Json的概念以及与XML的比较:
Json是什么?
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一种轻量级(轻量级?简单、易操作、快捷)的数据交换格式。主要目的就是给出一套通用的数据格式,大家按照这种格式定义自己的数据,方便数据的交换。特点是(相对来说)易于人阅读和编写,易于机器解析和生成。
Json与XML的比较:
- JSON和XML的数据可读性基本相同;
- JSON和XML同样拥有丰富的解析手段
- JSON相对于XML来讲,数据的体积小
- JSON与JavaScript的交互更加方便
- JSON对数据的描述性比XML较差
- JSON的速度要远远快于XML
Json的解析(Gson的用法)
1) 使用Gson解析较简单的数组类型Json数据
[{“name”:”xxx”,”age”:xx}]
这里我们直接把Json数据写入代码中。
首先我们需要定义一个Bean文件:
JavaBean类 Person.java
public class Person {
int id;
String name;
int age;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String toString(){
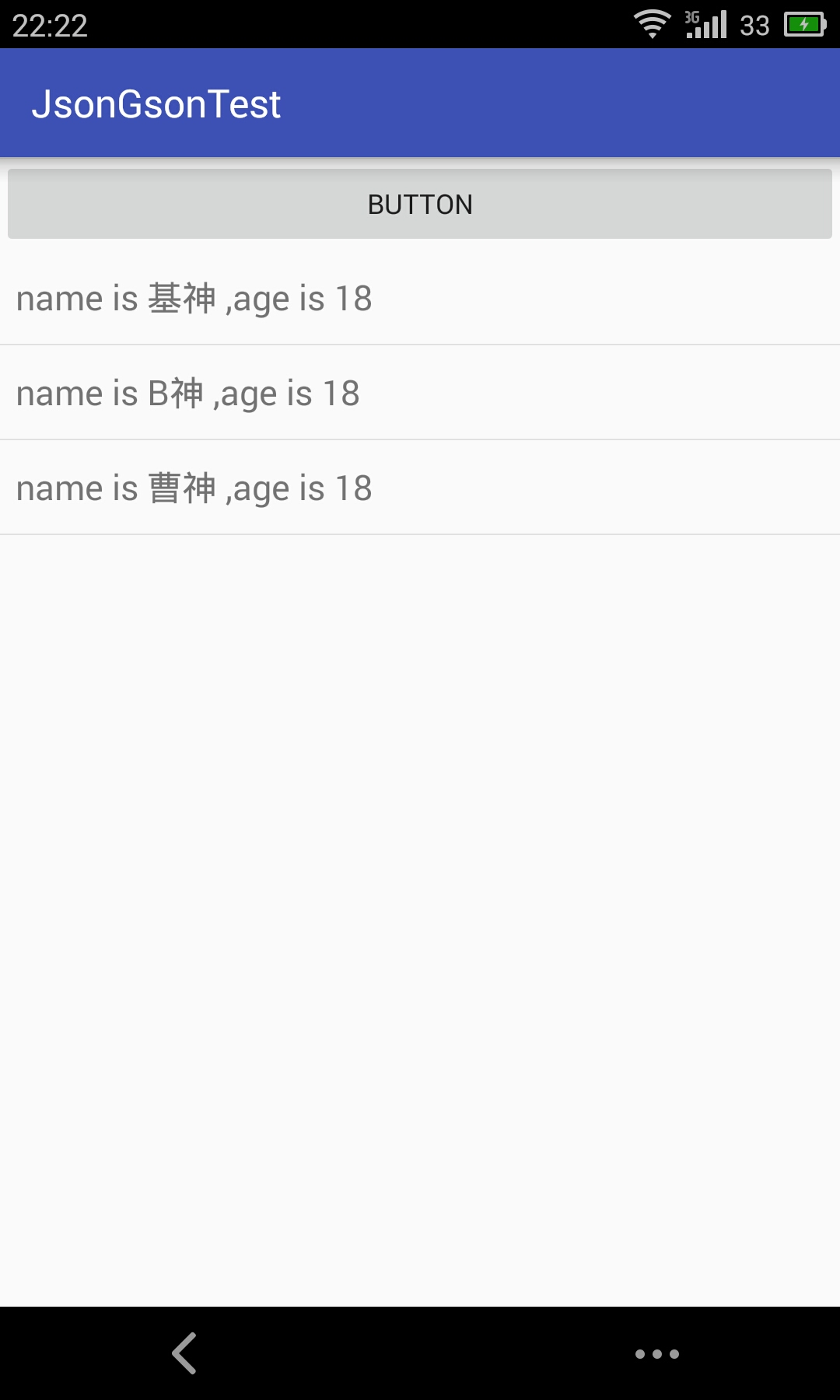
return "name is "+ name+" ,age is "+age;
}
}
MainActivity.class
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener{
String data = "[\n" +
"{ \"id\":\"1\",\"name\":\"基神\",\"age\":\"18\" },\n" +
"{ \"id\":\"2\",\"name\":\"B神\",\"age\":\"18\" },\n" +
"{ \"id\":\"3\",\"name\":\"曹神\",\"age\":\"18\" }\n" +
"]";
private Button button;
private ListView listVeiw;
private List<Person> persons;
private ArrayAdapter<Person> arrayAdapter;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initView();
}
private void initView() {
button = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(this);
listVeiw = (ListView)this.findViewById(R.id.listView);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if(v.getId()==R.id.button){
persons = readJsonForGson(data);
Log.i("GsonJson",persons.toString());
arrayAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<Person>(this,android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1,persons);
listVeiw.setAdapter(arrayAdapter);
}
}
private List<Person> readJsonForGson(String data) {
List<Person> personList = null;
Person person = new Person();
try{
//如果需要解析Json数组数据,先要生成一个Type对象
Type listType = new TypeToken<List<Person>>(){}.getType();
//创建Gson对象
Gson gson = new Gson();
