题目链接
题目内容
1119 Metro
Time limit: 0.5 second
Memory limit: 64 MB
Many of SKB Kontur programmers like to get to work by Metro because the main office is situated quite close the station Uralmash. So, since a sedentary life requires active exercises off-duty, many of the staff — Nikifor among them — walk from their homes to Metro stations on foot.
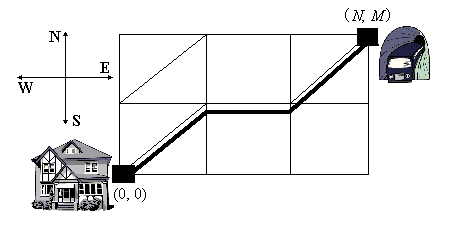
Problem illustration
Nikifor lives in a part of our city where streets form a grid of residential quarters. All the quarters are squares with side 100 meters. A Metro entrance is situated at one of the crossroads. Nikifor starts his way from another crossroad which is south and west of the Metro entrance. Naturally, Nikifor, starting from his home, walks along the streets leading either to the north or to the east. On his way he may cross some quarters diagonally from their south-western corners to the north-eastern ones. Thus, some of the routes are shorter than others. Nikifor wonders, how long is the shortest route.
You are to write a program that will calculate the length of the shortest route from the south-western corner of the grid to the north-eastern one.
Input
There are two integers in the first line: N and M (0 < N,M ≤ 1000) — west-east and south-north sizes of the grid. Nikifor starts his way from a crossroad which is situated south-west of the quarter with coordinates (1, 1). A Metro station is situated north-east of the quarter with coordinates (N, M). The second input line contains a number K (0 ≤ K ≤ 100) which is a number of quarters that can be crossed diagonally. Then K lines with pairs of numbers separated with a space follow — these are the coordinates of those quarters.
Output
Your program is to output a length of the shortest route from Nikifor’s home to the Metro station in meters, rounded to the integer amount of meters.
Sample
| input | output |
|---|---|
| 3 2 | 383 |
| 3 | |
| 1 1 | |
| 3 2 | |
| 1 2 |
题目大意
城市为正方形格子,每个格子的边长为100米。地铁站在其中一个十字路口。Nikanor从家里步行到地铁站。他沿着街道走,也可以穿越某一些格子的对角线,这样会近一些。 求Nikanor从西南角的家到东北角地铁站的最短路径。
思路
假设:已知倒数第二步的点i到起点的最短距离是d[n-1][i],则ans = min{ d[n-1][i]+最后一步的距离 };(每一步的距离我们已经知道了);
问题:实际上我们并不知道d[n-1][i]的值,问题转化为求起点到点i的最短距离,同理需要求助于d[n-2][i],最终到求第一个点到起点的最短距离;
结论:自顶向下的分析,自底向上的计算——动态规划求解;
状态转移方程:
if (有对角线)
dp[i][j] = min{dp[i][j-1]+100, dp[i-1][j]+100, dp[i-1][j-1]+sqrt(20000)};
else
dp[i][j] = min{dp[i][j-1]+100, dp[i-1][j]+100};算法步骤
1) 初始化边界:
dp[0][0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][0] + 100;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
dp[0][i] = dp[0][i-1] + 100;2) 自底向上求解:
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
if (diag[i][j])
dp[i][j] = min{dp[i][j-1]+100, dp[i-1][j]+100, dp[i-1][j-1]+sqrt(20000)};
else
dp[i][j] = min{dp[i][j-1]+100, dp[i-1][j]+100};
}题目源代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
double dp[1001][1001];
bool diag[1001][1001];
double min(const double &a, const double &b, const double &c)
{
double min = a<b?a:b;
return min<c?min:c;
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
int k;
cin>>k;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j <=m; j++)
diag[i][j] = false;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
int x, y;
cin>>x>>y;
diag[x][y] = true;
}
dp[0][0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][0] + 100;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
dp[0][i] = dp[0][i-1] + 100;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
if (diag[i][j])
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j]+100, dp[i][j-1]+100, dp[i-1][j-1]+sqrt(20000.0));
else
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j]+100, dp[i][j-1]+100, 999999999.0);
}
cout<<floor(dp[n][m]+0.5)<<endl;
return 0;
}空间优化
计算dp[i][j]时,只需要用到dp[i-1][j]或者dp[i][j-1]或者dp[i-1][j-1],其他之前的计算结果都不再需要,鉴于这个特点,我们可以用一维数组来看问题。
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
dp[j] = min (dp[j], dp[j-1]) + 100;事实上,此处的dp[j-1]代表的是dp[i][j-1],dp[j]代表的是dp[i-1][j]。
那么,如何用一维数组来代表dp[i-1][j-1]呢?
请看下面代码:
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
double t = dp[0];
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
double a = dp[j];
if (有对角边)
dp[j] = min (dp[j]+100, dp[j-1]+100,t+sqrt(20000));
else
dp[j] = min (dp[j], dp[j-1]) + 100;
t = a;
}
}在以上代码中,a中保存的是dp[i-1][j],在本次循环的末尾,将它赋值给t,之后t在下一个循环中才使用到,由于j++,所以在下一个循环中,t代表的就是dp[i-1][j-1]了。
至此,通过用1维数组代替2维数组,达到了空间复杂度优化的目的,优化后的空间复杂度为O(n)。
优化后的代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
double dp[1001];
bool diag[1001][1001];
double min(const double &a, const double &b, const double &c)
{
double min = a<b?a:b;
return min<c?min:c;
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
int k;
cin>>k;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j <=m; j++)
diag[i][j] = false;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
int x, y;
cin>>x>>y;
diag[x][y] = true;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
dp[i] = i*100;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
double t = dp[0];
dp[0] += 100;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
double a = dp[j];
if (diag[j][i])
dp[j] = min(dp[j]+100, dp[j-1]+100,t+sqrt(20000.0));
else
dp[j] = min(dp[j], dp[j-1], 999999999.0) + 100;
t = a;
}
}
cout<<floor(dp[n]+0.5)<<endl;
return 0;
}





















 119
119











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








