第一章 概述
32关键字 9种控制语句
优点:能直接访问物理地址,位操作,代码质量高,执行效率高
可移植性好
面向过程:以事件为中心
面向对象:以实物为中心
printf:系统定义的标准函数
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
void main()
{
double a,b;
printf("input number :\n");
scanf("%lf",&a);
b=sin(a);
printf("sine of %lf is %lf",a,b);
}
include:文件包含命令,拓展名为.h的文件称为头文件
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int max(int a,int b);//函数说明
void main()
{
int x,y,z;
int max(int a,int b);//函数说明
printf("input two numbers:\n");
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
z = max(x,y);//函数调用
printf("max = %d\n",z);
}
int max(int a,int b)//函数定义
{
if(a>b)
return a;
else
return b;
}
第二章 数据类型、运算符和表达式
基本数据类型:特点其值不可以再分解为其他类型
构造数据类型:根据已定义的一个或多个数据类型用构造的方法来定义,一个构造类型的值可以分解成若干个成员或者元素
比如 数组类型,结构体类型,共用体类型
指针类型:它的值用来表示某个变量在存储器中的地址
空类型:调用后不需要向调用者返回函数值,这种函数可以定义为空类型,说明符为void
#define 预处理命令
#include<stdio.h>
#define PRICE 30//符号常量
void main()
{
int num,total;
num = 10;
total = num * PRICE;
printf("total = %d\n",total);
}
变量定义必须放在变量使用之前,一般放在函数体的开头
类型占多少字节跟编译器有关
short int 2字节
long int 4字节
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a,b,c,d;
unsigned u;
a = 12;b=-24;u=10;
c= a+u;
d=b+u;
printf("a+u=%d,b+u=%d\n",c,d);
}
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
short int a,b;
a = 32767;
b = a+1;//变量溢出
printf("%d,%d\n",a,b);
}
实型常量也称实数或者浮点数,实数只采用十进制,他有两种形式:十进制小数形式,指数形式。
单精度4字节,双精度8字节
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
float a,b;
a = 123456.789e5;
b = a + 20;
printf("%f\n",a);
printf("%d\n",a);
}
\t:跳到下一个制表位
\r:回车
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char a,b;
a = 'a';
b = 'b';
a = a-32;
b = b-32;
printf("%c %c\n",a,b);
}
可以把一个字符常量赋予一个字符变量,但不能把一个字符串常量赋予一个字符变量。
可以char a = ‘a’;但是不能char a = “a”;
自动转换规则:double->long->unsigned->int->char,short
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
float PI = 3.14159;
int s,r=5;
s = r*r*PI;//右边转为s的数据类型
printf("s = %d\n",s);
}
双目运算符:有两个量参与加减乘除法运算(自左向右)
赋值运算符自右向左
i++:i参与运算后,i的值再自增1(单目运算符)
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int i = 8;
printf("%d\n",++i);
printf("%d\n",--i);
printf("%d\n",i++);
printf("%d\n",i--);
printf("%d\n",-i++);
printf("%d\n",-i--);
}
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int i =5,j = 5,p,q;
p = (i++)+(i++)+(i++);//18
q = (++j)+(++j)+(++j);//22?
