一、数据集介绍
【数据集】食品分类识别数据集 7792 张,目标检测,包含YOLO/VOC格式标注。
数据集中包含138种分类。
数据集图片来自国内外网站、网络爬虫、视频抽帧等;
可用于食品分类识别、超市商品识别。
检测场景为超市、食品加工厂等,可以应用于提高运营效率和管理水平,实现自动化、智能化的商品分类。
文章底部名片或主页私信获取数据集~


 1、数据概述
1、数据概述
食品分类识别的重要性
在食品加工厂或超市环境中,商品种类繁多,且摆放密集。为了提高运营效率和管理水平,实现自动化、智能化的商品分类识别显得尤为重要。通过目标检测算法,可以实时、准确地识别出超市货架上的商品种类、位置等信息,为超市的库存管理、销售分析、顾客行为研究等提供有力支持。
基于YOLO的食品分类识别算法
-
速度快:YOLO算法具有极高的处理速度,可以实时处理视频流,满足超市环境中对实时性的高要求。
-
准确度高:经过不断的发展和改进,YOLO算法在目标检测任务上的准确度不断提升,能够准确识别出超市货架上的各种商品。
-
端到端训练:YOLO算法采用端到端的训练方式,不需要复杂的预处理和后处理步骤,简化了算法的实现和部署过程。
-
迁移能力强:YOLO算法具有良好的迁移能力,可以方便地应用到不同的商品分类识别场景中,如不同超市、不同货架等。
该数据集含有 7792 张图片,包含Pascal VOC XML格式和YOLO TXT格式,用于训练和测试超市、食品加工厂流水线等场景进行食品分类识别。
图片格式为jpg格式,标注格式分别为:
YOLO:txt
VOC:xml
数据集均为手工标注,保证标注精确度。
2、数据集文件结构
super_detect/
——test/
————Annotations/
————images/
————labels/
——train/
————Annotations/
————images/
————labels/
——valid/
————Annotations/
————images/
————labels/
——data.yaml
- 该数据集已划分训练集样本,分别是:test目录(测试集)、train目录(训练集)、valid目录(验证集);
- Annotations文件夹为Pascal VOC格式的XML文件 ;
- images文件夹为jpg格式的数据样本;
- labels文件夹是YOLO格式的TXT文件;
- data.yaml是数据集配置文件,包含超市商品分类识别的目标分类和加载路径。




 Annotations目录下的xml文件内容如下:
Annotations目录下的xml文件内容如下:
<annotation>
<folder></folder>
<filename>ecdb5dcf-IMG_0993_JPG_jpg.rf.40c15ffc7a9878cfa518595b57f584f9.jpg</filename>
<path>ecdb5dcf-IMG_0993_JPG_jpg.rf.40c15ffc7a9878cfa518595b57f584f9.jpg</path>
<source>
<database>roboflow.ai</database>
</source>
<size>
<width>640</width>
<height>640</height>
<depth>3</depth>
</size>
<segmented>0</segmented>
<object>
<name>Egg</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<occluded>0</occluded>
<bndbox>
<xmin>537</xmin>
<xmax>641</xmax>
<ymin>245</ymin>
<ymax>426</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
<object>
<name>Egg</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<occluded>0</occluded>
<bndbox>
<xmin>505</xmin>
<xmax>633</xmax>
<ymin>385</ymin>
<ymax>584</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
<object>
<name>Egg</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<occluded>0</occluded>
<bndbox>
<xmin>104</xmin>
<xmax>560</xmax>
<ymin>1</ymin>
<ymax>299</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
<object>
<name>Egg</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<occluded>0</occluded>
<bndbox>
<xmin>127</xmin>
<xmax>481</xmax>
<ymin>169</ymin>
<ymax>412</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
<object>
<name>Egg</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<occluded>0</occluded>
<bndbox>
<xmin>492</xmin>
<xmax>603</xmax>
<ymin>553</ymin>
<ymax>641</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
<object>
<name>Egg</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<occluded>0</occluded>
<bndbox>
<xmin>573</xmin>
<xmax>641</xmax>
<ymin>85</ymin>
<ymax>260</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
</annotation>3、数据集适用范围
- 目标检测场景,监控摄像头识别
- yolo训练模型或其他模型
- 食品加工厂、超市百货场景下
- 可以用于提高运营效率和管理水平,实现自动化、智能化的商品分类等
4、数据集标注结果





