converted with an |
|
| For access to a part in a |
|
| For access to the model that is used in HTML controllers and exposed to templates as part of view rendering.通过这些类,可以将数据填充到模型中,最终这些数据会被放入请求范围内 |
|
| Specify attributes to use in case of a redirect (that is, to be appended to the query string) and flash attributes to be stored temporarily until the request after redirect. See Redirect Attributes and Flash Attributes.用于在重定向两个请求之间传数据的,简单属性就附加在url上,复杂的就通过session临时存储。 |
|
| For access to an existing attribute in the model (instantiated if not present) with data binding and validation applied. See Note that use of |
|
| For access to errors from validation and data binding for a command object (that is, a |
|
| For marking form processing complete, which triggers cleanup of session attributes declared through a class-level |
|
| For preparing a URL relative to the current request’s host, port, scheme, context path, and the literal part of the servlet mapping. See URI Links. |
|
| For access to any session attribute, in contrast to model attributes stored in the session as a result of a class-level |
|
| For access to request attributes. See |
| Any other argument | If a method argument is not matched to any of the earlier values in this table and it is a simple type (as determined by BeanUtils#isSimpleProperty, it is a resolved as a |
上面一些重要的稍后会介绍,在这之前先介绍类型转换。
4.2.1、类型转换(Type Conversion)
如果需要基于字符串类型的参数时(比如简单的请求参数@RequestParam、路径参数@PathVariable、字段头@RequestHeader、cookie @CookieValue等),而被注解的参数不是字符串类型,这时需要用到转换器(Converter<S,T>),比如将person字符串“tom-19-man”转化为person对象,需要实现Converter<Person,String>来对字符串进行转化。当然,如果person是一个pojo对象,可以直接传参转化为person对象(前提是请求参数名和person属性名分别对应)。
而spring mvc已经自动注册了很多Converter,基本能够满足要求。至于Formmatter,也是对字符串类型进行转化的,通常用于包含日期和数字的字符串的转化,不常用。
4.2.2、@RequestParam
该注解用于将请求参数绑定到控制器方法参数上,如果参数pojo,则绑定到对象属性上。
如下面的代码所示,通过get方法,如果请求参数名为petId,则解析为对应类型并传给该参数:
//官网上copy下来的,它没有给出url路径,会怎么样?我不晓滴
@GetMapping
public String setupForm(@RequestParam("petId") int petId, Model model) {
Pet pet = this.clinic.loadPet(petId);
model.addAttribute("pet", pet);
return "petForm";
}- 注解对应的请求参数必须存在(请求参数为空值也算作存在,如“name=”)。可设置属性required=false,允许请求参数不存在。一些特殊情况如下:
- 对于Integer、Long等基本类型的包装类,请求参数为空时,方法参数为null
- 对于String,请求参数为空时,请求参数为空时,方法参数为""
- 对于pojo,在required=true时,必须存在对象所有属性对应的请求参数,否则抛出异常;在required=false,对象属性对应请求参数可不存在。实际上,spring mvc会调用pojo的无参构造函数,通过setter方法设置属性。
- 对于基本类型,请求参数为空时,类型转化失败,抛出异常。
- 注解的value属性默认使用参数名
- 简单类型,如基本类型及它的包装类、string、pojo类,可以不使用注解,但实际上还是通过该注解解析。见4.2.4小节。
仔细探讨请求参数存在与不存在的情况:
- 请求参数类似“name=”时,为请求参数为空的情况,在jquery中可传{name:""}或{name:null}来实现
- 请求参数中不存在该字段,为不存在的情况,在jquery中无该字段 {} 或值为undefined {name:undefined} 来实现
4.2.3、@ModelAttribute
@ModelAttribute注解被用来从模型中找到属性并注入方法参数,如果不存在则实例化该属性然后注入。如果被注入的属性名与请求参数名相同,那么该属性会被覆盖。比如一个pojo对象有个name属性,然后也有同名请求参数,那么pojo对象的name属性会被覆盖。
@ModelAttribute可以注解在方法和方法参数上。
- 注解在方法上时,方法返回值将作为value,注解上指定的名字作为key(如果没有给出,则默认返回类型名,首字母小写)存入model中。在处理器被执行前先执行@ModelAttribute注解的方法。
