1. 简介
纯C语言编译,用于对称TSP问题求解。目前最大的应用案例为85900个城市。Concorde支持使用QSopt线性规划求解器获得bound。
1.1 求解算法简介
TSP问题模型如下,第二个约束条件是为了去除环,称为connect cut:

使用分枝定界法进行求解的原理如下:
首先将整数约束和去除环约束进行松弛,得到lp问题。
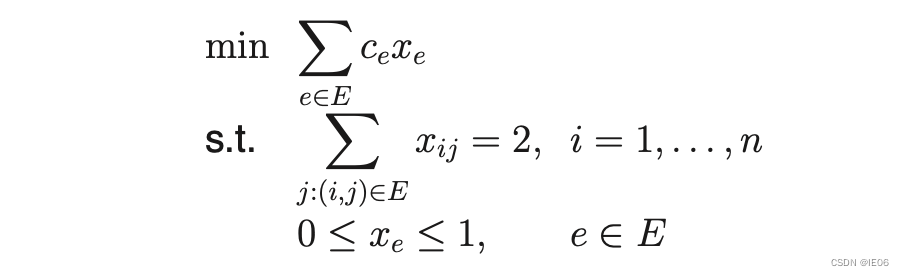
我们使用列生产方法来求解这个问题,令E‘是E的子集,比如说只允许最近的一些点参与组环。

获得的最优解x‘是原LP问题的可行解。我们通过对偶问题来寻找需要添加进来的变量:

对偶问题为:
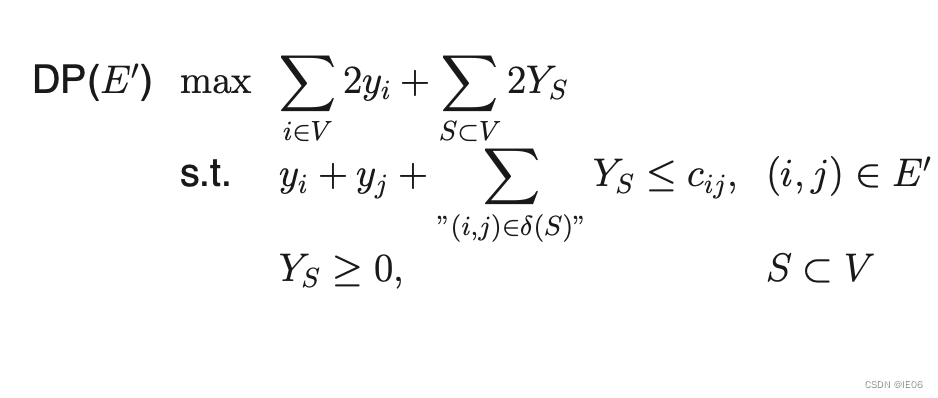

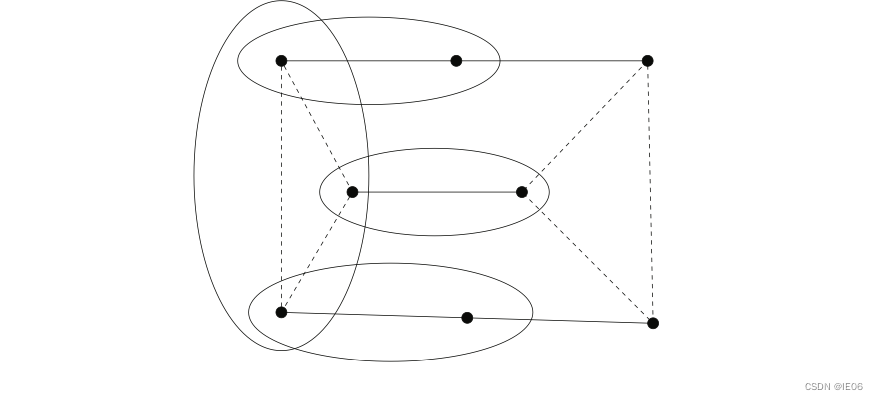
同时我们还需要用行生成法添加防止子环的约束条件。举例如下,为如图的边添加comb约束:
其他常用的cuts包括:
*
- Blossom (Padberg and Rao 1982)
- Path inequalities (Naddef and Rinaldi 1998)
- 2-handled clique tree (Padberg and Rinaldi 1991)
- Star inequalities (Fleischmann 1988)

