一、栈
- 栈是一种重要的线性结构,在数据结构而言,其本质操作是线性表操作的子集。但在数据类型来说,是一种重要的抽象数据类型。在面向对象的程序设计中,栈是多数据类型。
- 栈只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。不含任何元素的栈称为空栈,栈又称为后进先出的线性表,简称LIFO结构。栈可以将数据从一种序列变到另一种序列。
二、栈的分类
- 顺序栈,即栈的顺序存储结构是利用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存放自栈底到栈顶的元素,一般使用过程中所需的最大空间,故先给栈分配一个基本容量,在使用过程中然后增容。
- 链式栈,是一种不连续的存储结构,元素以Node的形式存储,包含数据域和指针域,指针域指向下一个节点,每个节点随机分布,为动态开辟节点。
三、栈的基本模块
无论是链式栈还是顺序栈其基本操作都一样,包含栈的创建,初始化,销毁,插入,删除,取栈顶元素等,只是其实现方式不同。下面就是顺序栈的模块。
- 栈代码:
头文件"Stack.h"
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//
//typedef int DataType;
//
//#define N 10
//typedef struct Stack
//{
// DataType _a[N];//规定数组空间大小
// int _top; // 栈顶
//}Stack;//静态栈
typedef struct Pos
{
int _row;
int _col;
}Pos;//迷宫位置点
typedef Pos DataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
DataType* _a; //节点指针
int _top; // 栈顶
int _capacity; // 容量
}Stack;
void StackInit(Stack* ps);//初始化
void StackDestory(Stack* ps);//销毁
void StackPush(Stack* ps, DataType x);//压栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps);//出栈
DataType StackTop(Stack* ps);//取栈顶元素
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps);//判空
int StackSize(Stack* ps);//栈的大小
//void TestStack();
函数文件"Stack.c"
#include "Stack.h"
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{
ps->_a = (DataType*)malloc(sizeof(DataType)* 3);//动态开辟空间
assert(ps);//防止开辟失败
ps->_capacity = 3;
ps->_top = 0;
}
void StackDestory(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);//断言
if (ps->_a)
{
free(ps->_a);
ps->_a = NULL;
ps->_capacity = ps->_top = 0;
}
while (ps->_top--)
{
free(ps->_top);
}
ps->_capacity = 0;
}
void StackPush(Stack* ps, DataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->_top == ps->_capacity)//越界
{
ps->_a = (DataType*)realloc(ps->_a, sizeof(DataType)*(ps->_capacity * 2));//增容
assert(ps->_a);
ps->_capacity *= 2;
}
ps->_a[ps->_top] = x;
ps->_top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps->_a);
assert(ps->_top > 0);
ps->_top--;
}
DataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps->_a && ps->_top > 0);
return ps->_a[ps->_top - 1];
}
//空 0
//非空 1