//这行代码就可以获得Json数据,是不是很简单
personList = gson.fromJson(data,listType);
Log.i("Gson",personList.toString());
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return personList;
}
}
解析效果展示:
2) Gson解析较复杂Json数据
我们将上面的Json数据变得复杂一点,如下:
{ “ch”:[
{ “id”:”1”,”name”:”基神”,”age”:”18” },
{ “id”:”2”,”name”:”B神”,”age”:”18” }
{ “id”:”3”,”name”:”曹神”,”age”:”18” }
]};
还是一样,先定义一个Bean类,定义Bean类很简单,看见一个{}就定义一个类,看见[]就定义一个List<>;
JavaBean类 Person类
public class Person {
public List<Ch> ch;
public List<Ch> getCh() {
return ch;
}
public void setCh(List<Ch> ch) {
this.ch = ch;
}
public String toString(){
return "result ——>"+ch;
}
}
ch类
public class Ch {
int id;
String name;
int age;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String toString(){
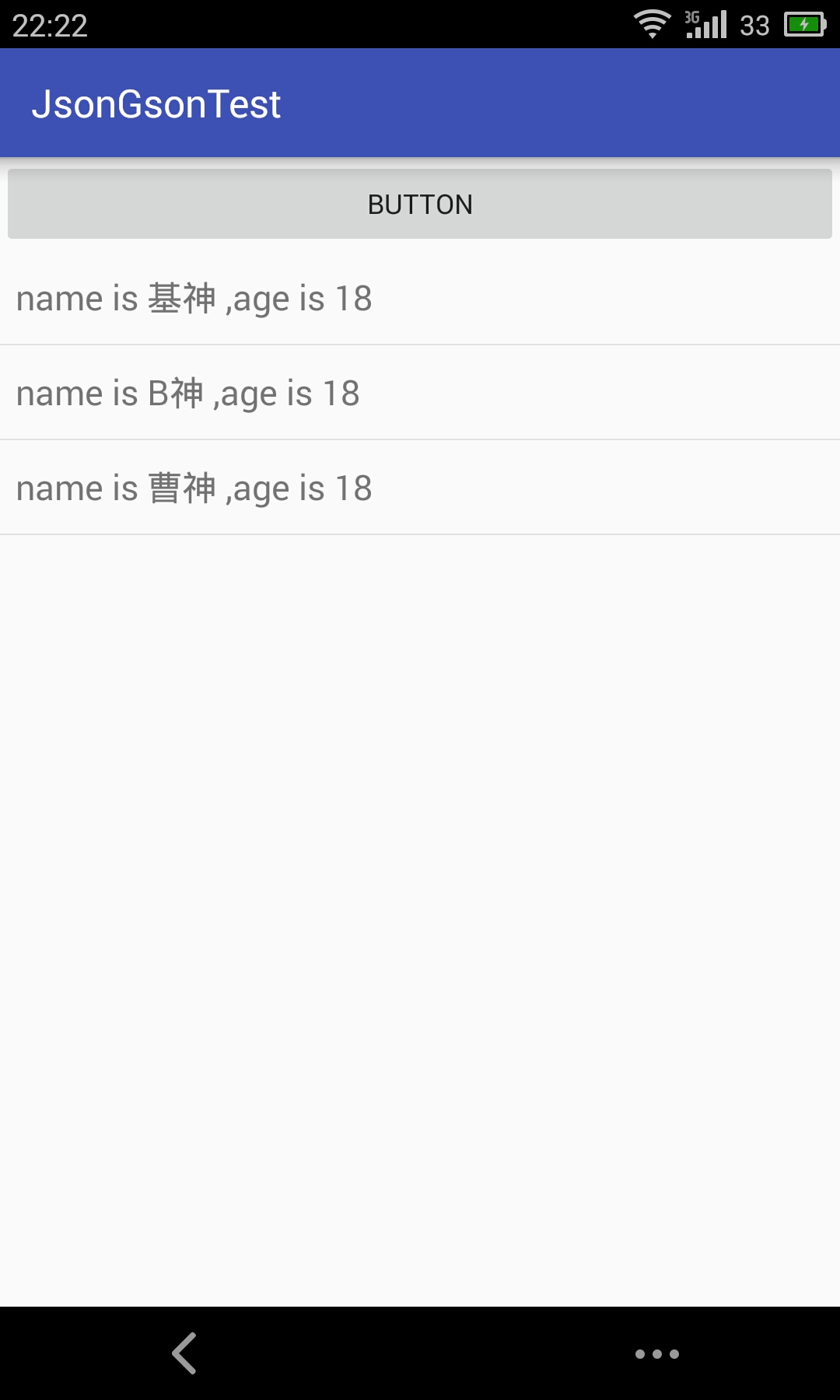
return "name is "+ name+" ,age is "+age;
}
}
MainActivity.class
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener{
String data = "{ \"ch\":[\n" +
"{ \"id\":\"1\",\"name\":\"基神\",\"age\":\"18\" },\n" +
"{ \"id\":\"2\",\"name\":\"B神\",\"age\":\"18\" },\n" +
"{ \"id\":\"3\",\"name\":\"曹神\",\"age\":\"18\" }\n" +
"]}";
private Button button;
private ListView listVeiw;
private List<Ch> persons;
private ArrayAdapter<Ch> arrayAdapter;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initView();
}
private void initView() {
button = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(this);
listVeiw = (ListView)this.findViewById(R.id.listView);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if(v.getId()==R.id.button){
persons = readJsonForGson(data);
Log.i("GsonJson",persons.toString());
arrayAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<Ch>(this,android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1,persons);
listVeiw.setAdapter(arrayAdapter);
}
}
private List<Ch> readJsonForGson(String data) {
List<Ch> chList = null;
try{
//如果需要解析Json数据,先要生成一个Type对象
