阅读MoreWindows大神的秒杀多线程系列至第十一篇读者写着问题,做一点小小的总结;
读者写者问题描述:有一个写者很多读者,多个读者可以同时读文件,但写者在写文件时不允许有读者在读文件,同样有读者在读文件时写者也不去能写文件,很简单的一个描述。
本文对于写者开始写文件时就将可读事件(g_hEventCanRead)设置为未触发状态,结束写作时将可读事件(g_hEventCanRead)设置为触发状态;对于多个读者,使用一计数器ReadCount计数正在阅读的读者个数,当ReadCount=1时,设置可写事件(g_hEventCanWrite)为未触发状态,当ReadCount=0时,设置可写事件(g_hEventCanWrite)为触发状态。以此来保证读者与写者的同步与互斥。
程序1:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <process.h>
const int READ_NUM = 5;
CRITICAL_SECTION g_cs,g_cs_reader_count;
/*
g_cs用来确保对stdout输出端的操作完整性;
g_cs_reader_count确保对readerCount计数的原子性
*/
HANDLE g_hEventCanRead,g_hEventCanWrite;
/*
g_hEventCanRead事件控制读者是否可读
g_hEventCanWrite事件控制写着是否可写
*/
int readerCount;
void WriterPrint(char *pstr)
{
EnterCriticalSection(&g_cs);
printf("\t%s\n",pstr);
LeaveCriticalSection(&g_cs);
}
unsigned int __stdcall WriterFun(PVOID PM)
{
WriterPrint("写者进入等待中。。。");
WaitForSingleObject(g_hEventCanWrite,INFINITE);
//Sleep(1000);
ResetEvent(g_hEventCanRead);
WriterPrint("写者开始写文件。。。");
Sleep(100);
WriterPrint("写者结束写文件。。。");
SetEvent(g_hEventCanRead);
return 0;
}
void ReadPrint(DWORD ID,char *pstr)
{
EnterCriticalSection(&g_cs);
printf("%d%s\n",ID,pstr);
LeaveCriticalSection(&g_cs);
}
unsigned int __stdcall ReaderFun(PVOID PM)
{
ReadPrint(GetCurrentThreadId(),"号读者进入等待。。。");
WaitForSingleObject(g_hEventCanRead,INFINITE);
EnterCriticalSection(&g_cs_reader_count);
readerCount++;
if(readerCount == 1)
ResetEvent(g_hEventCanWrite);
LeaveCriticalSection(&g_cs_reader_count);
ReadPrint(GetCurrentThreadId(),"号读者开始阅读");
ReadPrint(GetCurrentThreadId(),"号读者结束阅读");
EnterCriticalSection(&g_cs_reader_count);
readerCount--;
if(readerCount == 0)
SetEvent(g_hEventCanWrite);
LeaveCriticalSection(&g_cs_reader_count);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
InitializeCriticalSection(&g_cs);
InitializeCriticalSection(&g_cs_reader_count);
//事件手动置位,初始为有信号TRUE
g_hEventCanRead = CreateEvent(NULL,TRUE,TRUE,NULL);
g_hEventCanWrite = CreateEvent(NULL,TRUE,TRUE,NULL);
readerCount = 0;
int i;
HANDLE handle[READ_NUM+1];
for(i=1;i<=2;i++)
handle[i] = (HANDLE)_beginthreadex(NULL,0,ReaderFun,NULL,0,NULL);
handle[0] = (HANDLE)_beginthreadex(NULL,0,WriterFun,NULL,0,NULL);
for(;i<=READ_NUM;i++)
handle[i] = (HANDLE)_beginthreadex(NULL,0,ReaderFun,NULL,0,NULL);
WaitForMultipleObjects(READ_NUM+1,handle,TRUE,INFINITE);
for(i=0;i<=READ_NUM;i++)
CloseHandle(handle[i]);
CloseHandle(g_hEventCanRead);
CloseHandle(g_hEventCanWrite);
DeleteCriticalSection(&g_cs);
DeleteCriticalSection(&g_cs_reader_count);
return 0;
}
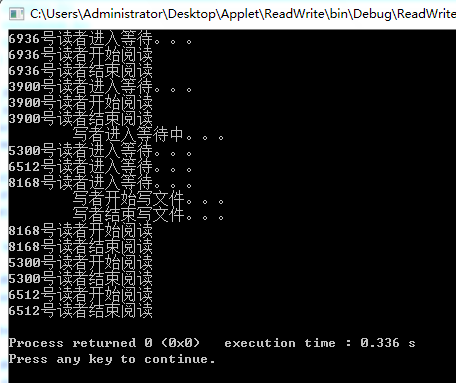
从运行结果可以看到:读者与写着的操作时互斥的。
但是,接着阅读下面的游客评论,找出其中BUG,产生BUG的片段如下:
WriterPrint("写者进入等待中。。。");
WaitForSingleObject(g_hEventCanWrite,INFINITE);
ResetEvent(g_hEventCanRead);
WriterPrint("写者开始写文件。。。");
Sleep(100);
WriterPrint("写者结束写文件。。。");
SetEvent(g_hEventCanRead);将BUG片段稍做更改,即可体现:
unsigned int __stdcall WriterFun(PVOID PM)