printf("%d,%d,%d,%d",p,q,i,j);
}
赋值运算符右结合性
字符型赋予整型,字符的ascll码放到整型量的低八位中,高八位为0
复合赋值运算符+=,-=,*=,/=
逗号运算符:表达式1,表达式2//以表达式2的值作为整个逗号表达式的值
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a=2,b=4,c=6,x,y;
y = (x = a+b),(b+c);//=优先级最高
printf("y = %d,x = %d",y,x);//y=6
}
条件语句:if switch 循环执行语句:do while while for
转向:break goto continue return
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int i = 8;
printf("%d\n%d\n%d\n%d\n%d\n%d\n%d\n",i,++i,--i,i++,i--,-i++,-i--);
return 0;
}
printf(“%d\n %d\n”,++i,–i);//同一语句中++i,–i相抵消
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int i = 8;
printf("%d\n",++i);9
printf("%d\n",--i);8
printf("%d\n",i++);8
printf("%d\n",i--);9
printf("%d\n",-i++);-8
printf("%d\n",-i--);-9
return 0;
}
scanf中没有精度
格式控制符中没有非格式字符作为数据之间间隔时可用空格
逻辑运算符>算术运算符
关系运算符左结合性
(a&&b)&&c
=赋值运算符 ==关系运算符
if语句两句以上用{ }
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a,b,max;
scanf("%d,%d",&a,&b);
max = a;
if(max<b) max = b;
printf("max = %d",max);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
printf("max = %d",a>b?a:b);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int score;
printf("input score:");
scanf("%d",&score);
if(score>=90)
printf("A\n");
else if(score>=80 && score<90)
printf("B\n");
else if(score>=70 && score<80)
printf("C\n");
else if(score>=60 && score<70)
printf("D\n");
else
printf("E\n");
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a,b,c,temp;
printf("input 3:");
scanf("%d,%d,%d",&a,&b,&c);
if(a>b)
{
temp = a;
a = b;
b =temp;
}
if(a>c)
{
temp = a;
a = c;
c = temp;
}
if(b>c)
{
temp = b;
b = c;
c = temp;
}
printf("input 3:%d,%d,%d",a,b,c);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char ch;
scanf("%c",&ch);
if(ch>='A' && ch<='Z'?ch+32:ch)
printf("ch = %c\n",ch);
return 0;
}
goto:使程序层次不清,且不易读,适用多层嵌套
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 1,sum = 0;
loop:if(i<=100)
{
sum += i;
i++;
goto loop;
}
printf("sum = %d",sum);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 0,sum = 0;
do{
sum = sum +i;
i++;
}while(i<=100);
printf("%d",sum);
return 0;
}
for:表达式1->表达式2->执行语句->表达式3->表达式2->执行语句->表达式3
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<7;i++)
{
putchar('\n');
for(j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
putchar('*');
}
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
float pi = 3.14159;
float area;
for(int r=1;r<10;r++)
{
area = pi*r*r;
if(area>100)
{
break;
}
printf("r = %d,area = %f\n",r,area);
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int i,j;
for(i=100;i<=200;i++)
{
if(i%3==0)
continue;
j++;
printf("%d\n",i);
}
printf("%d",j);
return 0;
}
数组:有序的数据集合
数组元素也称下标变量
逐个使用下标变量,而不能一次引用整个数组
#include <stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int i,a[10];
for(i=0;i<=9;i++)
{
a[i] = i;
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
for(i=9;i>=0;i--)
{
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
return 0;
}
数组赋初值时,由于数据的个数已经确定,可以不指定数组长度//int a[ ] = {1,2,3,4,5}
#include <stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int i,a[5] = {1,2,3},b[5];
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
printf("%5d",a[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
printf("%5d",b[i]);
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int i,max,temp,a[10];
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);//动态赋值
}
max = a[0];
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
if(max<a[i])
{
max = a[i];
}
}
printf("max = %d",max);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>//冒泡排序
int main()
{
int i,j,temp,a[6];
for(i=0;i<6;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
for(i=0;i<6;i++)
{
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<5-i;j++)//内循环,第一次循环5次
{
if(a[j]>a[j+1])//a[j]不是a[i],内循环控制次数
{
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j+1];
a[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
for(i=0;i<6;i++)
{
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
return 0;
}
如果对全部元素都赋初值,定义数组时对第一维的长度可以不指定,但第二维的长度不能省
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i,j,v[3],sum = 0,average,a[5][3] = {{80,75,92},{61,65,71},{59,63,70},{85,87,90},{76,77,85}};
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<5;j++)
{
sum = sum+a[i][j];
}
v[i] = sum/5;
sum = 0;
}
average = (v[0]+v[1]+v[2])/3;
printf("math = %d\n lan = %d\n eng = %d\n aver = %d\n",v[0],v[1],v[2],average);
return 0;
}
程序编译是以源文件为单位进行编译,而不是以函数为单位
函数有两种:1、标准函数2、用户自己定义的函数
void是不需要带回函数值,内容需要带回
定义函数,函数名后面括号中的变量称为形参
#include <stdio.h>
void main()
{
void pr();
void pri();
pr();
pri();
pr();
return 0;
}
void pr()
{
printf("***************\n");
}
void pri()
{
printf("12345\n");
}
#include <stdio.h>
int max(int x,int y);//函数声明,形参,只有调用才分配内存空间
void main()
{
int a,b,c;
scanf("%d,%d",&a,&b);
c = max(a,b);//函数调用,实参
printf("c = %d\n",c);
return 0;
}
int max(int x,int y)
{
int z;
z = x>y?x:y;
return z;
}
函数决定返回值类型
#include <stdio.h>
int max(int x,int y);
void main()
{
float a,b,c;
scanf("%f,%f",&a,&b);
c = max(a,b);
printf("c = %f\n",c);//c=5.0,c为浮点型
return 0;
}
int max(int x,int y)
{
float z;
z = x>y?x:y;
return z;
}
#include <stdio.h>
void main()
{
int f(int x,int y);
int p,i=2;
p = f(i,i++);//从右到左(3,2),c =1
printf("%d\n",p);
return 0;
}
int f(int x,int y)
{
int c;
if(x>y)
{
c = 1;
}
else if(x==y)
{
c = 0;
}
else
c = -1;
return c;
}
#include <stdio.h>
long fa(int p); // 阶乘
int main()
{
long s = 0;
s += 2 * fa(2); // 2*2!
