STL六大组件:
容器
算法
配接器
迭代器
仿函数
空间配置器
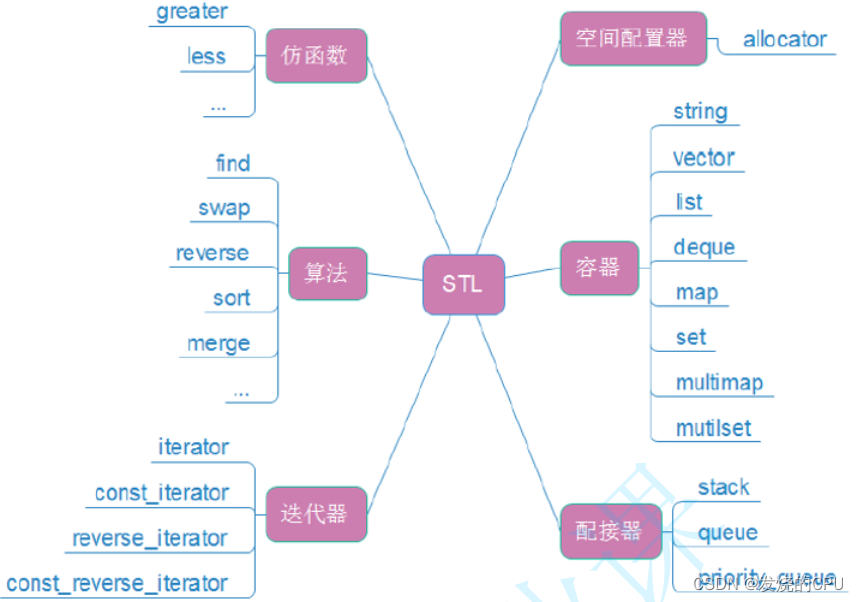
温馨提示:只讲常用接口,使用方法说明详见代码注释
目录
一、string类对象的常见构造
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//typedef basic_string<char16_t> u16string;
std::string s0("Initial string");
//构造空的string类对象,即空字符串(默认构造)
//default (1) explicit basic_string(const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
std::string s1;
//用C-string来构造string类对象
//copy(2) basic_string(const basic_string& str);
std::string s2(s0);
//拷贝构造函数
//copy(2) basic_string(const basic_string& str);
std::string s2(s0);
void Teststring()
{
string s1;//构造空的string类对象s1
string s2("hello sunlang");//用C格式字符串构造string类对象s2
string s3(s2);//拷贝构造s3
}二、string类对象的容量操作
//返回字符串有效字符长度
//size_type size() const;
int main()
{
std::string str("Test string");
std::cout << "The size of str is" << str.size() << "characters.\n";
return 0;
}//检测字符串释放为空串,是返回true,否则返回false
//bool empty() const;
int main()
{
std::string content;
std::string line;
std::cout << "Please introduce a text.Enter an empty line to finish:\n";
do
{
getline(std::cin, line);
content += line + '\n';
} while (!line.empty());
std::cout << "The text you introduced was:\n" << content;
return 0;
}
//清空有效字符
//void clear();
int main()
{
char c;
std::string str;
std::cout << "Please type some lines of text. Enter a dot (.) to finish:\n";
do {
c = std::cin.get();
str += c;
if (c == '\n')
{
std::cout << str;
str.clear();
}
} while (c != '.');
return 0;
}//为字符串预留空间**
//void reserve (size_type n = 0);
int main()
{
std::string str;
std::ifstream file("test.txt", std::ios::in | std::ios::ate);
if (file) {
std::ifstream::streampos filesize = file.tellg();
str.reserve(filesize);
file.seekg(0);
while (!file.eof())
{
str += file.get();
}
std::cout << str;
}
return 0;
}//将有效字符的个数改成n个,多出的空间用字符C填充
//void resize (size_type n);
//void resize(size_type n, charT c)
int main()
{
std::string str("I like to code in C");
std::cout << str << '\n';
std::string::size_type sz = str.size();
str.resize(sz + 2, '+');
std::cout << str << '\n';
str.resize(14);
std::cout << str << '\n';
return 0;
}三、类对象的访问及遍历操作
//返回pos位置的字符,const string类对象调用
//reference operator[] (size_type pos);
//const_reference operator[] (size_type pos) const;
int main()
{
std::string str("Test string");
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); ++i)
{
std::cout << str[i];
}
return 0;
}四、string类对象的修改操作
//在字符串后面追加字符串str
//string(1)
//basic_string& operator+= (const basic_string& str);
//c - string(2)
//basic_string & operator+= (const charT * s);
//character(3)
//basic_string& operator+= (charT c);
int main()
{
std::string name("John");
std::string family("Smith");
name += "K"; // c-string
name += family; // string
name += '\n'; // character
std::cout << name;
return 0;
}//返回C格式字符串