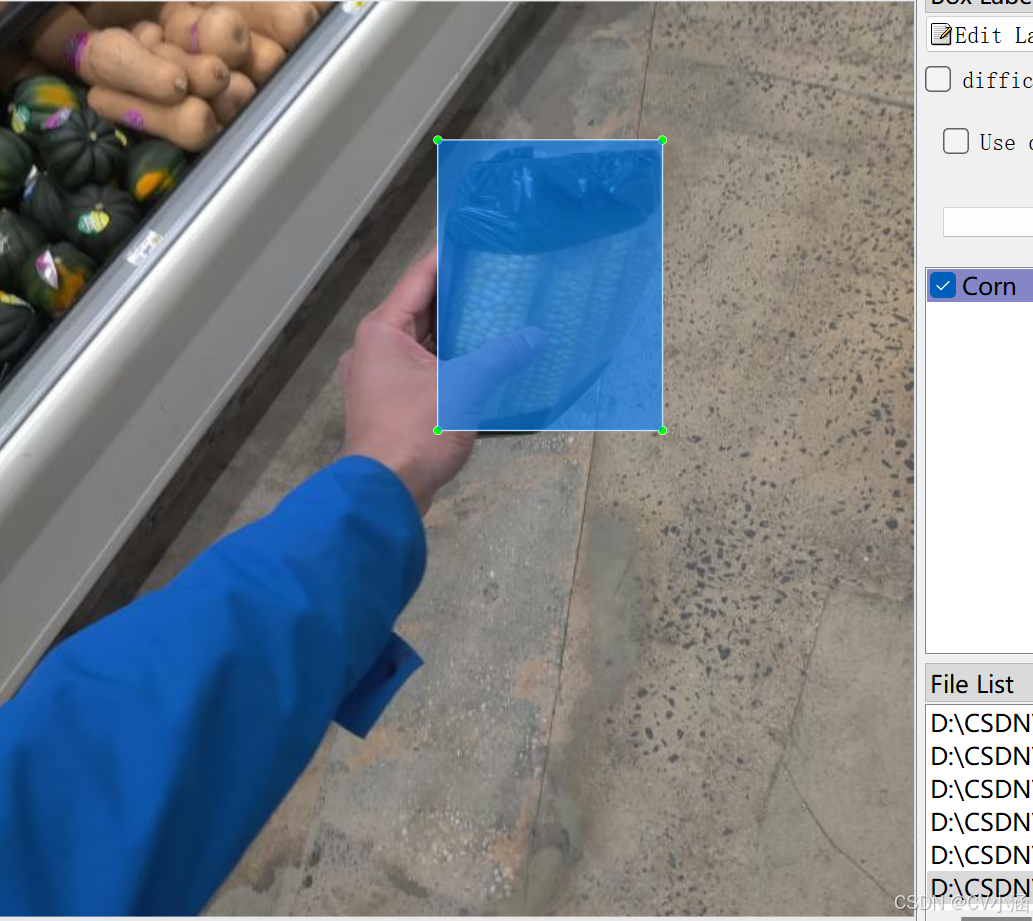
4.1、数据集内容
- 多角度场景:行人视角,监控摄像头视角;
- 标注内容:138个分类;
- 图片总量:7792 张图片数据;
- 标注类型:含有Pascal VOC XML格式和yolo TXT格式;
5、训练过程
5.1、导入训练数据
下载YOLOv8项目压缩包,解压在任意本地workspace文件夹中。
下载YOLOv8预训练模型,导入到ultralytics-main项目根目录下。

在ultralytics-main项目根目录下,创建data文件夹,并在data文件夹下创建子文件夹:Annotations、images、imageSets、labels,其中,将pascal VOC格式的XML文件手动导入到Annotations文件夹中,将JPG格式的图像数据导入到images文件夹中,imageSets和labels两个文件夹不导入数据。
data目录结构如下:
data/
——Annotations/ //存放xml文件
——images/ //存放jpg图像
——imageSets/
——labels/
整体项目结构如下所示:

5.2、数据分割
首先在ultralytics-main目录下创建一个split_train_val.py文件,运行文件之后会在imageSets文件夹下将数据集划分为训练集train.txt、验证集val.txt、测试集test.txt,里面存放的就是用于训练、验证、测试的图片名称。
import os
import random
trainval_percent = 0.9
train_percent = 0.9
xmlfilepath = 'data/Annotations'
txtsavepath = 'data/ImageSets'
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
ftrainval = open('data/ImageSets/trainval.txt', 'w')
ftest = open('data/ImageSets/test.txt', 'w')
ftrain = open('data/ImageSets/train.txt', 'w')
fval = open('data/ImageSets/val.txt', 'w')
for i in list:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
ftrain.write(name)
else:
fval.write(name)
else:
ftest.write(name)
ftrainval.close()
ftrain.close()
fval.close()
ftest.close()5.3、数据集格式化处理
在ultralytics-main目录下创建一个voc_label.py文件,用于处理图像标注数据,将其从XML格式(通常用于Pascal VOC数据集)转换为YOLO格式。
convert_annotation函数
-
这个函数读取一个图像的XML标注文件,将其转换为YOLO格式的文本文件。
-
它打开XML文件,解析树结构,提取图像的宽度和高度。
-
然后,它遍历每个目标对象(
object),检查其类别是否在classes列表中,并忽略标注为困难(difficult)的对象。 -
对于每个有效的对象,它提取边界框坐标,进行必要的越界修正,然后调用
convert函数将坐标转换为YOLO格式。 -
最后,它将类别ID和归一化后的边界框坐标写入一个新的文本文件。
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
from os import getcwd
sets = ['train', 'val', 'test']
classes = ['-', 'Apple', 'Artichoke', 'Asparagus', 'Avocado', 'Banana', 'Beans', 'Beetroot', 'Blackberries', 'Blueberries', 'Book', 'Broccoli', 'Brussel Sprouts', 'Butter', 'Cabbage', 'Cantaloupe', 'Carrots', 'Cauliflower', 'Cerealbox', 'Cheese', 'Clementine', 'Coffee', 'Corn', 'Cucumber', 'Detergent', 'Drinks', 'Egg', 'Eggplant', 'Eggs', 'Fish', 'Galia', 'Grapes', 'Honeydew', 'Juice', 'Lemon', 'Lettuce', 'Meat', 'Milk', 'Mushroom', 'Mushrooms', 'Nectarine', 'Onion', 'Orange', 'Oranges', 'Peas', 'Pineapple', 'Plum', 'Pomegranate', 'Potato', 'Raspberries', 'Salad', 'Sauce', 'Shallot', 'Spinach', 'Squash', 'Strawberries', 'Strawberry', 'Sweetcorn', 'Tofu', 'Tomato', 'Tomatoes', 'Watermelon', 'Yogurt', 'Zucchini', 'apple', 'apples', 'asparagus', 'aubergine', 'bacon', 'banana', 'bananas', 'bazlama', 'beef', 'blueberries', 'bread', 'broccoli', 'butter', 'carrot', 'carrots', 'cheese', 'chicken', 'chicken_breast', 'chocolate chips', 'chocolate', 'corn', 'courgettes', 'cream cheese', 'cream', 'dates', 'eggs', 'flour', 'ginger', 'goat_cheese', 'green beans', 'green bell pepper', 'green chilies', 'green_beans', 'ground_beef', 'ham', 'heavy_cream', 'juice', 'lemon', 'lemons', 'lettuce', 'lime', 'mango', 'meat', 'milk', 'mineral water', 'mushroom', 'mushrooms', 'olive', 'olives', 'onion', 'orange', 'parsley', 'peach', 'peppers', 'potato', 'potatoes', 'red bell pepper', 'red grapes', 'red onion', 'salami', 'sauce', 'sausage', 'shrimp', 'spinach', 'spring onion', 'strawberries', 'strawberry', 'sugar', 'sweet_potato', 'tomato paste', 'tomato', 'tomatoes', 'yellow bell pepper', 'yoghurt'] # 根据标签名称填写类别
abs_path = os.getcwd()
print(abs_path)
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return x, y, w, h
def convert_annotation(image_id):
in_file = open('data/Annotations/%s.xml' % (image_id), encoding='UTF-8')
out_file = open('data/labels/%s.txt' % (image_id), 'w')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
b1, b2, b3, b4 = b
# 标注越界修正
if b2 > w:
b2 = w
if b4 > h:
b4 = h
b = (b1, b2, b3, b4)
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
wd = getcwd()
for image_set in sets:
if not os.path.exists('data/labels/'):
os.makedirs('data/labels/')
image_ids = open('data/ImageSets/%s.txt' % (image_set)).read().strip().split()
list_file = open('data/%s.txt' % (image_set), 'w')
for image_id in image_ids:
list_file.write(abs_path + '/data/images/%s.jpg\n' % (image_id))
convert_annotation(image_id)
list_file.close()5.4、修改数据集配置文件
在ultralytics-main目录下创建一个wheat.yaml文件
train: data/train.txt
val: data/val.txt
test: data/test.txt
nc: 138