s += 3 * fa(3); // 3*3!
printf("%ld\n", s);
return 0;
}
long fa(int p)
{
long c = 1;
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= p; i++) // 注意这里应该是 <=p,因为阶乘包括p本身
{
c = c * i;
}
return c;
}
#include <stdio.h>//递归
long rec(int n);
void main()
{
int n;
long result;
scanf("%d",&n);
result = rec(n);
printf("%d! = %ld\n",n,result);
return 0;
}
long rec(int n)
{
long res;
if(n<0)
{
printf("error\n");
}
else if(n == 0 || n==1)
{
res = 1;
}
else
{
res = rec(n-1)*n;
}
return res;
}
#include <stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a[10] = {1,2,3,4,-1,-2,-3,-4,2,3};
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
test(a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
void test(int v)
{
if(v>0)
{
printf("%d ",v);
}
else
{
printf("0 ");
}
}
数组名作为实参传递共用一段内存跟形参
#include <stdio.h>
double aver(double b[10]);
void main()
{
double a[10] = {82,100,87.5,89,78,85,67.5,92.5,93,94},res;
res = aver(a);//实参传递数组名跟形参共用内存空间
printf("aver is %3.2lf\n",res);
putchar('\n');
return 0;
}
double aver(double b[10])
{
int i = 0;
double sum = 0;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
sum += b[i];
}
sum /= 10;
return sum;
}
#include <stdio.h>//全局变量正方形体积
int s1,s2,s3;
int vs(int a,int b,int c)
{
int v;
v = a*b*c;
s1 = a*b;
s2 = b*c;
s3 = a*c;
return v;
}
void main()
{
int v,l,w,h;
scanf("%d%d%d",&l,&w,&h);
v = vs(l,w,h);
printf("%d %d %d %d\n",v,s1,s2,s3);
return 0;
}
存储分为两大类:静态,动态
具体:自动的,静态的,寄存器的,外部的
局部变量存储在栈区
#include <stdio.h>
int fa(int a)
{
auto int b = 0;//自动变量赋初值不是在编译时进行,而是函数调用时进行,每调用一次重新给一次初值
static int c = 3;//static修饰的全局变量不会变,静态局部变量编译时只赋初值一次,保留上次函数调用结束的值
b = b + 1;
c = c + 1;
return (a+b+c);
}
void main()
{
int a = 2,i;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
printf("%d\n",fa(a));
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
float max = 0,min = 0;
float aver(float ave[],int n);
void main()
{
float ave,sco[10];
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
scanf("%f",&sco[i]);
}
ave = aver(sco,10);
printf("max = %6.2f,min = %6.2f,ave = %6.2f\n",max,min,ave);
}
float aver(float ave[],int n)
{
int i = 0;
float av,sum = 0;
max = min = ave[0];
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(max <ave[i])
{
max = ave[i];
}
else if(min > ave[i])
{
min = ave[i];
}
sum +=ave[i];
}
av = sum/10;
return av;
}
静态局部变量不赋初值,编译自动赋0,动态局部变量不赋初值是个不确定的值
内存——运算器(存数,取数),regist变量存储在cpu的寄存器中,缺点容易撑爆内存
extern来声明外部变量,以拓展外部变量的作用域
#include <stdio.h>
int max(int a,int b)
{
int z;
z = a>b?a:b;
return z;
}
void main()
{
extern a,b;
printf("%d\n",max(a,b));
}
int a = 10,b = 15;
#include<stdio.h>
int fa(int i)
{
static int l = 1;
l = l*i;
return (l);
}
void main()
{
int i,sum = 0;
for(i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
int result = fa(i);//需要中层变量保存函数返回的值,因为static是静态局部变量
printf("%d\n",result);
sum += result;
}
printf("%d\n",sum);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int a;
int main()
{
int power(int);
int b = 3,c,d,m;
scanf("%d %d",&a,&m);
c = a * b;
printf("%d * %d = %d\n",a,b,c);
d = power(m);
printf("%d ^ %d = %d\n",a,m,d);
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
extern int a;
int power(int n)
{
int i,y = 1;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
y *= a;
}
return y;
}
定义变量:建立存储空间
声明:引用
静态存储:程序在整个运行空间都存在
动态存储:调用函数时临时分配


- :指针变量存放的是地址