1.2 添加cut的例子

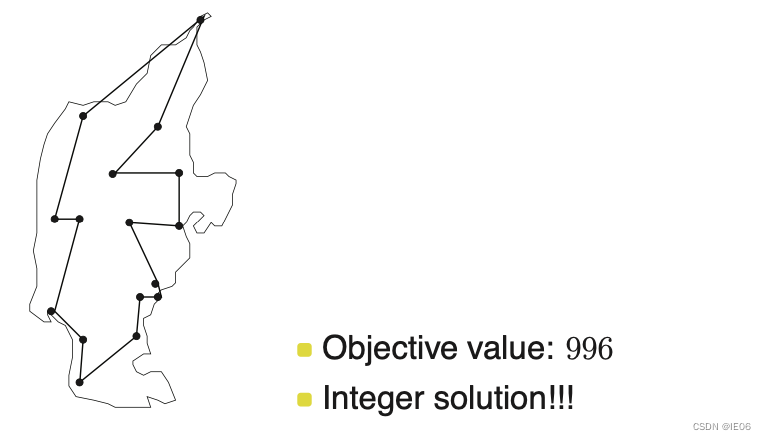
第一步,求解LP松弛问题,使用行生成不断去除环






2. 使用方法
2.1 julia
Julia使用方法:
using Concorde
M = [
0 16 7 14
16 0 3 5
7 3 0 16
14 5 16 0
]
opt_tour, opt_len = solve_tsp(M)
或者
using Concorde
n_nodes = 10
x = rand(n_nodes) .* 10000
y = rand(n_nodes) .* 10000
opt_tour, opt_len = solve_tsp(x, y; dist="EUC_2D")
或者
opt_tour, opt_len = solve_tsp("gr17.tsp")
2.2 mac应用
在应用商店中搜索concorde TSP即可,安装完成后,主界面如下:

使用方法:点击exact solver,然后点击下面的load按钮,加载位置文件(每行两个浮点数),返回后,点击下方的run即可,结果如下图:
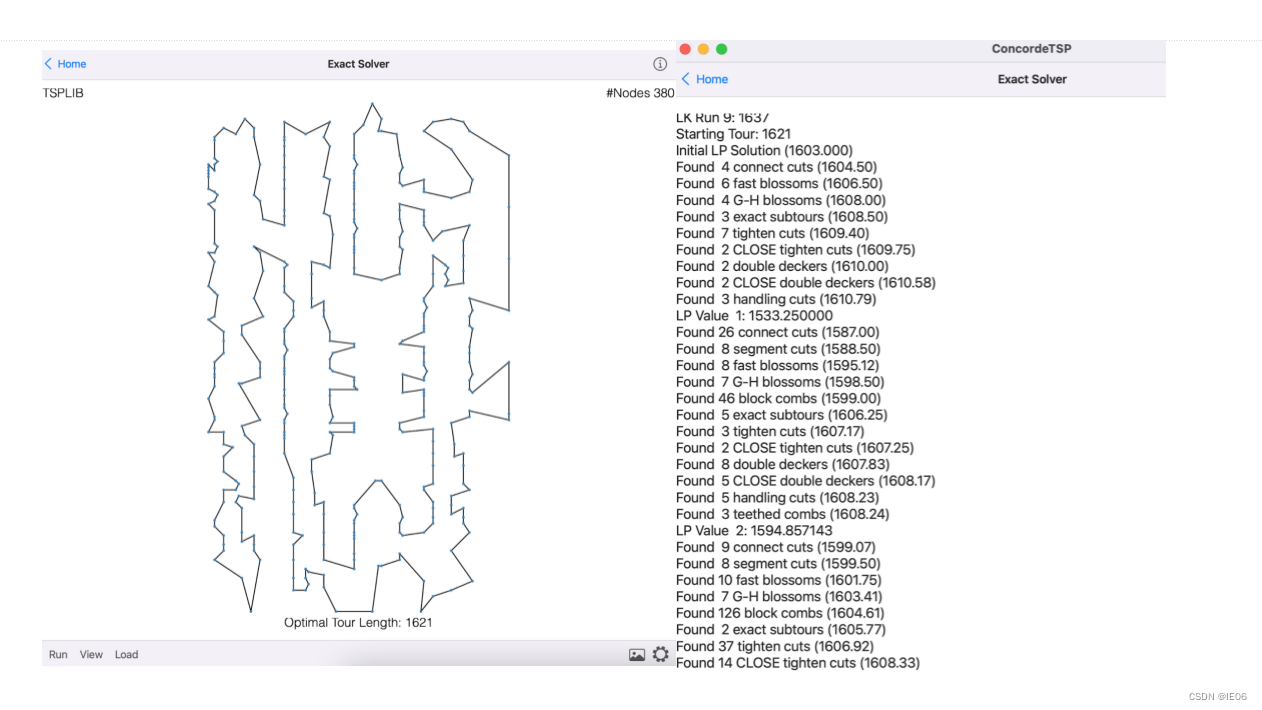
3. 代码分析
3.1 编译
文件夹结构如下,编译代码:
$ ./configure --host=avr --with-qsopt=DIR #--with-cplex=DIR
$ make
程序编译生成静态库文件concorde.a,头文件concorde.h,以及一些可执行文件:
TSP/concorde the TSP solver
LINKERN/linkern the Lin-Kernighan TSP heuristic
EDGEGEN/edgegen generates edge sets
FMATCH/fmatch solves fractional 2-matching problems
例如concorde程序在TSP文件夹下:

测试:
$ ./concorde -s 99 -k 100
Current process id: 75398
Using random seed 99
Random 100 point set
XSet initial upperbound to 780 (from tour)
LP Value 1: 738.500000 (0.00 seconds)
LP Value 2: 765.000000 (0.01 seconds)
LP Value 3: 774.660000 (0.04 seconds)
LP Value 4: 778.000000 (0.06 seconds)
LP Value 5: 778.465517 (0.09 seconds)
LP Value 6: 778.705882 (0.12 seconds)
LP Value 7: 779.538462 (0.15 seconds)
LP Value 8: 779.937500 (0.19 seconds)
LP Value 9: 780.000000 (0.20 seconds)
New lower bound: 780.000000
Final lower bound 780.000000, upper bound 780.000000
Exact lower bound: 780.000000
DIFF: 0.000000
Final LP has 180 rows, 336 columns, 2921 nonzeros
Optimal Solution: 780.00
Number of bbnodes: 1
Total Running Time: 0.26 (seconds)
可用参数说明:
Usage: ./concorde [-see below-] [dat_file]
-B do not branch
-C # maximum chunk size in localcuts (default 16)
-d use dfs branching instead of bfs
-D f edgegen file for initial edge set
-e f initial edge file
-E f full edge file (must contain initial edge set)
-f write optimal tour as edge file (default is tour file)
-F f read extra cuts from file
-g h be a grunt for boss h
-h be a boss for the branching
-i just solve the blossom polytope
-I just solve the subtour polytope
-J # number of tentative branches
-k # number of nodes for random problem
-K h use cut server h
-M f master file
-m use multiple passes of cutting loop
-n s problem location (just a name or host:name, not a file name)
-o f output file name (for optimal tour)
-P f cutpool file
-q do not cut the root lp
-r # use #x# grid for random points, no dups if #<0
-R f restart file
-s # random seed
-S f problem file
-t f tour file (in node node node format)
-u v initial upperbound
-U do not permit branching on subtour inequalities
-v verbose (turn on lots of messages)
-V just run fast cuts
-w just subtours and trivial blossoms
-x delete files on completion (sav pul mas)
-X f write the last root fractional solution to f
-y use simple cutting and branching in DFS
-z # dump the #-lowest reduced cost edges to file xxx.rcn
-N # norm (must specify if dat file is not a TSPLIB file)
0=MAX, 1=L1, 2=L2, 3=3D, 4=USER, 5=ATT, 6=GEO, 7=MATRIX,
8=DSJRAND, 9=CRYSTAL, 10=SPARSE, 11-15=RH-norm 1-5, 16=TOROIDAL
17=GEOM, 18=JOHNSON
3.2 代码调试分析
编译完了之后,在vs中打开concorde.c,然后新建launch.json,主要修改program和args:
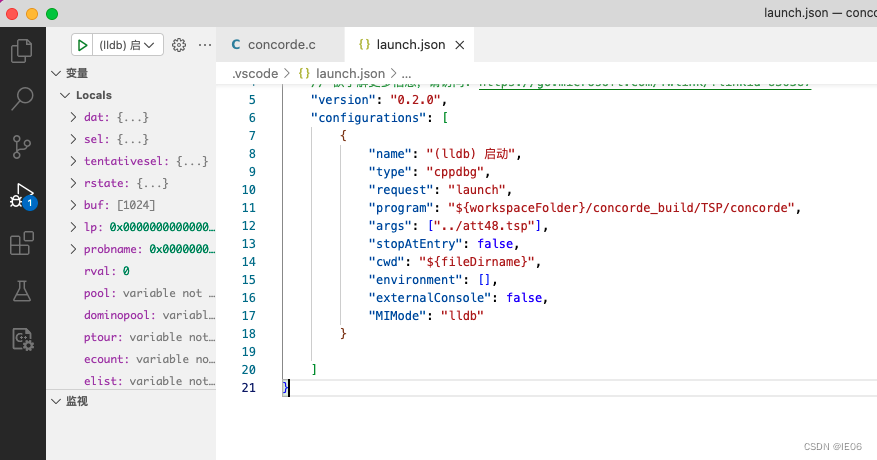
3.2.1 读取数据
读取命令行参数后,会配置如下参数:

这些函数在control.c中:
然后在getdata.c中读取tsp数据:

并打印tsp读取后的配置:

3.2.2 获取初始ub
调用findtour函数,获得一个ub。findtour函数又调用CClinkern_tour函数获得一个初始解。linkern算法可以参考之前的文章。

3.2.3 获取初始lb
调用build_edges或者build_fulledges函数,获取可行边集合,然后使用CCtsp_init_cutpool初始化cut集合。
CCtsp_generate_edges方法用于构造边集合,选取len(i,j) - pi[i] - pi[j]<0的边进入集合。伺候会从10条LK构造的解中添加边进入集合。
使用CCfmatch_fractional_2match方法找到最优解。
besttour初始化为1~n,CCtsp_bfs_restart开启广度搜索。
CCtsp_cutting_loop迭代求解lp问题。具体可参见tsp_lp.c。然后用x_heuristic构造新的路径。所谓x_heuristic,就是将可行边按照x轴进行排序,然后依次访问。如果调用的是CCtsp_x_greedy_tour_lk,则在之后再用lk进行一次优化。
3.2.4 分枝查找
接下来时核心代码:

分枝涉及到的函数在bcontrol.c中。








 Concorde是一个用纯C编写的解决对称TSP问题的工具,最大处理过85900个城市。它利用线性规划求解器QSopt进行边界优化。文章介绍了分枝定界法的原理,列生成和行生成方法,以及如何在Julia环境中使用Concorde。此外,还提供了Mac应用的使用方法和编译、调试代码的步骤。
Concorde是一个用纯C编写的解决对称TSP问题的工具,最大处理过85900个城市。它利用线性规划求解器QSopt进行边界优化。文章介绍了分枝定界法的原理,列生成和行生成方法,以及如何在Julia环境中使用Concorde。此外,还提供了Mac应用的使用方法和编译、调试代码的步骤。
















 298
298

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