- 注解在方法参数上时,会从model中找到属性,然后注入给参数,如果没有则创建该实例。
注解在参数时的解析过程:
先从模型(model)中找到存在的属性,如果不存在则从@SessionAttributes中找到属性,如果未找到则从URI中通过Converter解析对应的路径变量,如果没有对应的路径变量则调用默认构造方法,如果有更合适的构造函数,它的参数和请求参数名一致,那么会调用该构造函数并传入请求参数来构造该属性。
注意
如果方法参数不用注解,且不是简单类型,那么会被当做@ModelAttribute解析。注意,它可以被请求参数覆盖,因此仍然可通过@ModelAttribute获取参数值,如果类型太复杂,可以注册自己的Converter实例。
4.2.4、无注解参数
无注解参数,其实上面已经谈及过了。无注解的参数如果是简单类型,则会被当作@RequesParam解析,如果不是简单类型,则会被当作@ModelAttribute解析。简单类型由 BeanUtils#isSimpleProperty给出,比如 a primitive, a String or other CharSequence, a Number, a Date, a URI, a URL, a Locale, a Class, or a corresponding array都是简单类型。
无注解参数都可以为空(除了基本类型,考虑用包装类),然后都有一些默认值。一些简单类型为空时,值为null;pojo参数为空时时,会创建默认pojo对象;非简单类型为空时,参考上一节的解析过程。
4.2.5、@SessionAttributes和@SessionAttribute
@SessionAttributes用于将模型属性存入session中。只能注解在controller类上,在注解属性上指定属性名或者属性的类型:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/attribute")
//可以配置属性名或类型,两者取或关系
@SessionAttributes(names={"id"},types={Role.class})
public class EditPetForm {
// ...
}@SessionAttributes处理过程:每当处理器执行完毕后,如果模型中有@SessionAttributes注解指定的属性,那么该属性会被拷贝到session中。通过SessionStatus的setComplete方法可以清除session中被注解指定的属性。
@SessionAttribute的作用很简单,就是从session中获得属性,默认不为空,可以省略value,使用参数名。
4.2.6、@RequestAttribute
从请求范围内获取属性,默认不为空,可以省略value,使用参数名。在其他控制器或者servlet、jsp使用RequestDispatcher转发请求时,可以使用该注解获取请求范围内的属性。
为什么没有@RequestAttributes来设置请求范围属性呢?因为Model在处理器执行完后最终会被放入到请求范围的,也就是没有使用@RequestAttributes的必要了。
4.2.7、@RequestBody
根据请求中content-Type指定的MIME类型,找到对应的HttpMessageConverter将请求消息体反序列化成一个对象。
常用于接收JSON参数,比如当一个content-type为application/json类型的请求到来时,会找到对应的MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter,由它将消息体转化为对应的实体类(Entity)。
前提是jackson2的jar包已存在classpath路径上,否则白搭。
例子如下,consumes元素表示请求中content-Type必须含有application/json
@PostMapping(path = "/members", consumes = "application/json")
public void addMember(@RequestBody Member member) {
//code
}4.2.8、其他
还有很多重要的,但是表格中已经明确给出,所以不必详细介绍。
Map、Model、ModelMap代表模型,用于存储数据到模型中。
4.3、返回值
spring mvc支持很多中控制器方法的返回值。有很多种,我都不认识。。下面给出全部允许的返回值,但只强调常用的。其中,注解写在方法上。
| Controller method return value | Description |
|---|---|
|
| The return value is converted through |
|
| The return value that specifies the full response (including HTTP headers and body) is to be converted through |
|
| For returning a response with headers and no body. |
|
| A view name to be resolved with |
|
| A |
|
| Attributes to be added to the implicit model, with the view name implicitly determined through a |
|
| An attribute to be added to the model, with the view name implicitly determined through a Note that |
|
| The view and model attributes to use and, optionally, a response status. |
|
| A method with a If none of the above is true, a |
|
| Produce any of the preceding return values asynchronously from any thread — for example, as a result of some event or callback. See Asynchronous Requests and |
|