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int *p,*p1,*p2,a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
p1 = &a;
p2 = &b;
if(a<b)
{
p = p1;
p1 = p2;
p2 = p;
}
printf("max = %d min = %d",*p1,*p2);
}
#include<stdio.h>//用函数方式交换2个数
void swap(int *p1,int *p2);
void main()
{
int *p1,*p2,a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
p1 = &a;
p2 = &b;
if(a<b)
{
swap(p1,p2);
}
printf("%d>%d",*p1,*p2);
}
void swap(int *p1,int *p2)
{
int temp;
temp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = temp;
}
#include<stdio.h>//从小到大排序3个值
void exch(int *p1,int *p2,int *p3);
void main()
{
int *p1,*p2,*p3,a,b,c;
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
p1 = &a;
p2 = &b;
p3 = &c;
exch(p1,p2,p3);
printf("%d %d %d\n",a,b,c);
}
void exch(int *p1,int *p2,int *p3)
{
int temp;
void swap(int *p1,int *p2);
if(*p1 < *p2)
{
swap(p1,p2);
}
if(*p1 < *p3)
{
swap(p1,p3);
}
if(*p2 < *p3)
{
swap(p2,p3);
}
}
void swap(int *p1,int *p2)
{
int temp;
if(*p1 < *p2)
{
temp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = temp;
}
}
#include<stdio.h>//指针变量指向数组首元素地址输出
void main()
{
int i;
int a[5];
int *p;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
for(p = a;p<(a+5);p++)
{
printf("%d ",*p);
}
}
#include<stdio.h>
void res(int *p,int n);
void main()
{
int a[5] = {1,2,3,4,5},i;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
res(a,5);
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
}
void res(int *p,int n)
{
int m,*i,*j,*x,temp;
m = (n-1)/2;
i = p;//指向数组首元素
j = p+n-1;//指向数组最后一位
x = p+m;//指向数组中间一位
for(i=p;i<x;i++,j--)
{
temp = *i;
*i = *j;
*j = temp;
}
}
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a[3][4] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12};
int i,j,(*p)[4];
p = a;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
{
printf("%2d ",*(*(p+i)+j));
}
putchar('\n');
}
}
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char a[] = "l love you !",b[40];
int i;
for(i=0;*(a+i) != '\0';i++)
{
*(b+i) = *(a+i);
}
*(b+i) = '\0';//确保 b 字符串以 '\0' 结尾
printf("%s\n",a);
for(i = 0;b[i] !='\0';i++)
{
printf("%c",b[i]);
}
}
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char a[]="l love you !",b[40];
int *p1,*p2,i;
p1 = a;
p2 = b;
for(;*p1 !='\0';p1++,p2++)
{
*p2 = *p1;
}
*p2 = '\0';
printf("%s\n",a);
for(i=0;b[i] !='\0';i++)
{
printf("%c",b[i]);
}
}
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
void copy(char *p1,char *p2);
char a[]="l love you !",b[] = "l love you too!";
copy(a,b);
printf("%s\n",b);
}
void copy(char p1[],char p2[])//字符数组作参数实现字符串复制
{
int i;
while(p1[i] !='\0')
{
p2[i] = p1[i];
i++;
}
p2[i] = '\0';
}
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
void copy(char *p1,char *p2);
char *a ="l love you !",b[] = "l love you too!";//字符串常量不能被赋值
copy(a,b);
printf("%s\n",b);
}
void copy(char *p1,char *p2)
{
int i;
for(;*p1 !='\0';p1++,p2++)
{
*p2 = *p1;
}
*p2 = '\0';
}




#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char *p = "l love you marry";
int i;
printf("%c\n",p[8]);//字符指针用下标也可以表示某个元素
for(i=0;p[i] !='\0';i++)
{
printf("%c",p[i]);
}
}
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int max(int a,int b);
int a,b,c;
int (*p)();//指针变量要加()
p = max;//指向函数的指针
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
c = (*p)(a,b);//函数指针
printf("%d",c);
}
int max(int a,int b)
{
int c;
if(a>b)
{