{
WriterPrint("写者进入等待中。。。");
WaitForSingleObject(g_hEventCanWrite,INFINITE);
WriterPrint("写者开始写文件。。。");
Sleep(1000);
ResetEvent(g_hEventCanRead);
Sleep(100);
WriterPrint("写者结束写文件。。。");
SetEvent(g_hEventCanRead);
return 0;
}
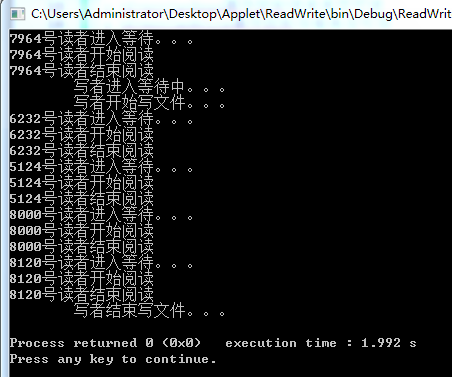
从结果看出,写者开始写文件到结束写文件之间,有读者在进行阅读,即程序没有实现读写的互斥。
是什么导致程序失去了读写的互斥性呢,个人看法是,没有保证读写的同步,个人认为只能先写后读,读者只有在写者的写作任务结束之后才能进行阅读,而程序1则使读者和写着一开始就都获得了可读和可写的权限,即在创建可读可写事件时,手动将事件设置为触发状态:
g_hEventCanRead = CreateEvent(NULL,TRUE,TRUE,NULL);
g_hEventCanWrite = CreateEvent(NULL,TRUE,TRUE,NULL);程序2:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <process.h>
const int READ_NUM = 5;
CRITICAL_SECTION g_cs,g_cs_reader_count;
/*
g_cs用来确保对stdout输出端的操作完整性;
g_cs_reader_count确保对readerCount计数的原子性
*/
HANDLE g_hEventCanRead,g_hEventCanWrite;
/*
g_hEventCanRead事件控制读者是否可读
g_hEventCanWrite事件控制写着是否可写
*/
int readerCount;
void WriterPrint(char *pstr)
{
EnterCriticalSection(&g_cs);
printf("\t%s\n",pstr);
LeaveCriticalSection(&g_cs);
}
unsigned int __stdcall WriterFun(PVOID PM)
{
WriterPrint("写者进入等待中。。。");
WaitForSingleObject(g_hEventCanWrite,INFINITE);
WriterPrint("写者开始写文件。。。");
Sleep(1000);
WriterPrint("写者结束写文件。。。");
SetEvent(g_hEventCanRead);
return 0;
}
void ReadPrint(DWORD ID,char *pstr)
{
EnterCriticalSection(&g_cs);
printf("%d%s\n",ID,pstr);
LeaveCriticalSection(&g_cs);
}
unsigned int __stdcall ReaderFun(PVOID PM)
{
ReadPrint(GetCurrentThreadId(),"号读者进入等待。。。");
WaitForSingleObject(g_hEventCanRead,INFINITE);
EnterCriticalSection(&g_cs_reader_count);
readerCount++;
if(readerCount == 1)
ResetEvent(g_hEventCanWrite);
LeaveCriticalSection(&g_cs_reader_count);
ReadPrint(GetCurrentThreadId(),"号读者开始阅读");
ReadPrint(GetCurrentThreadId(),"号读者结束阅读");
EnterCriticalSection(&g_cs_reader_count);
readerCount--;
if(readerCount == 0)
SetEvent(g_hEventCanWrite);
LeaveCriticalSection(&g_cs_reader_count);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
InitializeCriticalSection(&g_cs);
InitializeCriticalSection(&g_cs_reader_count);
//事件手动置位,初始为有信号TRUE
g_hEventCanRead = CreateEvent(NULL,TRUE,FALSE,NULL);
g_hEventCanWrite = CreateEvent(NULL,TRUE,TRUE,NULL);
readerCount = 0;
int i;
HANDLE handle[READ_NUM+1];
for(i=1;i<=2;i++)
handle[i] = (HANDLE)_beginthreadex(NULL,0,ReaderFun,NULL,0,NULL);
handle[0] = (HANDLE)_beginthreadex(NULL,0,WriterFun,NULL,0,NULL);
for(;i<=READ_NUM;i++)
handle[i] = (HANDLE)_beginthreadex(NULL,0,ReaderFun,NULL,0,NULL);
WaitForMultipleObjects(READ_NUM+1,handle,TRUE,INFINITE);
for(i=0;i<=READ_NUM;i++)
CloseHandle(handle[i]);
CloseHandle(g_hEventCanRead);
CloseHandle(g_hEventCanWrite);
DeleteCriticalSection(&g_cs);
DeleteCriticalSection(&g_cs_reader_count);
return 0;
}
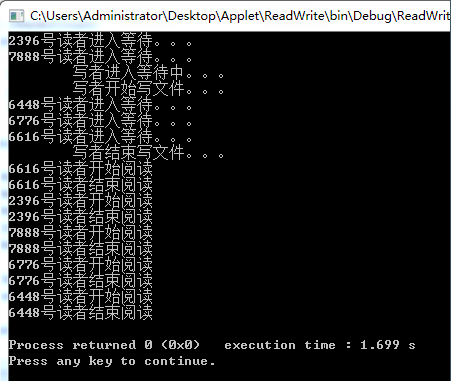
从结果看出,读者和写着之间的操作实现了互斥操作。
总结,以上两段程序的思想有一些出入,仅个人写下作为以后提醒复习用之。






















 1504
1504

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