| Produce any of the above return values asynchronously in a Spring MVC-managed thread. See Asynchronous Requests and |
|
| Alternative to |
|
| Emit a stream of objects asynchronously to be written to the response with |
|
| Write to the response |
| Reactive types — Reactor, RxJava, or others through | Alternative to For streaming scenarios (for example, See Asynchronous Requests and Reactive Types. |
| Any other return value | Any return value that does not match any of the earlier values in this table and that is a |
这里说明下,上面的command object指的是model中的请求参数,因为请求参数被传入控制器时也被加入到了model中。4.2.2小结有提到过。command object估计指这个:@ModelAttribute
4.3.1、@ResponseBody
根据请求的accept头字段,选择对应HttpMessageConverter将控制器的返回值序列化到响应消息体中。返回值一般是Map对象或者pojo对象。
常用于返回json数据,当一个请求到来时,如果请求的accept字段为application/json,控制器方法被@ResponseBody注释,此时返回值被MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter序列化成json到消息体中。
同样前提是jackson2的jar包已存在classpath路径上。
例子如下,produces元素表示请求中accept字段必须含有application/json
@PostMapping(path = "/members", produces = "application/json")
@ResponseBody
public Map<...> addMember(Member member) {
...
//map对象或者pojo对象
return map;
}如果注解上没有指定produces时,使用哪个转换器呢?见6.2 Content-Type
4.3.2、String
可以返回一个视图名,这个视图名会被ViewResolver解析找到对应视图,然后渲染。如:
//根据之前的配置,视图解析器会找到/WEB-INF/jsp/test.jsp这个视图
@RequestMapping("/index2.do")
public String test(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("msg", "aaaa");
return "test";
}如果字符串含有redirect:或forward:前缀,那么会执行重定向、请求转发,后面介绍。
4.3.3、ModelAndView
代表模型和视图,通过该注解可以直接返回视图和模型。如果用的是逻辑视图,那么存在视图解析的过程,只需要返回视图名和模型即可。如:
@RequestMapping("/test4")
public ModelAndView test4() {
ModelAndView mView=new ModelAndView();
Item item=new Item();
item.setName("apple");
item.setPrice(23);
mView.addObject("item", item);
mView.setViewName("test");
return mView;
}如果是非逻辑视图,没有视图解析的过程,需要指定视图和模型。比如指定json视图和模型,那么最终会返回json结果:
@RequestMapping(value = "/y", method = { RequestMethod.GET })
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest arg0,
HttpServletResponse arg1) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ModelAndView view = new ModelAndView(new MappingJackson2JsonView());
view.addObject("status", "y");
view.addObject("info", "success");
return view;
} 五、其他
5.1、Model和请求、会话范围
在控制器开发中,可以在方法参数中传入模型,然后对模型添加数据。也可以方法内创建ModelAndView,添加数据后返回该对象。一般控制器生成视图后,会将model中的属性放入到请求范围内,供视图访问。通过@SessionAttribute声明的属性,此时也会从model拷贝到session作用范围内。
5.2、重定向
spring mvc框架中,重定向同时也可以传递参数,一共有两种方法,一是通过在url后添加参数,二是将参数临时保留在session中,重定向后将其清除。
能够在url中传递的数据都是简单类型,能够以字符串传递。下面的例子中,model中的数据会通过url传递:
//这里进行重定向
@RequestMapping("/addRole")
public String addRole(Model model,String roleName,String note){
...
model.addAttribute("roleName",roleName);
model.addAttribute("note",note);
model.addAttribute("id",role.getId());
return "redirect:./showRoleJsonInfo.do";
}
//这里是被重定向的方法,方法参数来接收数据
@RequestMapping("/showRoleJsonInfo")
public ModelAndView showRoleJsonInfo(Long id,String roleName,String note){
...