//Type listType = new TypeToken<List<Person>>(){}.getType();
Gson gson = new Gson();
//这里和刚才有所变化,也很简单吧
Person person = gson.fromJson(data,Person.class);
// personList = gson.fromJson(data,listType);
Log.i("Gson",person.toString());
chList = person.getCh();
Log.i("Gson",chList.toString());
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//返回List数据
return chList;
}
}
解析效果展示:
3)使用Gson解析网络较复杂Json数据
实际运用中,我们不可能把Json数据直接添加到我们的项目中,而更多的是以访问网络来获得Json数据,比如,这里我们用一个自己搭建的网页来作为一个例子:
你需要配置一个tomcat服务器,这里就不教大家了,网上有详细的教程,然后在 【你的tomcat存放位置\apache-tomcat-7.0.55\webapps\ROOT】 中新建一个weather.html文件,将json数据写进去,双击bin目录下面的startup.bat就可以启动服务器,再然后输入网址:【http://你的ip地址:8080/weather.html】
再教大家一个查看ip的小技巧:cmd中输入命令行ipconfig
好了,准备工作做好之后,我们就可以看到如下数据了:
{ "error": 0, "status": "success", "date": "2015-03-10", "results": [ { "currentCity": "北京", "weather_data": [ { "date": "周一(今天, 实时:19℃)", "dayPictureUrl": "http://api.map.baidu.com/images/weather/day/dayu.png", "nightPictureUrl": "http://api.map.baidu.com/images/weather/night/dayu.png", "weather": "大雨", "wind": "东南风5-6级", "temperature": "18℃" }, { "date": "周二", "dayPictureUrl": "http://api.map.baidu.com/images/weather/day/zhenyu.png", "nightPictureUrl": "http://api.map.baidu.com/images/weather/night/duoyun.png", "weather": "阵雨转多云", "wind": "西北风4-5级", "temperature": "21 ~ 14℃" }, { "date": "周三", "dayPictureUrl": "http://api.map.baidu.com/images/weather/day/leizhenyu.png", "nightPictureUrl": "http://api.map.baidu.com/images/weather/night/leizhenyu.png", "weather": "雷阵雨", "wind": "西北风4-5级", "temperature": "22 ~ 18℃" }, { "date": "周四", "dayPictureUrl": "http://api.map.baidu.com/images/weather/day/qing.png", "nightPictureUrl": "http://api.map.baidu.com/images/weather/night/qing.png", "weather": "晴", "wind": "东南风2级", "temperature": "28℃" } ] } ] }
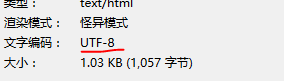