names: ['-', 'Apple', 'Artichoke', 'Asparagus', 'Avocado', 'Banana', 'Beans', 'Beetroot', 'Blackberries', 'Blueberries', 'Book', 'Broccoli', 'Brussel Sprouts', 'Butter', 'Cabbage', 'Cantaloupe', 'Carrots', 'Cauliflower', 'Cerealbox', 'Cheese', 'Clementine', 'Coffee', 'Corn', 'Cucumber', 'Detergent', 'Drinks', 'Egg', 'Eggplant', 'Eggs', 'Fish', 'Galia', 'Grapes', 'Honeydew', 'Juice', 'Lemon', 'Lettuce', 'Meat', 'Milk', 'Mushroom', 'Mushrooms', 'Nectarine', 'Onion', 'Orange', 'Oranges', 'Peas', 'Pineapple', 'Plum', 'Pomegranate', 'Potato', 'Raspberries', 'Salad', 'Sauce', 'Shallot', 'Spinach', 'Squash', 'Strawberries', 'Strawberry', 'Sweetcorn', 'Tofu', 'Tomato', 'Tomatoes', 'Watermelon', 'Yogurt', 'Zucchini', 'apple', 'apples', 'asparagus', 'aubergine', 'bacon', 'banana', 'bananas', 'bazlama', 'beef', 'blueberries', 'bread', 'broccoli', 'butter', 'carrot', 'carrots', 'cheese', 'chicken', 'chicken_breast', 'chocolate chips', 'chocolate', 'corn', 'courgettes', 'cream cheese', 'cream', 'dates', 'eggs', 'flour', 'ginger', 'goat_cheese', 'green beans', 'green bell pepper', 'green chilies', 'green_beans', 'ground_beef', 'ham', 'heavy_cream', 'juice', 'lemon', 'lemons', 'lettuce', 'lime', 'mango', 'meat', 'milk', 'mineral water', 'mushroom', 'mushrooms', 'olive', 'olives', 'onion', 'orange', 'parsley', 'peach', 'peppers', 'potato', 'potatoes', 'red bell pepper', 'red grapes', 'red onion', 'salami', 'sauce', 'sausage', 'shrimp', 'spinach', 'spring onion', 'strawberries', 'strawberry', 'sugar', 'sweet_potato', 'tomato paste', 'tomato', 'tomatoes', 'yellow bell pepper', 'yoghurt']5.5、执行命令
执行train.py
model = YOLO('yolov8s.pt')
results = model.train(data='wheat.yaml', epochs=200, imgsz=640, batch=16, workers=0, device=0)也可以在终端执行下述命令:
yolo train data=wheat.yaml model=yolov8s.pt epochs=200 imgsz=640 batch=16 workers=0 device=05.6、模型预测
你可以选择新建predict.py预测脚本文件,输入视频流或者图像进行预测。
代码如下:
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load the YOLOv8 model
model = YOLO("./best.pt") # 自定义预测模型加载路径
# Open the video file
video_path = "./demo.mp4" # 自定义预测视频路径
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
# Get the video properties
frame_width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
frame_height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
# Define the codec and create VideoWriter object
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v') # Be sure to use lower case
out = cv2.VideoWriter('./outputs.mp4', fourcc, fps, (frame_width, frame_height)) # 自定义输出视频路径
# Loop through the video frames
while cap.isOpened():
# Read a frame from the video
success, frame = cap.read()
if success:
# Run YOLOv8 inference on the frame
# results = model(frame)
results = model.predict(source=frame, save=True, imgsz=640, conf=0.5)
results[0].names[0] = "道路积水"
# Visualize the results on the frame
annotated_frame = results[0].plot()
# Write the annotated frame to the output file
out.write(annotated_frame)
# Display the annotated frame (optional)
cv2.imshow("YOLOv8 Inference", annotated_frame)
# Break the loop if 'q' is pressed
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord("q"):
break
else:
# Break the loop if the end of the video is reached
break
# Release the video capture and writer objects
cap.release()
out.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()也可以直接在命令行窗口或者Annoconda终端输入以下命令进行模型预测:
yolo predict model="best.pt" source='demo.jpg'6、获取数据集
文章底部名片或主页私信获取数据集~
二、基于QT的目标检测可视化界面
1、环境配置
# 安装torch环境
pip install torch -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
# 安装PySide6依赖项
pip install PySide6 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
# 安装opencv-python依赖项
pip install opencv-python -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple2、使用说明

