上篇讲了下mycat是如何启动服务、如何接受前端请求,这篇主要来看下遇到跨数据结点时需要做哪些事情,并且,如何把数据返回前端。
另外提一句,发现csdn对于图片处理不是很好,时序图都有点小了,需要手动放大才能查看。
在 io.mycat.server.ServerConnection 的execute方法中会先进行数据库路由并SQL执行的方法,RouteResultset rrs为路由结果
public void routeEndExecuteSQL(String sql, int type, SchemaConfig schema) {
// 路由计算
RouteResultset rrs = null;
try {
rrs = MycatServer
.getInstance()
.getRouterservice()
.route(MycatServer.getInstance().getConfig().getSystem(),
schema, type, sql, this.charset, this);
} catch (Exception e) {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
LOGGER.warn(s.append(this).append(sql).toString() + " err:" + e.toString(),e);
String msg = e.getMessage();
writeErrMessage(ErrorCode.ER_PARSE_ERROR, msg == null ? e.getClass().getSimpleName() : msg);
return;
}
if (rrs != null) {
// session执行
session.execute(rrs, type);
}
}上面代码中的session,为每个前后端的链接会话io.mycat.server.NonBlockingSession,有以下成员变量
private final ServerConnection source;
private final ConcurrentHashMap<RouteResultsetNode, BackendConnection> target; //算是后端数据库链接缓存吧
// life-cycle: each sql execution
private volatile SingleNodeHandler singleNodeHandler;
private volatile MultiNodeQueryHandler multiNodeHandler;
private volatile RollbackNodeHandler rollbackHandler;
private final MultiNodeCoordinator multiNodeCoordinator;
private final CommitNodeHandler commitHandler;
private volatile String xaTXID;
session.execute()是个重要的方法,直接区分了两种路——单结点模式和多结点模式
@Override
public void execute(RouteResultset rrs, int type) {
// clear prev execute resources
clearHandlesResources();
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
LOGGER.debug(s.append(source).append(rrs).toString() + " rrs ");
}
// 检查路由结果是否为空
RouteResultsetNode[] nodes = rrs.getNodes();
if (nodes == null || nodes.length == 0 || nodes[0].getName() == null || nodes[0].getName().equals("")) {
source.writeErrMessage(ErrorCode.ER_NO_DB_ERROR,
"No dataNode found ,please check tables defined in schema:" + source.getSchema());
return;
}
if (nodes.length == 1) {
singleNodeHandler = new SingleNodeHandler(rrs, this);
if( this.isPrepared() ) {
singleNodeHandler.setPrepared(true);
}
try {
singleNodeHandler.execute();
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.warn(new StringBuilder().append(source).append(rrs).toString(), e);
source.writeErrMessage(ErrorCode.ERR_HANDLE_DATA, e.toString());
}
} else {
boolean autocommit = source.isAutocommit();
multiNodeHandler = new MultiNodeQueryHandler(type, rrs, autocommit, this);
if(this.isPrepared()) {
multiNodeHandler.setPrepared(true);
}
try {
multiNodeHandler.execute();
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.warn(new StringBuilder().append(source).append(rrs).toString(), e);
source.writeErrMessage(ErrorCode.ERR_HANDLE_DATA, e.toString());
}
}
if(this.isPrepared()) {
this.setPrepared(false);
}
}单结点模式下 SingleNodeHandler 指定回调方法并调用后调mysqlConnection的execute方法。
private void _execute(BackendConnection conn) {
if (session.closed()) {
endRunning();
session.clearResources(true);
return;
}
conn.setResponseHandler(this);
try {
conn.execute(node, session.getSource(), session.getSource()
.isAutocommit());
} catch (Exception e1) {
executeException(conn, e1);
return;
}
}
io.mycat.backend.mysql.nio.MySQLConnection 的同步执行方法中根据mysql内部通过协议规则生成出最后需要执行的语句并在sendQueryCmd方法中调用
private void synAndDoExecute(String xaTxID, RouteResultsetNode rrn,
int clientCharSetIndex, int clientTxIsoLation,
boolean clientAutoCommit) {
String xaCmd = null;
boolean conAutoComit = this.autocommit;
String conSchema = this.schema;
// never executed modify sql,so auto commit
boolean expectAutocommit = !modifiedSQLExecuted || isFromSlaveDB()
|| clientAutoCommit;
if (expectAutocommit == false && xaTxID != null && xaStatus == 0) {
clientTxIsoLation = Isolations.SERIALIZABLE;
xaCmd = "XA START " + xaTxID + ';';
}
int schemaSyn = conSchema.equals(oldSchema) ? 0 : 1;
int charsetSyn = 0;
if (this.charsetIndex != clientCharSetIndex) {
//need to syn the charset of connection.
