geodesic distance
1、python实现geodesic距离
其中见到的出现最多的名词之一就是 geodesic distance ,这个单词的中文翻译是测地距离,其实测地距离的意思就是在三维空间中,两点之间的最短路径,归根究底就是最短路径,在三维中间从一个点到另外一个点的路径有无数种,但是最短路径只有一条,那么这个最短路径的长度就是测地距离 geodesic distance。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Mon Jan 24 15:00:35 2022
@author: wmz
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy.ma as ma
# %pylab
from scipy.ndimage.morphology import distance_transform_edt
l = 100
x, y = np.indices((l, l))
center1 = (50, 20)
center2 = (28, 24)
center3 = (30, 50)
center4 = (60,48)
radius1, radius2, radius3, radius4 = 15, 12, 19, 12
circle1 = (x - center1[0])**2 + (y - center1[1])**2 < radius1**2
circle2 = (x - center2[0])**2 + (y - center2[1])**2 < radius2**2
circle3 = (x - center3[0])**2 + (y - center3[1])**2 < radius3**2
circle4 = (x - center4[0])**2 + (y - center4[1])**2 < radius4**2
# 3 circles
img = circle1 + circle2 + circle3 + circle4
mask = ~img.astype(bool)
img = img.astype(float)
m = np.ones_like(img)
m[center1] = 0
#imshow(distance_transform_edt(m), interpolation='nearest')
m = ma.masked_array(distance_transform_edt(m), mask)
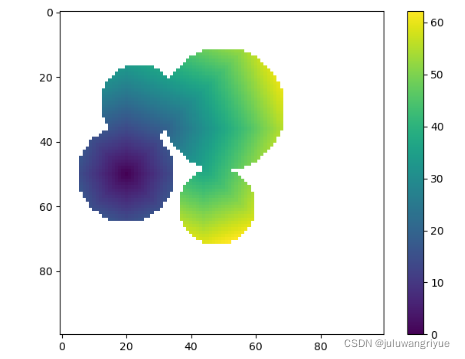
plt.imshow(m, interpolation='nearest')
plt.show()

I implemented the Dijkstra algorithm to apply a geodesic distance transform to the shape above:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Mon Jan 24 15:43:44 2022
@author: wmz
"""
import numpy
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy.ma as ma
from math import *
from numpy import *
# %pylab
from scipy.ndimage.morphology import distance_transform_edt
def geodesic_distance_transform(m):
visit_mask = mask.copy() # mask visited cells
m = m.filled(numpy.inf)
m[m!=0] = numpy.inf
distance_increments = numpy.asarray([sqrt(2), 1., sqrt(2), 1., 1., sqrt(2), 1., sqrt(2)])
connectivity = [(i,j) for i in [-1, 0, 1] for j in [-1, 0, 1] if (not (i == j == 0))]
cc = unravel_index(m.argmin(), m.shape) # current_cell
while (~visit_mask).sum() > 0:
neighbors = [tuple(e) for e in asarray(cc) - connectivity
if not visit_mask[tuple(e)]]
tentative_distance = [distance_increments[i] for i,e in enumerate(asarray(cc) - connectivity)
if not visit_mask[tuple(e)]]
for i,e in enumerate(neighbors):
d = tentative_distance[i] + m[cc]
if d < m[e]:
m[e] = d
visit_mask[cc] = True
m_mask = ma.masked_array(m, visit_mask)
cc = unravel_index(m_mask.argmin(), m.shape)
return m
if __name__ == "__main__":
l = 100
x, y = np.indices((l, l))
center1 = (50, 20)
center2 = (28, 24)
center3 = (30, 50)
center4 = (60,48)
radius1, radius2, radius3, radius4 = 15, 12, 19, 12
circle1 = (x - center1[0])**2 + (y - center1[1])**2 < radius1**2
circle2 = (x - center2[0])**2 + (y - center2[1])**2 < radius2**2
circle3 = (x - center3[0])**2 + (y - center3[1])**2 < radius3**2
circle4 = (x - center4[0])**2 + (y - center4[1])**2 < radius4**2
# 3 circles
img = circle1 + circle2 + circle3 + circle4
mask = ~img.astype(bool)
img = img.astype(float)
m = np.ones_like(img)
m[center1] = 0
m = ma.masked_array(distance_transform_edt(m), mask)
gdt = geodesic_distance_transform(m)
plt.imshow(gdt, interpolation='nearest')
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
执行时间:
0.22861695289611816 s
安装软件包
conda install sscikit-fmm
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Mon Jan 24 15:43:44 2022
@author: wmz
"""
import numpy
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy.ma as ma
from math import *
from numpy import *
import skfmm
import time
# %pylab
from scipy.ndimage.morphology import distance_transform_edt
def geodesic_distance_transform(m):
visit_mask = mask.copy() # mask visited cells
m = m.filled(numpy.inf)
m[m!=0] = numpy.inf
distance_increments = numpy.asarray([sqrt(2), 1., sqrt(2), 1., 1., sqrt(2), 1., sqrt(2)])
connectivity = [(i,j) for i in [-1, 0, 1] for j in [-1, 0, 1] if (not (i == j == 0))]
cc = unravel_index(m.argmin(), m.shape) # current_cell
while (~visit_mask).sum() > 0:
neighbors = [tuple(e) for e in asarray(cc) - connectivity