}如果传递的参数是对象,那么url不能够有效的以字符串传递参数了,那么要使用到会话:
//进行重定向
@RequestMapping("/addRole3")
public String addRole3(RedirectAttributes ra,Role role){
...
ra.addFlashAttribute("role",role);
return "redirect:./showRoleJsonInfo2.do";
}
//接收session中的参数
@RequestMapping("/showRoleJsonInfo2")
public ModelAndView showRoleJsonInfo(Role role){
...
}关于RedirectAttribute,请参考4.2的表格
5.3、数据模型
控制器为模型添加数据时,ModelAndView、ModelMap、Model和Map都能够添加数据到模型中,那它们的关联呢?看看一下类图:

实际上,spring创建的是BindingAwareModelMap,因此它们之间都可以相互转化,都可以添加模型数据。
5.4、解决中文乱码
在tomcat中,默认使用iso-8859-1解码参数,而一般参数是以utf-8发送的,这样就造成了控制器乱码的现象。可以在web.xml中配置过滤器,为每个请求指定解码编码。spring已经提供了这样的编码过滤器,不必自己写一个,只需在web.xml中添加如下代码:
<!-- 编码过滤器 -->
<filter>
<filter-name>encoding</filter-name>
<filter-class>
org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter
</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encoding</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>5.5、自定义转换器(Converter)
在请求参数传入到控制器参数时,涉及到参数解析的过程,通过HttpMessageConverter、Converter、Fomatter完成。这里只讲Converter,spring mvc中已经定义了很多的Converter,能够满足一般要求。但是如果没有对应的Converter进行转换时,则需要自己定义Converter。好了介绍到这里,以后有缘再补充,,,或参考:https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/web.html#mvc-config-conversion
。。。
5.6、静态资源访问
一般将DispatcherServlet的url配置成"/",这样会覆盖默认servlet。我们知道,默认servlet能够处理静态资源,比如css、js、html。但是默认servlet被DispatcherServlet覆盖后仍然能够让客户端访问到静态资源,需要配置了一个DefaultServletHttpRequestHandler(见5.6.2) 。它映射到URL:/**,但拥有最低的优先级,也就是找不到匹配的后端控制器时,就将请求交给了servlet容器的默认servlet处理了。
注意
- 如果DispatcherServlet的url配置成“/*”,那么访问jsp的请求也被拦截,如果没有对应的后端控制器,那么会被交给servlet容器的默认servlet处理,它会直接将jsp源码发出来,而不是解析生成的html数据(jsp是通过名为jsp的jsp引擎解析的)。关于这些内容可以参考我的另一篇博客:servlet映射
- 如果不能正常访问静态资源,可以检查下是不是被拦截器拦截了请求哦~
5.6.1、配置静态资源
在spring mvc中通过mvc:resources可以配置静态资源,其中mapping指静态资源对应的URL,location值静态资源的实际路径,可以相对于web根路径,classpath路径。cache-period指定静态资源过期时间,对于缓存服务器和客户端都会缓存该静态资源,尤其是缓存服务器,用处极大。关于url匹配模式参考4.1.1小结。
<mvc:resources mapping="/resources/**"
location="/public, classpath:/static/"
cache-period="31556926" />估计该url下的资源会被servlet容器的默认servlet处理吧, 没有找到相关资料。
5.6.2、配置默认servlet
配置了DefaultServletHttpRequestHandler 后,不能被控制器匹配的url会被默认servlet处理。配置如下
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>该元素有个属性default-servlet-name可以指定默认servlet的名字,每个servlet容器的默认servlet名字都不相同,但是spring mvc使用一个常用的默认servlet名字列表来尝试检测默认serlvet。如果自己把默认servlet名字改了,可以显示指出,如:
<mvc:default-servlet-handler default-servlet-name="myCustomDefaultServlet"/>5.6.3、配置web.xml
servlet-mapping配置的url映射有先后关系,后面的可以覆盖前面的,因此web.xml后面为容器的默认servlet追加几条servlet-mapping映射,可以直接让默认servlet来处理静态资源:
<!-- 假设默认servlet名为default,不过一般都叫defaul -->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>default</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.js</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>default</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.css</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>5.7、文件上传
文件上传需要配置MultipartResolver Bean,bean名字必须为multipartResolver。当一个content-type为multipart/form-data的post请求到来时,解析器解析消息体并包裹HttpServletRequest为MultipartHttpServletRequest。multipart/form-data类型数据由多个part组成,每个part就是表单中的一个字段,在spring mvc中被表示为MultipartFile类。通过该类,可以获得上传文件信息、保存文件等。
控制器中获得字段的方法:
- 参数传入HttpServletRequest,然后类型转化为MultipartHttpServletRequest,通过该类获得MultipartFile和其他字段。如果一个字段上传多个文件,则使用该类的getFiles方法。
- 直接传入字段参数,但MultipartFile必须使用注解@RequestParam,见4.2小节。如果一个字段同时上传多个文件,则传入List<MultipartFile>。
MultipartResolver是一个接口,spring mvc有两种实现类:CommonsMultipartResolver和StandardServletMultipartResolver。CommonsMultipartResolver使用了Apache Commons项目下的FileUpload包,因此需要而外添加jar包;而StandardServletMultipartResolver使用了servlet3.0的multipart request parsing的解析功能,不需要额外的jar包。但是我对servlet3.0的功能不太熟悉,就使用第一个实现类。
CommonsMultipartResolver用到了如下jar包:
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.3.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
</dependency>然后在spring mvc中配置MultipartResolver:
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8"/>
</bean>CommonsMultipartResolver常用属性:
- defaultEncoding:设置解析请求的默认编码,默认ISO-8859-1
- maxUploadSizePerFile:每个文件的最大上传长度,以字节为单位
- maxUploadSize:单次请求,最大的上传大小,以字节为单位
保存文件可以使用MultipartFile的transferTo方法。
简单的控制器:
@RequestMapping("/fileUpload")
@ResponseBody
public Map<String, String> fileUpload(@RequestParam MultipartFile filename) {
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
if(!filename.isEmpty()) {
map.put("state", "ok");
map.put("filename", filename.getOriginalFilename());
}else {
map.put("state", "bad");
}
return map;
}参考:
Multipart Resolver
multipart/form-data
5.8、文件下载
文件的下载主要由Content-Disposition头字段控制,该字段会让浏览器将消息体保存在文件中,需要指定文件名。还需要指定文件MIME类型,一般设置为application/octet-stream。
可以直接使用servlet的最原始的方法,比如:
response.setContentType("application/pdf");
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename=\"somefile.pdf\""); 这里讲spring mvc的方法,在4.3小节中,ResponseEntity可以作为返回值直接写入到消息体中,并且能够传入头字段、状态码信息。使用例子如下:
@RequestMapping("/download/{name:\\w+\\.\\w+}")
public ResponseEntity<byte[]> fileDownload(HttpServletRequest request,@PathVariable String name){
String filename=request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/css/"+name);
File file =new File(filename);
if(!file.exists()) {
return new ResponseEntity<byte[]>(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
HttpHeaders headers=new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentDispositionFormData("attachment", name);
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM);
try {
return new ResponseEntity<byte[]>(Files.readAllBytes(file.toPath()),headers,HttpStatus.OK);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
return new ResponseEntity<byte[]>(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
}
@Requehttp协议头部中只能存在ascii字符,Content-Disposition中文件名含有其他编码方式的字符,会显示乱码。因此使用之前需要对文件名进行url编码(url encoding,见html4.2小节),如下所示:
headers.setContentDispositionFormData("attachment", URLEncoder.encode(name,"utf-8"));一般文件下载最好允许被缓存:
headers.setCacheControl(CacheControl.maxAge(30, TimeUnit.DAYS));//设置缓存时间六、MVC配置
6.1、拦截器
spring mvc启动期间会通过@RequestMapping注解和配置文件找到和URI对应的处理器与拦截器,构建一条执行链(HandlerExecutionChain对象)。其中,拦截器需要实现HandlerIntercept接口:
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
default boolean | preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, java.lang.Object handler) 处理器执行之前执行。返回true,让剩下的拦截器或处理器执行;false则表明已经处理了响应,不在继续执行 |
default void | postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, java.lang.Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) 处理器结束后执行。 |