//set current connection charset to client charset.
//otherwise while sending commend to server the charset will not coincidence.
setCharset(CharsetUtil.getCharset(clientCharSetIndex));
charsetSyn = 1;
.......
if (schemaCmd != null) {
schemaCmd.write(this);
}
// and our query sql to multi command at last
sb.append(rrn.getStatement());
// syn and execute others
this.sendQueryCmd(sb.toString());
// waiting syn result...这里的 CommandPacket 是mysql最终的二进制报文封装。
protected void sendQueryCmd(String query) {
CommandPacket packet = new CommandPacket();
packet.packetId = 0;
packet.command = MySQLPacket.COM_QUERY;
try {
packet.arg = query.getBytes(charset);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
lastTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();
packet.write(this);
}再来看下connection.write方法(from super abstract class AbstractConnection) ,这里又切换成了异步的形式,往queue里丢进去之后,调用了selector唤醒前置方法 doNextWriteCheck()
@Override
public final void write(ByteBuffer buffer) {
if (isSupportCompress()) {
ByteBuffer newBuffer = CompressUtil.compressMysqlPacket(buffer, this, compressUnfinishedDataQueue);
writeQueue.offer(newBuffer);
} else {
writeQueue.offer(buffer);
}
// if ansyn write finishe event got lock before me ,then writing
// flag is set false but not start a write request
// so we check again
try {
this.socketWR.doNextWriteCheck();
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.warn("write err:", e);
this.close("write err:" + e);
}
}NIOSocketWR 中的校验是否需要写出数据的方法,wirte0()是最终的写出方法,和普通的NIO BYTEBUFFER操作无异,这里就不展开看了。
public void doNextWriteCheck() {
-- 这里是个原子化的锁标识,防止多线程同时调用写出事件
if (!writing.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
return;
}
try {
--- 这个是最终的字节流写出方法
boolean noMoreData = write0();
writing.set(false);
if (noMoreData && con.writeQueue.isEmpty()) {
if ((processKey.isValid() && (processKey.interestOps() & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0)) {
disableWrite();
}
} else {
if ((processKey.isValid() && (processKey.interestOps() & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) == 0)) {