if not visit_mask[tuple(e)]]
tentative_distance = [distance_increments[i] for i,e in enumerate(asarray(cc) - connectivity)
if not visit_mask[tuple(e)]]
for i,e in enumerate(neighbors):
d = tentative_distance[i] + m[cc]
if d < m[e]:
m[e] = d
visit_mask[cc] = True
m_mask = ma.masked_array(m, visit_mask)
cc = unravel_index(m_mask.argmin(), m.shape)
return m
if __name__ == "__main__":
l = 100
x, y = np.indices((l, l))
center1 = (50, 20)
center2 = (28, 24)
center3 = (30, 50)
center4 = (60,48)
radius1, radius2, radius3, radius4 = 15, 12, 19, 12
circle1 = (x - center1[0])**2 + (y - center1[1])**2 < radius1**2
circle2 = (x - center2[0])**2 + (y - center2[1])**2 < radius2**2
circle3 = (x - center3[0])**2 + (y - center3[1])**2 < radius3**2
circle4 = (x - center4[0])**2 + (y - center4[1])**2 < radius4**2
# 3 circles
img = circle1 + circle2 + circle3 + circle4
mask = ~img.astype(bool)
img = img.astype(float)
m = np.ones_like(img)
m[center1] = 0
m = ma.masked_array(m, mask) # distance_transform_edt(m)
t1 = time.time()
# gdt = geodesic_distance_transform(m)
distance = skfmm.distance(m)
t2 = time.time()
eclipsed = t2 - t1
print(eclipsed, "s")
# plt.imshow(gdt, interpolation='nearest')
plt.imshow(distance, interpolation='nearest')
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
执行时间:
0.0009877681732177734 s
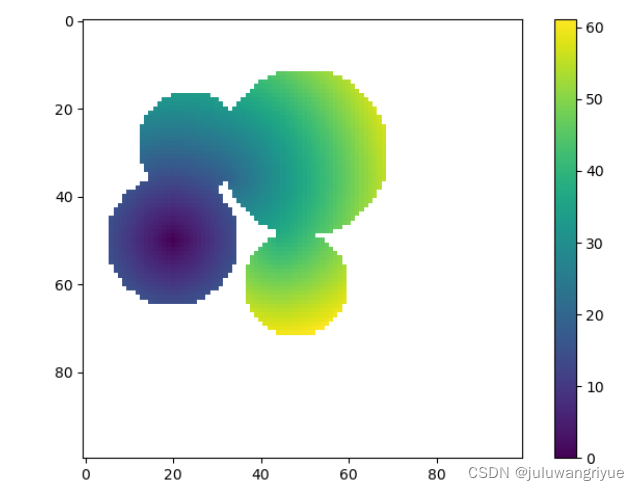
速度skfmm.distance是前者的231倍,效果skfmm.distance还要好于前者。
参考:关于 geodesic distance 的通俗解释
参考:geodesic distance transform in python
2、c++实现geodesic距离
编译与安装参考 GeographicLib 1.52
测试程序:
In order to use GeographicLib from C++ code, you will need to
Include the header files for the GeographicLib classes in your code. E.g.,
#include <GeographicLib/LambertConformalConic.hpp>
Include the GeographicLib:: namespace prefix to the GeographicLib classes, or include
using namespace GeographicLib;
in your code.
- Finally compile and link your code. You have two options here.
- Use cmake to build your package. If you are familiar with cmake this typically will be far the simplest option.
- Set the include paths and linking options “manually”.
- Building your code with cmake. In brief, the necessary steps are:
include in your CMakeLists.txt files
find_package (GeographicLib REQUIRED)
add_executable (program source1.cpp source2.cpp)
target_link_libraries (program ${GeographicLib_LIBRARIES})
- configure your package, e.g., with
mkdir BUILD
cd BUILD
cmake -G "Visual Studio 14" -A x64 \
-D CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH="C:/Program Files" \
-D CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX="C:/Program Files/testgeog" \
..
Here is a very simple test code, which uses the Geodesic class:
// Small example of using the GeographicLib::Geodesic class
#include <iostream>
#include <GeographicLib/Geodesic.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace GeographicLib;
int main() {
const Geodesic& geod = Geodesic::WGS84();
// Distance from JFK to LHR
double
lat1 = 40.6, lon1 = -73.8, // JFK Airport
lat2 = 51.6, lon2 = -0.5; // LHR Airport
double s12;
geod.Inverse(lat1, lon1, lat2, lon2, s12);
cout << s12 / 1000 << " km\n";
}
完整CMakeLists.txt
project (geodesictest)
cmake_minimum_required (VERSION 3.1.0)
find_package (GeographicLib REQUIRED)
if (NOT MSVC)
set (CMAKE_INSTALL_RPATH_USE_LINK_PATH TRUE)
endif ()
add_executable (${PROJECT_NAME} example-Geodesic-small.cpp)
target_link_libraries (${PROJECT_NAME} ${GeographicLib_LIBRARIES})
if (MSVC)
get_target_property (_LIBTYPE ${GeographicLib_LIBRARIES} TYPE)
if (_LIBTYPE STREQUAL "SHARED_LIBRARY")
# On Windows systems, copy the shared library to build directory
add_custom_command (TARGET ${PROJECT_NAME} POST_BUILD
COMMAND ${CMAKE_COMMAND} -E
copy $<TARGET_FILE:${GeographicLib_LIBRARIES}> ${CMAKE_CFG_INTDIR}
COMMENT "Copying shared library for GeographicLib")
endif ()
endif ()




























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