default void | afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, java.lang.Object handler, java.lang.Exception ex) Callback after completion of request processing, that is, after rendering the view.处理请求结束后,一般在渲染了视图之后执行。 |
单个拦截器执行过程:

多个拦截器执行过程:
preHandler1-->preHandler2-->preHandler3-->handler-->postHandler3-->postHanlder2-->postHandler1-->afterCompletion3-->afterCompletion2-->afterCompletion1
拦截器配置:
<mvc:interceptors>
<!-- 全局拦截器配置 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.LocaleChangeInterceptor"/>
<!-- 只拦截匹配url -->
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/admin/**"/>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.ThemeChangeInterceptor"/>
</mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/secure/*"/>
<bean class="org.example.SecurityInterceptor"/>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>path路径参考4.1.1小结。
6.2 Content Types
spring mvc通过media类型来决定使用何种HttpMessageConverter来解析或生成消息体,但必须有对应的jar包位于classpath下。判断过程如下:
- 首先检查URL的路径扩展,如xxx.json,xxx.xml,xxx.rss等等。
- 然后才检查Accept头字段。
- 最后使用默认Content-Type。默认为第一个找到的与HttpMessageConverter相关的ar包
通过配置ContentNegotiationManagerFactoryBean可以更改它的默认行为,如下所示:

下面通过xml配置,关闭步骤一的行为,设置默认Content-Type为application/json:
<mvc:annotation-driven content-negotiation-manager="contentNegotiationManager">
<!-- 不使用后缀匹配 -->
<mvc:path-matching suffix-pattern="false"/>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
<!--配置Content Type解析行为-->
<bean id="contentNegotiationManager" class="org.springframework.web.accept.ContentNegotiationManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="favorPathExtension" value="false"/><!--关闭url路径扩展-->
<property name="defaultContentType"><!--配置默认Content Type-->
<bean class="org.springframework.http.MediaType">
<constructor-arg value="application"/>
<constructor-arg value="json"/>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>如果在浏览器中测试发现,即使设置默认使用json,也返回xml,请检查下请求的头字段。在chrome中,默认会发送接收xml的accept。本人在linux中使用curl测试正确。
参考
《Java EE 互联网轻量级框架整合开发 --SSM框架和Redis实现》 杨开振
《Java EE 企业级应用开发教程》黑马程序员
spring mvc官网:https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/web.html#mvc
Ant-style path patterns:https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/javadoc-api/org/springframework/util/AntPathMatcher.html#match-java.lang.String-java.lang.String-
Http Message Converters with the Spring Framework:https://www.baeldung.com/spring-httpmessageconverter-rest
How does @ModelAttribute Work?:https://www.codelooru.com/2010/11/how-does-modelattribute-work.html
What is @ModelAttribute in Spring MVC?:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/3423262/what-is-modelattribute-in-spring-mvc
what is the command object in spring framework:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/7583577/what-is-the-command-object-in-spring-framework
Understanding Spring MVC Model and Session Attributes:https://www.intertech.com/Blog/understanding-spring-mvc-model-and-session-attributes/
json示例:http://sb33060418.iteye.com/blog/2374518
servlet映射:https://blog.csdn.net/jdbdh/article/details/83039387






















 2846
2846











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