需要注意的是你的页面文字编码和你的Android studio一定要保持一致。比如说我的页面文字编码是UTF-8,那么开发工具也一定要是UTF-8,不然会出现乱码。
好了,下面我们正式开始解析这个复杂的Json数据:
使用Gson解析数据我们一开始需要定义一个序列化的Bean,那么,这个Bean怎么定义呢,其实很简单:
- 看到JSON结构里面有{ }你就定义一个类,看到[ ]你就定义一个List;
- 最后只剩下最简单的如String、int等基本类型直接定义就好;
- 内部嵌套的类,请使用public static class className { };
- 类内部的属性名,必须与JSON串里面的Key名称保持一致。
根据上面的规则我们定义如下三个Bean文件:
最外层的Bean文件
package com.example.httpjsontest;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2016/9/7 0007.
*/
public class Status {
private String error;
private String status;
private String date;
private List<Results> results;
public String getError() {
return error;
}
public void setError(String error) {
this.error = error;
}
public String getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(String status) {
this.status = status;
}
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public List<Results> getResults() {
return results;
}
public void setResults(List<Results> results) {
this.results = results;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Status [error=" + error + ", status=" + status + ", date="
+ date + ", result=" + results + "]";
}
}
第二层的Bean文件
package com.example.httpjsontest;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2016/9/7 0007.
*/
public class Results {
private String currentCity;
private List<WeatherDate> weather_data;
public String getCurrentCity() {
return currentCity;
}
public void setCurrentCity(String currentCity) {
this.currentCity = currentCity;
}
public List<WeatherDate> getWeather_data() {
return weather_data;
}
public void setWeather_data(List<WeatherDate> weather_data) {
this.weather_data = weather_data;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "results [curentCity=" + currentCity + ", weather_data="
+ weather_data + "]";
}
}
最后一层Bean文件
package com.example.httpjsontest;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2016/9/7 0007.