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top == 0 ? 0 : 1;
}
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top;
}
//测试代码
//void TestStack()
//{
// Stack s;
// StackInit(&s);
//
// StackPush(&s, 1);
// StackPush(&s, 2);
// StackPush(&s, 3);
// StackPush(&s, 4);
//
// while (StackEmpty(&s))
// {
// printf("%d ",StackTop(&s));
// StackPop(&s);
// }
// printf("\n");
//
//
// StackDestory(&s);
//}
四、迷宫
- 迷宫问题,望文生义就是在迷宫当中找到出口,出入口自定义,解决迷宫问题的过程中以回溯法为思想,应用栈的知识来解决这个问题。对于迷宫问题的思考是由解决简单的迷宫然后到环路迷宫这样一个过程的。
回溯法:对一个包括有很多个结点,每个结点有若干个搜索分支的问题,把原问题分解为若干个子问题进行求解的算法;当搜索到某个结点发现无法再继续搜索下去时,就让搜索过程回溯到该结点的前一个结点,继续搜索该结点外的其他尚未搜索的分支;如果发现该结点无法再搜索下去,就让搜索过程回溯到这个结点的前一个结点继续这样的搜索过程。
1.简单迷宫--------从出口处将开始进行压栈,判断其上,下,左,右方向是否可走,若某个方向可走将其坐标进行压栈,并将坐标上的值置为2,再探测该坐标的分支,直到出口,返回1即找到出口,若在某一个结点处四个方向均不可走则返回上一个坐标,并将该坐标从栈中释放,若栈为空时仍未到出口处则返回0即未找到出口。
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 1 0
0 0 1 0 1 1
0 0 1 0 0 0
2.多路迷宫--------在简单迷宫的基础上当找到出口时并不返回值,当栈为空即回溯到出口时返回到主函数。
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 1 1
0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 1 1
0 0 1 0 0 0
3.环路迷宫--------在多路迷宫的基础上,在设置压入栈的坐标的值时换为前一个坐标的值加1,即递增的。在判断某个坐标是否可走时变换条件,进而达到目的。
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 1 0
0 0 1 0 1 0
0 0 1 0 1 0
0 0 1 1 1 1
0 0 1 0 0 0
- 迷宫代码(环路迷宫代码):
头文件"maze.h"
#pragma once
#include"Stack.h"
#define N 6
int size;
static int maze[N][N] = {//static,只在maze.c中可见
/*{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },*/
/*{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },*/
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
};
int GetMazePath(Pos entry, Pos exit);//获取迷宫通路:找到通路/找不到通路
int CheckAccess(Pos cur, Pos next);
void PrintfMaze();
void TestMaze();
函数文件"maze.c"
#include"Maze.h"
int CheckAccess(Pos cur, Pos next)
{
if (next._row >= 0 && next._row < N
&&next._col >= 0 && next._col < N
&& (maze[next._row][next._col] == 1 || maze[next._row][next._col] > maze[cur._row][cur._col] + 1))//当下一个坐标的值为1 或者比当前值加一还大就可以走
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
int size = 0;
int GetMazePath(Pos entry, Pos exit)
{
Stack path;
int flag = 0;
