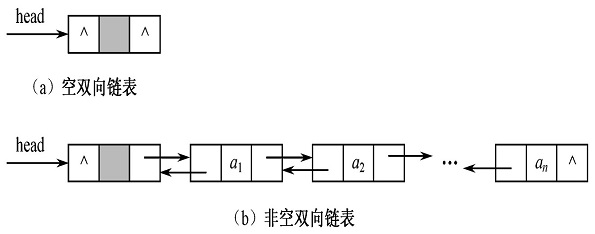
在循环链表中,虽然从任一结点出发均可以扫描到其他结点,但是要找到其前驱结点则需要遍历整个链表。如果希望快速确定表中任一结点的前驱结点,可以再每个结点中再设置一个指向其前驱结点的指针域,这样就形成的双链表(doubly linked list),如第一张图所示,prior为前驱指针域,next为后继指针域。
结点的C++描述为:
template<class Type>
struct DulNode
{
Type data; //数据域
DulNode<Type> *prior, *next; //指向前驱结点的指针和指向后继结点的指针
};和单链表类似,双链表一般也是由头指针唯一确定,增加头结点也能使双链表的某些操作变得方便,将头结点和尾结点链接起来就构成了循环双链表,这样无论是插入还是删除操作,对链表中开始结点、终端结点和中间结点的操作过程相同。实际上常用带头结点的循环双链表,实现如下:
dullinklist类的声明:
template<class Type>
class Dullist{
private:
DulNode<Type>* first; //头指针指向头结点
public:
Dullist(); //显示默认构造函数
Dullist(Type a [], int len); //构造函数
~Dullist(); //析构函数
int getLength(); //求双链表的长度
Type Get(int i); //按位查找数据
int Locate(Type x); //按值查找数据位置
void Insert(int i, Type x); //在线性表第i个位置上插入值为x的结点
Type Delete(int i); //删除第i个元素
void Print(); //遍历循环双链表
bool isEqual(); //判断循环双链表是否是对称
};类实现:
template<class Type>
Dullist<Type>::Dullist(){
first = new DulNode<Type>;
first->next = first;
first->prior = first;
}
template<class Type>
Dullist<Type>::Dullist(Type a [], int len){
first = new DulNode<Type>;
first->next = first;
first->prior = first;
DulNode<Type>* r = first;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){
DulNode<Type>* s = new DulNode<Type>;
s->data = a[i];
r->next = s;
s->prior = r;
r = s;
}
r->next = first;
first->prior = r;
}
template<class Type>
Dullist<Type>::~Dullist(){
int len = getLength();
DulNode<Type>* p = first;
while (len+1){
p = first;
first = first->next;
delete p;
len--;
}
}
template<class Type>
int Dullist<Type>::getLength(){
int count = 0;
DulNode<Type>* p = first->next;
while (p != first){
count++;
p = p->next;
}
return count;
}
template<class Type>
void Dullist<Type>::Print(){
cout<< "头结点";
DulNode<Type>* p =first->next;
while (p != first){
cout << "-->" << p->data;
p = p->next;
}
cout << "-->头结点" << endl;
}
template<class Type>
Type Dullist<Type>::Get(int i){
int count = 1;
DulNode<Type>* p = first->next;
while (p != first&&count < i){
count++;
p = p->next;
}
if (p == first)throw"位置";
else{
return p->data;
}
}
template<class Type>
int Dullist<Type>::Locate(Type x){
int count = 1;
DulNode<Type>* p = first->next;
while (p != first){
if (p->data == x)return count;
p = p->next;
count++;
}
return 0;
}
template<class Type>
void Dullist<Type>::Insert(int i, Type x){
int count = 0;
DulNode<Type>* p = first;
while (count < i - 1){
p = p->next;
count++;
}
DulNode<Type>* s = new DulNode<Type>;
s->data = x;
s->prior = p;
s->next = p->next;
p->next->prior = s;
p->next = s;
}
template<class Type>
Type Dullist<Type>::Delete(int i){
DulNode<Type>* p = first;
int count = 0;
while (count < i ){
p = p->next;
count++;
}
if (p == first)throw"位置";
else{
p->prior->next = p->next;
p->next->prior = p->prior;
delete p;
}
}
template<class Type>
bool Dullist<Type>::isEqual(){
DulNode<Type>* p = first->next;
DulNode<Type>* q = first->prior;
while (p != q&&p->prior != q){
if (p->data == q->data){
p = p->next;
q = q->prior;
}
else return false;
}
return true;
}main.cpp
#include "dullist.cpp"
#include "dullist.h"
int main(){
int a[7] = { 1, 2, 3, 4,3,2,1 };
Dullist<int> dl(a, 7);
dl.Print();
cout << "dl的长度是:" << dl.getLength() << endl;
cout << "第6个结点是:" << dl.Get(6) << endl;
cout << "4是第" << dl.Locate(4) << "个结点" << endl;
dl.Insert(4, 10);
cout << "在第四个位置上插入10:";
dl.Print();
dl.Delete(1);
cout << "删除第1个结点:";
dl.Print();
cout << "dl" << (dl.isEqual() == true ? "是" : "不是") << "对称的" << endl;
return 0;
}测试结果:


























 579
579

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