enableWrite(false);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
if (AbstractConnection.LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
AbstractConnection.LOGGER.debug("caught err:", e);
}
con.close("err:" + e);
}
}
到这里为止,单结点的数据请求已发向了后端的数据库实例。
回头再来看下最复杂的多结点模式。
MultiNodeQueryHandler
光从新增数据库链接和SQL执行上感觉和单结点模式类似,没有撒差别,只多了一层 for each 调用。
public void execute() throws Exception {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
this.reset(rrs.getNodes().length);
this.fieldsReturned = false;
this.affectedRows = 0L;
this.insertId = 0L;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
MycatConfig conf = MycatServer.getInstance().getConfig();
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
LOGGER.debug("rrs.getRunOnSlave()-" + rrs.getRunOnSlave());
for (final RouteResultsetNode node : rrs.getNodes()) {
BackendConnection conn = session.getTarget(node);
if (session.tryExistsCon(conn, node)) {
LOGGER.debug("node.getRunOnSlave()-" + node.getRunOnSlave());
node.setRunOnSlave(rrs.getRunOnSlave()); // 实现 master/slave注解
LOGGER.debug("node.getRunOnSlave()-" + node.getRunOnSlave());
_execute(conn, node);
} else {
// create new connection
LOGGER.debug("node.getRunOnSlave()1-" + node.getRunOnSlave());
node.setRunOnSlave(rrs.getRunOnSlave()); // 实现 master/slave注解
LOGGER.debug("node.getRunOnSlave()2-" + node.getRunOnSlave());
PhysicalDBNode dn = conf.getDataNodes().get(node.getName());
dn.getConnection(dn.getDatabase(), autocommit, node, this, node);
// 注意该方法不仅仅是获取连接,获取新连接成功之后,会通过层层回调,最后回调到本类 的connectionAcquired
// 这是通过 上面方法的 this 参数的层层传递完成的。
// connectionAcquired 进行执行操作:
// session.bindConnection(node, conn);
// _execute(conn, node);
}
}
}
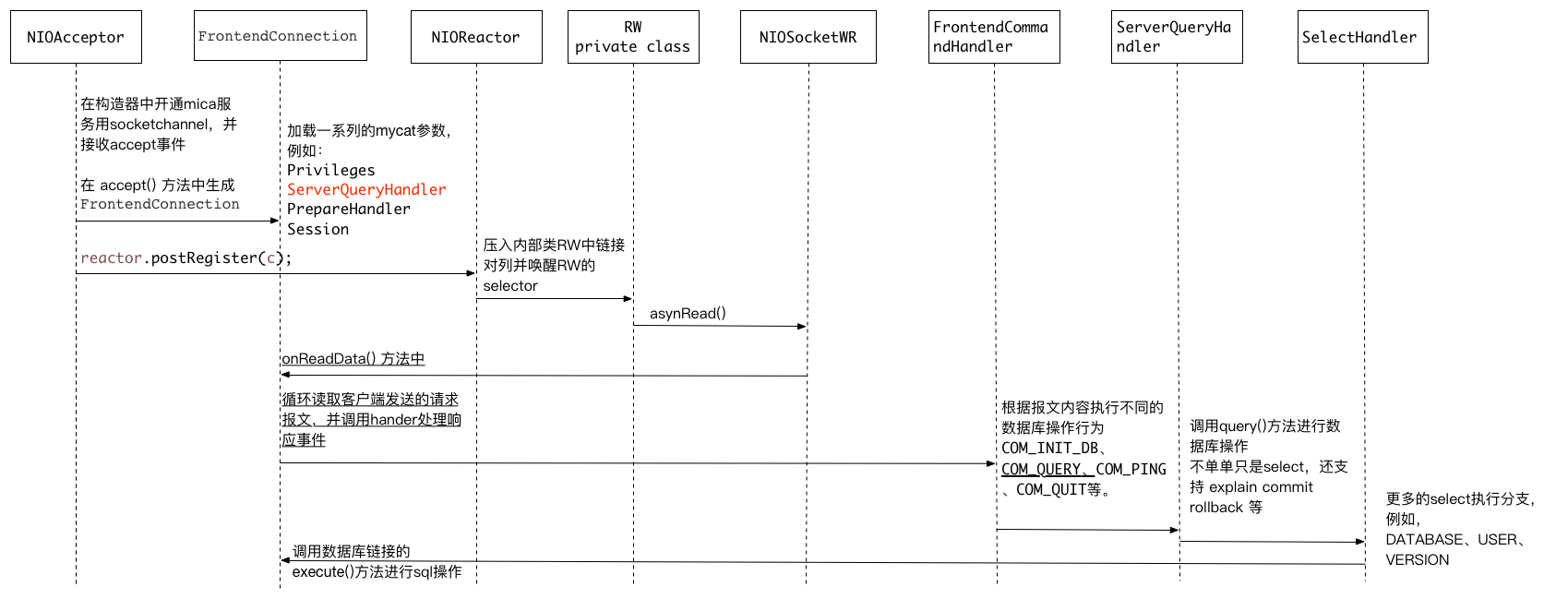
看下程序方法调用时序图
最后再来看下后端数据库如何反馈响应结果至 mycat,其实这块内容和mycat前端读取请求信息类似还是走SocketRW类,只是后端指向了 io.mycat.backend.mysql.nio.MySQLConnectionHandler 解析报文,handleRowPacket()这个方法是处理通用响应报文的入口。
@Override
protected void handleData(byte[] data) {
switch (resultStatus) {
case RESULT_STATUS_INIT:
switch (data[4]) {
case OkPacket.FIELD_COUNT:
handleOkPacket(data);
break;
case ErrorPacket.FIELD_COUNT:
handleErrorPacket(data);
break;
case RequestFilePacket.FIELD_COUNT:
handleRequestPacket(data);
break;
default:
resultStatus = RESULT_STATUS_HEADER;
header = data;
fields = new ArrayList<byte[]>((int) ByteUtil.readLength(data,
4));
}
break;
case RESULT_STATUS_HEADER:
switch (data[4]) {
case ErrorPacket.FIELD_COUNT:
resultStatus = RESULT_STATUS_INIT;
handleErrorPacket(data);
break;
case EOFPacket.FIELD_COUNT:
resultStatus = RESULT_STATUS_FIELD_EOF;
handleFieldEofPacket(data);
break;
default:
fields.add(data);
}
break;
case RESULT_STATUS_FIELD_EOF:
switch (data[4]) {
case ErrorPacket.FIELD_COUNT:
resultStatus = RESULT_STATUS_INIT;
handleErrorPacket(data);
break;
case EOFPacket.FIELD_COUNT:
resultStatus = RESULT_STATUS_INIT;
handleRowEofPacket(data);
break;
default:
handleRowPacket(data);
}
break;
default:
throw new RuntimeException("unknown status!");
}
}
/**
* 行数据包处理
*/
private void handleRowPacket(byte[] data) {
ResponseHandler respHand = responseHandler;
if (respHand != null) {
respHand.rowResponse(data, source);
} else {
closeNoHandler();
}
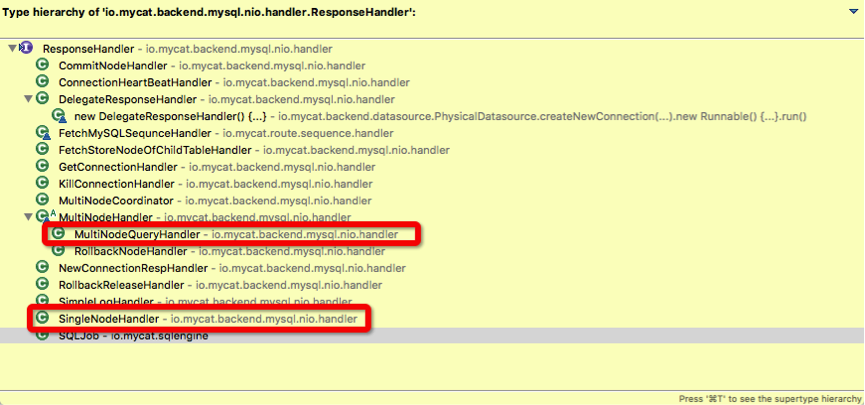
}看到这里,大家肯定会有个感觉,mycat里面使用了好多 handler 接口。是的在上面代码中出现的 ResponseHandler 中有两个重要的实现:
我们重点看下 MultiNodeQueryHandler 的 rowResponse 方法。
@Override
public void rowResponse(final byte[] row, final BackendConnection conn) {
if (errorRepsponsed.get()) {
// the connection has been closed or set to "txInterrupt" properly
//in tryErrorFinished() method! If we close it here, it can
// lead to tx error such as blocking rollback tx for ever.
// @author Uncle-pan
// @since 2016-03-25
//conn.close(error);
return;
}
lock.lock();
try {
RouteResultsetNode rNode = (RouteResultsetNode) conn.getAttachment();
String dataNode = rNode.getName();
if (dataMergeSvr != null) {
// even through discarding the all rest data, we can't
//close the connection for tx control such as rollback or commit.
// So the "isClosedByDiscard" variable is unnecessary.