*/
public class WeatherDate {
private String date;
private String dayPictureUrl;
private String nightPictureUrl;
private String weather;
private String wind;
private String temperature;
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public String getDayPictureUrl() {
return dayPictureUrl;
}
public void setDayPictureUrl(String dayPictureUrl) {
this.dayPictureUrl = dayPictureUrl;
}
public String getNightPictureUrl() {
return nightPictureUrl;
}
public void setNightPictureUrl(String nightPictureUrl) {
this.nightPictureUrl = nightPictureUrl;
}
public String getWeather() {
return weather;
}
public void setWeather(String weather) {
this.weather = weather;
}
public String getWind() {
return wind;
}
public void setWind(String wind) {
this.wind = wind;
}
public String getTemperature() {
return temperature;
}
public void setTemperature(String temperature) {
this.temperature = temperature;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
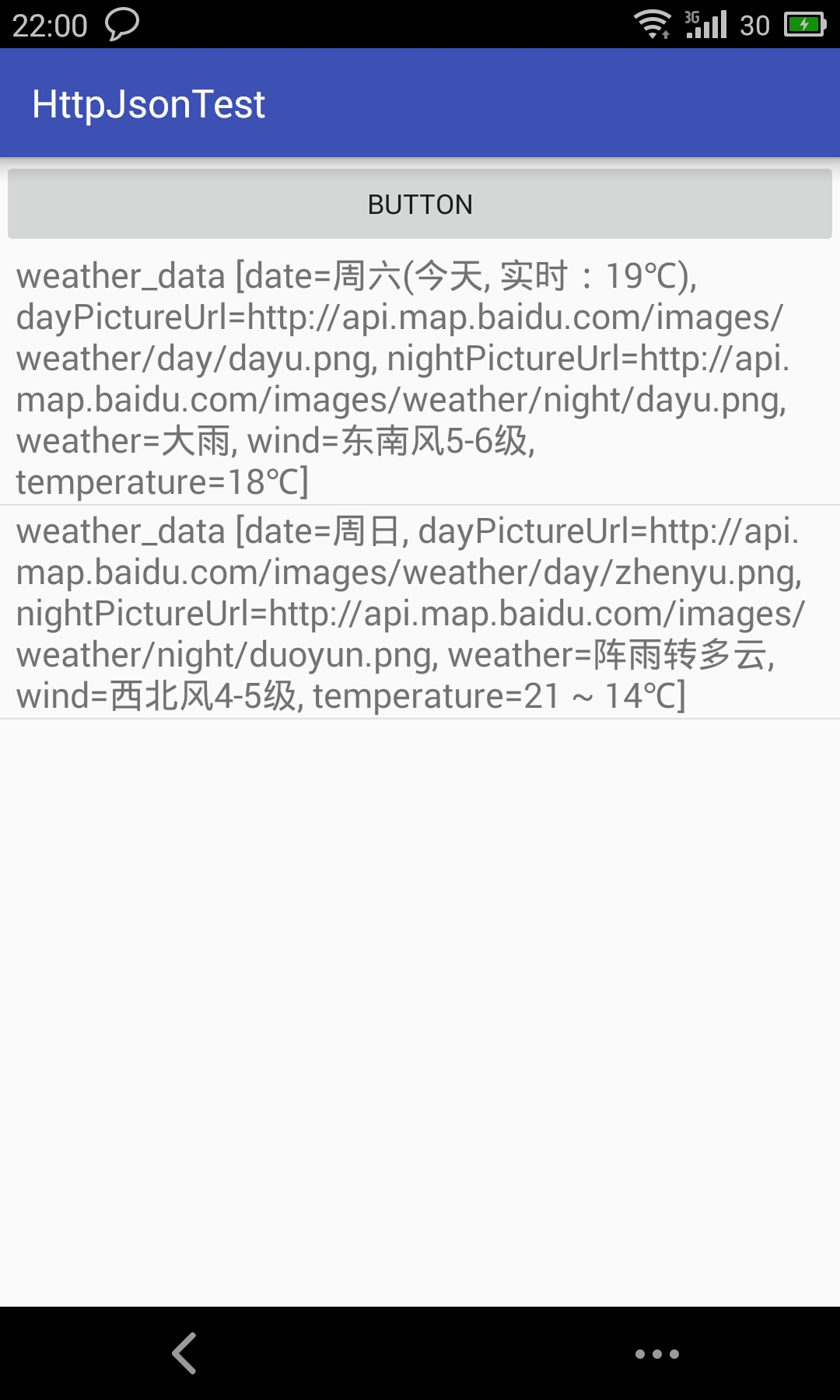
return "weather_data [date=" + date + ", dayPictureUrl="
+ dayPictureUrl + ", nightPictureUrl="
+ nightPictureUrl + ", weather=" + weather + ", wind="
+ wind + ", temperature=" + temperature + "]";
}
}
有不懂的可以返回去看一看Bean文件的规则。
具体的JavaBean定义好了,我们就开始真正地解析Json数据:
(1)先写一个工具类(HttpUtils)用来获得json数据:
public class HttpUtils {
public HttpUtils(){
}
//通过HttpURLCnnection获取链接(urlPath)里的数据,放到输入流(InputStream)里
public static String getJsonContent(String urlPath) {
try {
URL url = new URL(urlPath);
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
connection.setConnectTimeout(3000);
connection.setRequestMethod("GET");
connection.setDoInput(true);
int code = connection.getResponseCode();
if (code == 200) {
return changeInputStream(connection.getInputStream());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
return "";
}
//将流转换为字符串
private static String changeInputStream(InputStream inputStream) {
String result = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream outStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
try{
while((len=inputStream.read(buffer))!=-1){
outStream.write(buffer,0,len);
}
inputStream.close();
result = new String(outStream.toByteArray());
Log.i("Jsontest",result);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
}
这是HttpURLConnection和IO流的相关用法,这里不进行介绍了。
获得数据之后,就可以开始使用Gson解析Json数据了,在onCreate方法里开启一个子线程:
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
listView = (ListView)this.findViewById(R.id.listView);
button = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(this);
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try{