界面功能介绍:
- 原视频/图片区:上半部分左边区域为原视频/图片展示区;
- 检测区:上半部分右边区域为检测结果输出展示区;
- 文本框:打印输出操作日志,其中告警以json格式输出,包含标签框的坐标,标签名称等;
- 加载模型:下拉框绑定本地文件路径,按钮加载路径下的模型文件;
- 置信度阈值:自定义检测区的置信度阈值,可以通过滑动条的方式设置;
- 文件上传:选择目标文件,包含JPG格式和MP4格式;
- 开始检测:执行检测程序;
- 停止:终止检测程序;
3、预测效果展示
3.1、图片检测

切换置信度再次执行:

上图左下区域可以看到json格式的告警信息,用于反馈实际作业中的管理系统,为管理员提供道路养护决策 。
3.2、视频检测

3.3、日志文本框

4、前端代码
class MyWindow(QtWidgets.QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.init_gui()
self.model = None
self.timer = QtCore.QTimer()
self.timer1 = QtCore.QTimer()
self.cap = None
self.video = None
self.file_path = None
self.base_name = None
self.timer1.timeout.connect(self.video_show)
def init_gui(self):
self.folder_path = "model_file" # 自定义修改:设置文件夹路径
self.setFixedSize(1300, 650)
self.setWindowTitle('目标检测') # 自定义修改:设置窗口名称
self.setWindowIcon(QIcon("111.jpg")) # 自定义修改:设置窗口图标
central_widget = QtWidgets.QWidget(self)
self.setCentralWidget(central_widget)
main_layout = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout(central_widget)
# 界面上半部分: 视频框
topLayout = QtWidgets.QHBoxLayout()
self.oriVideoLabel = QtWidgets.QLabel(self)
# 界面下半部分: 输出框 和 按钮
groupBox = QtWidgets.QGroupBox(self)
groupBox.setStyleSheet('QGroupBox {border: 0px solid #D7E2F9;}')
bottomLayout = QtWidgets.QHBoxLayout(groupBox)
main_layout.addWidget(groupBox)
btnLayout = QtWidgets.QHBoxLayout()
btn1Layout = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout()
btn2Layout = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout()
btn3Layout = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout()
# 创建日志打印文本框
self.outputField = QtWidgets.QTextBrowser()
self.outputField.setFixedSize(530, 180)
self.outputField.setStyleSheet('font-size: 13px; font-family: "Microsoft YaHei"; background-color: #f0f0f0; border: 2px solid #ccc; border-radius: 10px;')
self.detectlabel = QtWidgets.QLabel(self)
self.oriVideoLabel.setFixedSize(530, 400)
self.detectlabel.setFixedSize(530, 400)
self.oriVideoLabel.setStyleSheet('border: 2px solid #ccc; border-radius: 10px; margin-top:75px;')
self.detectlabel.setStyleSheet('border: 2px solid #ccc; border-radius: 10px; margin-top: 75px;')
topLayout.addWidget(self.oriVideoLabel)
topLayout.addWidget(self.detectlabel)
main_layout.addLayout(topLayout)5、代码获取
更多数据集请查看置顶博文!
以上内容均为原创。
























 991
991

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








