1. 基本语法
一般我们在用tensorflow编程时,会分为以下几个步骤:
- 创建Tensors(变量)
- 编写Tensors间的操作符
- 初始化Tensors
- 创建一个Session
- 运行Session
示例如下:
y_hat = tf.constant(36, name='y_hat') # 定义一个常量y_hat,赋值为36
y = tf.constant(39, name='y') # 定义一个常量,赋值为39
loss = tf.Variable((y - y_hat)**2, name='loss') # 创建一个变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer() # 当执行(session.run(init))时,
# 变量loss会被初始化并且做好了计算的准备
with tf.Session() as session: # 创建一个Session用于print输出
session.run(init) # 初始化变量
print(session.run(loss)) # 运行Session并输出loss有时候,我们需要先定义一个变量,然后在运行的时候才进行赋值,这就是tensorflow的placeholder对象了。基本用法就是先创建一个placeholder对象,然后在调用的时候通过feed_dict把值传过去,示例如下:
def sigmoid(z):
# 创建一个placeholder对象x
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name = "x")
# 利用tf的sigmoid()函数计算sigmod
sigmoid = tf.sigmoid(x)
# 创建一个session并运行
# 通过feed_dict把z的值传给x
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 运行session然后染回"result"
result = sess.run(sigmoid, feed_dict = {x : z})
return result
2. 实现神经网络
2.1 数据集准备
加载数据:
# Loading the dataset
X_train_orig, Y_train_orig, X_test_orig, Y_test_orig, classes = load_dataset()# 把训练集和测试集的图像展开
X_train_flatten = X_train_orig.reshape(X_train_orig.shape[0], -1).T
X_test_flatten = X_test_orig.reshape(X_test_orig.shape[0], -1).T
# 归一化
X_train = X_train_flatten/255.
X_test = X_test_flatten/255.
# 把训练集和测试集的标签转换成一个hot矩阵
Y_train = convert_to_one_hot(Y_train_orig, 6)
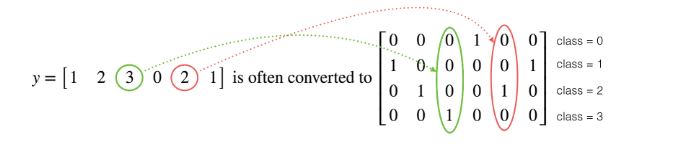
Y_test = convert_to_one_hot(Y_test_orig, 6)这里的one hot编码,如下图所示:
2.2 定义placeholder
为了在运行session时把训练数据传过去,需要定义placeholder,代码如下:
def create_placeholders(n_x, n_y):
"""
Creates the placeholders for the tensorflow session.
Arguments:
n_x -- scalar, size of an image vector (num_px * num_px = 64 * 64 * 3 = 12288)
n_y -- scalar, number of classes (from 0 to 5, so -> 6)
Returns:
X -- placeholder for the data input, of shape [n_x, None] and dtype "float"
Y -- placeholder for the input labels, of shape [n_y, None] and dtype "float"
Tips:
- You will use None because it let's us be flexible on the number of examples you will for the placeholders.
In fact, the number of examples during test/train is different.
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines)
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape = [n_x, None], name = "X")
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape = [n_y, None], name = "Y")
### END CODE HERE ###
return X, Y2.3 参数初始化
代码如下:
def initialize_parameters():
"""
Initializes parameters to build a neural network with tensorflow. The shapes are:
W1 : [25, 12288]
b1 : [25, 1]
W2 : [12, 25]
b2 : [12, 1]
W3 : [6, 12]
b3 : [6, 1]
Returns:
parameters -- a dictionary of tensors containing W1, b1, W2, b2, W3, b3
"""
tf.set_random_seed(1) # so that your "random" numbers match ours
### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 6 lines of code)
W1 = tf.get_variable("W1", shape = [25, 12288], initializer = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed = 1))
b1 = tf.get_variable("b1", shape = [25, 1], initializer = tf.zeros_initializer())
W2 = tf.get_variable("W2", shape = [12, 25], initializer = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed = 1))
b2 = tf.get_variable("b2", shape = [12, 1], initializer = tf.zeros_initializer())
W3 = tf.get_variable("W3", shape = [6, 12], initializer = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed = 1))
b3 = tf.get_variable("b3", shape = [6, 1], initializer = tf.zeros_initializer())
### END CODE HERE ###
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2,
"W3": W3,
"b3": b3}
return parameters2.4 前向传播
代码如下:
# GRADED FUNCTION: forward_propagation
def forward_propagation(X, parameters):
"""
Implements the forward propagation for the model: LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SOFTMAX
Arguments:
X -- input dataset placeholder, of shape (input size, number of examples)
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "b1", "W2", "b2", "W3", "b3"
the shapes are given in initialize_parameters
Returns:
Z3 -- the output of the last LINEAR unit
"""
# Retrieve the parameters from the dictionary "parameters"
W1 = parameters['W1']
b1 = parameters['b1']
W2 = parameters['W2']
b2 = parameters['b2']
W3 = parameters['W3']
b3 = parameters['b3']
### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 5 lines) # Numpy Equivalents:
Z1 = tf.add(tf.matmul(W1, X), b1) # Z1 = np.dot(W1, X) + b1
A1 = tf.nn.relu(Z1) # A1 = relu(Z1)
Z2 = tf.add(tf.matmul(W2, A1), b2) # Z2 = np.dot(W2, a1) + b2
A2 = tf.nn.relu(Z2) # A2 = relu(Z2)
Z3 = tf.add(tf.matmul(W3, A2), b3) # Z3 = np.dot(W3,Z2) + b3
### END CODE HERE ###
return Z32.5 计算代价函数
def compute_cost(Z3, Y):
"""
Computes the cost
Arguments:
Z3 -- output of forward propagation (output of the last LINEAR unit), of shape (6, number of examples)
Y -- "true" labels vector placeholder, same shape as Z3
Returns:
cost - Tensor of the cost function
"""