HttpUtils httpUtils = new HttpUtils();
detail = httpUtils.getJsonContent(urlPath);
Log.i("JsonOne",detail);
Gson gson = new Gson();
status = gson.fromJson(detail,Status.class);
Log.i("status ",status.toString());
results = status.getResults();
Log.i("results",results.toString());
weatherdate = results.get(0).getWeather_data();
Log.i("weatherDate",weatherdate.get(0).toString());
String weather = weatherdate.get(0).getWeather();
Log.i("weather",weather);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
} 我们可以在logCat里面查看数据是否获得。
布局文件(activity_main.xml):
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="BUTTON" />
<ListView
android:id="@+id/listView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
定义一个listView来存放数据,点击按钮,显示数据传入ListView:
public void onClick(View v) {
if(v.getId()==R.id.button){
arrayAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<WeatherDate>(this,android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1,weatherdate);
listView.setAdapter(arrayAdapter);
}
}
最后把MainActivity的代码放上来看一下:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener{
private Button button;
private ListView listView;
private String urlPath = "http://172.30.18.222:8080/weather.html";
String detail = "";
private Status status;
private List<Results> results;
private List<WeatherDate> weatherdate;
private ArrayAdapter<WeatherDate> arrayAdapter;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
listView = (ListView)this.findViewById(R.id.listView);
button = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(this);
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try{
HttpUtils httpUtils = new HttpUtils();
detail = httpUtils.getJsonContent(urlPath);
Log.i("JsonOne",detail);
Gson gson = new Gson();
status = gson.fromJson(detail,Status.class);
Log.i("status ",status.toString());
results = status.getResults();
Log.i("results",results.toString());
weatherdate = results.get(0).getWeather_data();
Log.i("weatherDate",weatherdate.get(0).toString());
String weather = weatherdate.get(0).getWeather();
Log.i("weather",weather);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if(v.getId()==R.id.button){
arrayAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<WeatherDate>(this,android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1,weatherdate);
listView.setAdapter(arrayAdapter);
}
}
} 最后别忘了在清单文件中添加权限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />放上效果展示图:
这只是简单地将数据放进listView中,其实还可以自定义Adapter,将里面的数据再进行获取和解析,再填充进listView即可,这里不过多介绍。






















 1885
1885

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