c = a;
}
else
{
c = b;
}
return c;
}

#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
double score[][4] = {{60.0,70.0,80.5,90.5},{54.0,59.0,61.0,62.0},{75.5,76.0,85.0,89.0}};
double *search(double (*po)[4],int n);
double *p;
int i,m;
scanf("%d",&m);
p = search(score,m);
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
printf("%5.2f\t",*(p+i));
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
double *search(double (*po)[4],int n)
{
double *pt;
pt = *(po+n);// 直接返回指向第 n 行的指针
return pt;
}
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a[5] = {1,2,3,4,5};
int *b[5] = {&a[0],&a[1],&a[2],&a[3],&a[4]};
int i;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
printf("%d ",*b[i]);//指向整型数组的指针
}
}
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char *name[] = {"hello","world","bye"};
char **p;//指向指针的指针
int i;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
p = name+i;
printf("%s\n",*p);
}
}
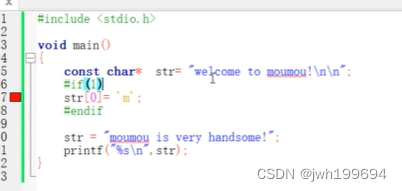
内容不能改变,字符串存放在常量区
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
const char *str ="welcome to!";//加const,字符串单个值不能改变
str = "see you bye!";
printf("%s\n",str);
}

#include<stdio.h>
#define PI 3.14
#define S PI*r*r
void main()
{
int r;
double s;
scanf("%d",&r);
s = S;//宏定义
printf("%g\n",s);
}
typedef是在编译时处理的
#include<stdio.h>
#define ROUND 1//0 1
#define PI 3.14159
void main()
{
int r;
double s;
scanf("%d",&r);
#if ROUND
s = r * r*PI;
printf("%6.5f\n",s);
#else
#endif // ROUND
}
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
struct date
{
int month;
int year;
int day;
};
struct
{
int num;
char name[20];
struct date bir;
}boy1,boy2;//结构体变量
scanf("%d",&boy1.bir.year);
scanf("%d",&boy1.bir.month);
scanf("%d",&boy1.bir.day);
printf("year = %d,month = %d,day = %d",boy1.bir.year,boy1.bir.month,boy1.bir.day);
}
结构体变量的地址跟第一个成员的地址相同
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
struct stu
{
int num;
char *name;
char sex;
float score;
}boy1,boy2 = {102,"mou",'m',75};//赋初值
boy1 = boy2;
printf("%d,%s,%c,%f",boy1.num,boy1.name,boy1.sex,boy1.score);
}

#include<stdio.h>
#define N 3
struct person
{
char name[20];
char phone[20];
};
void main()
{
struct person man[N];//结构体数组
int i;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
printf("input name:");
gets(man[i].name);
printf("input phone:");
gets(man[i].phone);
}
printf("name\t\tphone\n");
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
printf("%s\t\t%s\t\t\n",man[i].name,man[i].phone);
}
}
#include<stdio.h>
struct person
{
int num;
char *name;
char sex;
float score;
}boy1 = {1,"wang",'m',65.5};
void main()
{
struct person *pst;//指向结构体类型数据的指针
pst = &boy1;
printf("%d,%s,%c,%f\n",pst->num,pst->name,pst->sex,pst->score);
printf("%d,%s,%c,%f",(*pst).num,(*pst).name,(*pst).sex,(*pst).score);
}

#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct person
{
int num;
char *name;
char sex;
float score;
};
void print(struct person *p);
void main()
{
struct person pst;
pst.num = 8;
//strcpy(pst.name,"wang");//字符数组专用
pst.name = "wang";
pst.sex = 'm';
pst.score = 80;
print(&pst);
}
void print(struct person *p)
{
printf("%d,%s,%c,%f\n",p->num,p->name,p->sex,p->score);
printf("%d,%s,%c,%f",(*p).num,(*p).name,(*p).sex,(*p).score);
}






















 2125
2125











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