# to fit the tensorflow requirement for tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(...,...)
logits = tf.transpose(Z3)
labels = tf.transpose(Y)
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line of code)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits = logits, labels = labels))
### END CODE HERE ###
return cost2.6 后向传播和参数更新
tensorflow封装了这个过程,所有的反向传播和参数更新只需要一行代码就可以完成。当你计算完代价函数之后,只需要创建一个“optimizer”对象。 在运行tf.session时,必须调用这个“optimizer”对象和成本函数。“optimizer”对象被调用时,它将根据所选择的梯度下降方法和learning rate对给定的代价函数进行优化。代码如下:
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate = learning_rate).minimize(cost) # 创建optimizer对象
_ , c = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict={X: minibatch_X, Y: minibatch_Y}) # 执行反向传播及参数更新
一般,"_"表示作为“一次性”变量来存储我们以后不需要使用的值。
2.7 定义神经网络模型
def model(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test, learning_rate = 0.0001,
num_epochs = 1500, minibatch_size = 32, print_cost = True):
"""
实现一个3层tensorflow神经网络: LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->SOFTMAX.
输入参数:
X_train -- 训练集, (输入特征数 = 12288, 样例数 = 1080)
Y_train -- 训练集, (输出维度 = 6, 样例数 = 1080)
X_test -- 测试集, (输入特征数 = 12288, 样例数 = 120)
Y_test -- 测试集, (输入特征数 = 12288, 样例数 = 120)
learning_rate -- 参数更新的learning rate
num_epochs -- 迭代次数
minibatch_size -- minibatch大小
print_cost -- 是否每迭代100输出代价
返回参数:
parameters -- 学习到的模型参数,用于预测新的数据集.
"""
ops.reset_default_graph() # to be able to rerun the model without overwriting tf variables
tf.set_random_seed(1) # to keep consistent results
seed = 3 # to keep consistent results
(n_x, m) = X_train.shape # (n_x: input size, m : number of examples in the train set)
n_y = Y_train.shape[0] # n_y : output size
costs = [] # To keep track of the cost
# 创建 Placeholders
X, Y = create_placeholders(n_x, n_y)
# 初始化参数
parameters = initialize_parameters()
# 前向传播: 用tensorflow graph建立前向传播
Z3 = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
# 计算代价
cost = compute_cost(Z3, Y)
# 后向传播: 定义tensorflow optimizer对象,这里使用AdamOptimizer.
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate = learning_rate).minimize(cost)
# 初始化所有的参数
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 启动session来计算tensorflow graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Run the initialization
sess.run(init)
# 循环迭代
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
epoch_cost = 0. # 定义每一大次迭代的代价
num_minibatches = int(m / minibatch_size) # 训练集minibatch的数量
seed = seed + 1
minibatches = random_mini_batches(X_train, Y_train, minibatch_size, seed)
for minibatch in minibatches:
# 选择一个minibatch
(minibatch_X, minibatch_Y) = minibatch
# IMPORTANT: The line that runs the graph on a minibatch.
# Run the session to execute the "optimizer" and the "cost", the feedict should contain a minibatch for (X,Y).
_ , minibatch_cost = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict = {X : minibatch_X, Y: minibatch_Y})
epoch_cost += minibatch_cost / num_minibatches
# Print the cost every epoch
if print_cost == True and epoch % 100 == 0:
print ("Cost after epoch %i: %f" % (epoch, epoch_cost))
if print_cost == True and epoch % 5 == 0:
costs.append(epoch_cost)
# plot the cost
plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)')
plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate))
plt.show()
# lets save the parameters in a variable
parameters = sess.run(parameters)
print ("Parameters have been trained!")
# Calculate the correct predictions
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(Z3), tf.argmax(Y))
# Calculate accuracy on the test set
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
print ("Train Accuracy:", accuracy.eval({X: X_train, Y: Y_train}))
print ("Test Accuracy:", accuracy.eval({X: X_test, Y: Y_test}))
return parameters
2.8 模型调用
parameters = model(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test)3. 实验结果
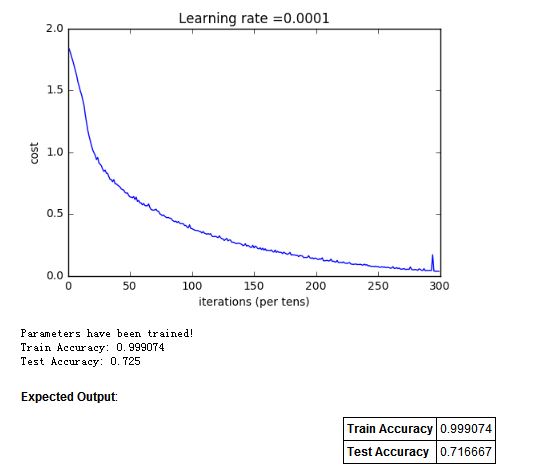






















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