// @author Uncle-pan
// @since 2016-03-25
---- 数据merge整合服务
dataMergeSvr.onNewRecord(dataNode, row);
} else {
// cache primaryKey-> dataNode
if (primaryKeyIndex != -1) {
RowDataPacket rowDataPkg = new RowDataPacket(fieldCount);
rowDataPkg.read(row);
String primaryKey = new String(
rowDataPkg.fieldValues.get(primaryKeyIndex));
LayerCachePool pool = MycatServer.getInstance()
.getRouterservice().getTableId2DataNodeCache();
pool.putIfAbsent(priamaryKeyTable, primaryKey, dataNode);
}
row[3] = ++packetId;
session.getSource().write(row);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
handleDataProcessException(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}DataMergeService 还是一个独立的线程,依赖MycatServer 实例中的 bussinessExecutor 进行异步合并处理。
public boolean onNewRecord(String dataNode, byte[] rowData) {
// 对于需要排序的数据,由于mysql传递过来的数据是有序的,
// 如果某个节点的当前数据已经不会进入,后续的数据也不会入堆
if (canDiscard.size() == rrs.getNodes().length) {
// "END_FLAG" only should be added by MultiNodeHandler.rowEofResponse()
// @author Uncle-pan
// @since 2016-03-23
//LOGGER.info("now we output to client");
//addPack(END_FLAG_PACK);
return true;
}
if (canDiscard.get(dataNode) != null) {
return true;
}
final PackWraper data = new PackWraper();
data.node = dataNode;
data.data = rowData;
addPack(data);
return false;
}
/**
* Add a row pack, and may be wake up a business thread to work if not running.
* @param pack row pack
* @return true wake up a business thread, otherwise false
*
* @author Uncle-pan
* @since 2016-03-23
*/
private final boolean addPack(final PackWraper pack){
packs.add(pack);
if(running.get()){
return false;
}
final MycatServer server = MycatServer.getInstance();
----把DataMergeServer丢入exector里
server.getBusinessExecutor().execute(this);
return true;
}看下DataMergeServer的异步运行逻辑 ,如果不是最后一个响应结果的话则先做数据整合,如果已是最后一条则在multiQueryHandler.outputMergeResult 方法中通过SocetRW写出数据。
for (; ; ) {
final PackWraper pack = packs.poll();
// async: handling row pack queue, this business thread should exit when no pack
// @author Uncle-pan
// @since 2016-03-23
if(pack == null){
nulpack = true;
break;
}
// eof: handling eof pack and exit
if (pack == END_FLAG_PACK) {
final int warningCount = 0;
final EOFPacket eofp = new EOFPacket();
final ByteBuffer eof = ByteBuffer.allocate(9);
BufferUtil.writeUB3(eof, eofp.calcPacketSize());
eof.put(eofp.packetId);
eof.put(eofp.fieldCount);
BufferUtil.writeUB2(eof, warningCount);
BufferUtil.writeUB2(eof, eofp.status);
---- 即为前端链接
final ServerConnection source = multiQueryHandler.getSession().getSource();
final byte[] array = eof.array();
---- 这里向前端链接写出最终的数据 multiQueryHandler.outputMergeResult(source, array, getResults(array));
break;
}
// merge: sort-or-group, or simple add
final RowDataPacket row = new RowDataPacket(fieldCount);
row.read(pack.data);
if (grouper != null) {
grouper.addRow(row);
} else if (sorter != null) {
if (!sorter.addRow(row)) {
canDiscard.put(pack.node, true);
}
} else {
result.add(row);
}
}// rof排序到哪里去了?从多个数据源中获取数后,如何保证数据返回到真正的客户端时,数据是按order by顺序排列,OK,看下io.mycat.sqlengine.mpp.tmp.RowDataSorter的addRow方法,由于每次从数据库中拿出来的数据在内存在组合后再放到前端是有限制的,因此过量数据会被直接丢弃。
@Override
public synchronized boolean addRow(RowDataPacket row) {
if (heap.getData().size() < total) {
heap.add(row);
return true;
}
// 堆已满,构建最大堆,并执行淘汰元素逻辑
if (heap.getData().size() == total && hasBuild == false) {
heap.buildHeap();
hasBuild = true;
}
return heap.addIfRequired(row);
}
数据写出的流程可以理解为
以上便是mycat整体的内部逻辑, 总体上还是很NB,有值得学习借鉴的地方。
花了半天时间才看明白大概是怎么回事。用了不少多线程回调机制,不过有些地方看上去有点绕, 特别有蛮多层 if else,希望以后能有所改善吧。
本篇完。





















 846
846

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