StackInit(&path);
StackPush(&path, entry);
maze[entry._row][entry._col] = 2;//入口初始化为2
while (StackEmpty(&path))
{
//Pos cur = entry;//当前位置
Pos cur = StackTop(&path);//栈顶取出的当前位置
//if (cur._col == 5)//多条通路
if (cur._row == exit._row
&&cur._col == exit._col)//当一条路径找到出口时,打印路径并且看路径长短
{
flag = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < path._top; i++)
{
printf("[%d %d]->", path._a[i]._row, path._a[i]._col);
}
printf(" Exit\n\n");
if (size == 0 || StackSize(&path) < size)
{
size = StackSize(&path);//路径的长短
}
}
Pos next;
//上
next = cur;//当前位置
next._row -= 1;//下一个位置
if (CheckAccess(cur, next))
{
maze[next._row][next._col] = maze[cur._row][cur._col] + 1;
StackPush(&path, next);//下一个位置可以通,入栈
continue;
}
//下
next = cur;
next._row += 1;
if (CheckAccess(cur, next))
{
maze[next._row][next._col] = maze[cur._row][cur._col] + 1;
StackPush(&path, next);//下一个位置可以通,入栈
continue;
}
//左
next = cur;
next._col -= 1;
if (CheckAccess(cur, next))
{
maze[next._row][next._col] = maze[cur._row][cur._col] + 1;
StackPush(&path, next);//下一个位置可以通,入栈
continue;
}
//右
next = cur;
next._col += 1;
if (CheckAccess(cur, next))
{
maze[next._row][next._col] = maze[cur._row][cur._col] + 1;
StackPush(&path, next);//下一个位置可以通,入栈
continue;
}
//走到四个方向不通的位置
//回溯
StackPop(&path);
}
if (flag == 0)//判断是否找到出口
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
void PrintfMaze()
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
{
printf("%d ", maze[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
主函数文件"main.c"
#include "maze.h"
void TestMaze()
{
Pos entry;
entry._row = 5;
entry._col = 2;
Pos exit;
exit._row = 4;
exit._col = 5;
printf("迷宫地图:\n");
PrintfMaze();
if (GetMazePath(entry, exit))
{
printf("有出口,最短路径为:%d \n\n", size);
}
else
{
printf("无出口!\n\n");
}
printf("走出后迷宫地图:\n");
PrintfMaze();
}
int main()
{
TestMaze();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
五、运行结果
1.简单迷宫
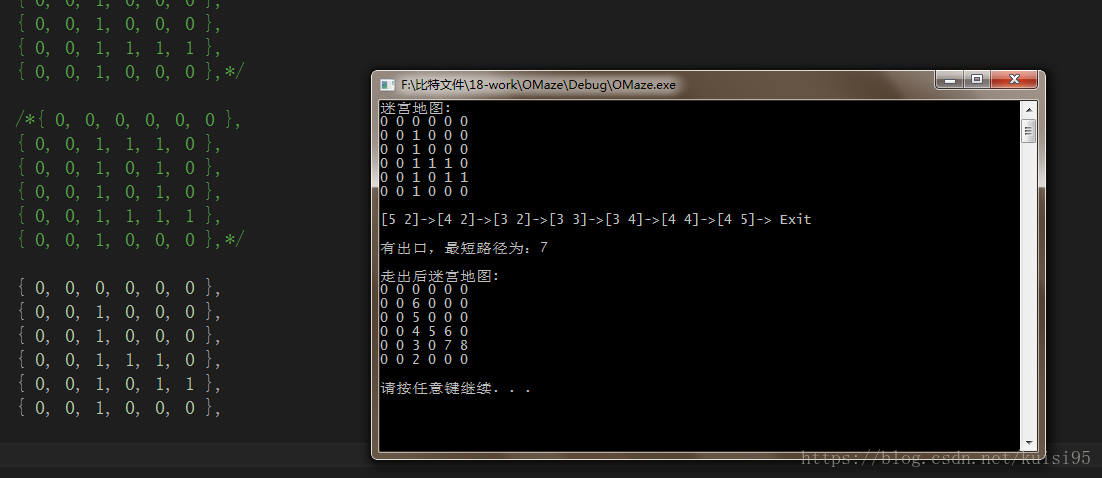
2.多路迷宫

3.环路迷宫
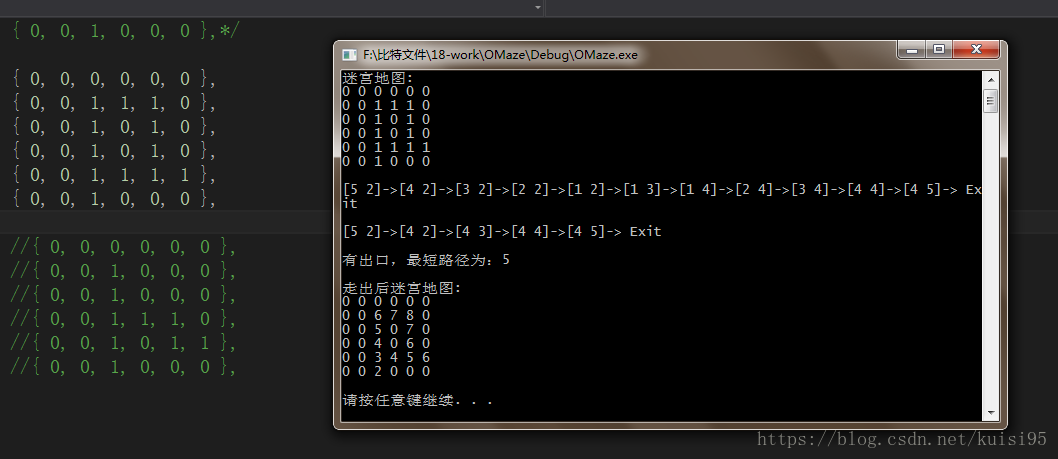
结合之前的栈的基本操作代码就可以解决迷宫问题了。-( ̄▽ ̄)-*






















 2200
2200

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