//const charT* c_str() const;
int main()
{
std::string str("Please split this sentence into tokens");
char* cstr = new char[str.length() + 1];
std::strcpy(cstr, str.c_str());
// cstr now contains a c-string copy of str
char* p = std::strtok(cstr, " ");
while (p != 0)
{
std::cout << p << '\n';
p = strtok(NULL, " ");
}
delete[] cstr;
return 0;
}//从字符串pos位置开始往后找字符C,返回该字符在字符串中的位置
//string(1)
//size_type find(const basic_string& str, size_type pos = 0) const;
//c - string(2)
//size_type find(const charT * s, size_type pos = 0) const;
//buffer(3)
//size_type find(const charT* s, size_type pos, size_type n) const;
//character(4)
//size_type find(charT c, size_type pos = 0) const;
int main()
{
std::string str("There are two needles in this haystack with needles.");
std::string str2("needle");
// different member versions of find in the same order as above:
std::string::size_type found = str.find(str2);
if (found != std::string::npos)
std::cout << "first 'needle' found at: " << found << '\n';
found = str.find("needles are small", found + 1, 6);
if (found != std::string::npos)
std::cout << "second 'needle' found at: " << found << '\n';
found = str.find("haystack");
if (found != std::string::npos)
std::cout << "'haystack' also found at: " << found << '\n';
found = str.find('.');
if (found != std::string::npos)
std::cout << "Period found at: " << found << '\n';
// let's replace the first needle:
str.replace(str.find(str2), str2.length(), "preposition");
std::cout << str << '\n';
return 0;
}五、string类非成员函数
//输入运算符重载
//template <class charT, class traits, class Alloc>
//basic_istream<charT, traits>& operator>> (basic_istream<charT, traits>& is,
// basic_string<charT, traits, Alloc>& str);
int main()
{
std::string name;
std::cout << "Please, enter your name: ";
std::cin >> name;
std::cout << "Hello, " << name << "!\n";
return 0;
}//输出运算符重载
//template <class charT, class traits, class Alloc>
//basic_ostream<charT, traits>& operator<< (basic_ostream<charT, traits>& os,
// const basic_string<charT, traits, Alloc>& str);
int main()
{
std::string str = "Hello world!";
std::cout << str << '\n';
return 0;
}//获取一行字符串
//template <class charT, class traits, class Alloc>
//(1)basic_istream<charT, traits>& getline(basic_istream<charT, traits>& is,
// basic_string<charT, traits, Alloc>& str, charT delim);
//(2)
//template <class charT, class traits, class Alloc>
//basic_istream<charT, traits>& getline(basic_istream<charT, traits>& is,
// basic_string<charT, traits, Alloc>& str);
int main()
{
std::string name;
std::cout << "Please, enter your full name: ";
std::getline(std::cin, name);
std::cout << "Hello, " << name << "!\n";
return 0;
}//大小比较
int main()
{
std::string foo = "alpha";
std::string bar = "beta";
if (foo == bar) std::cout << "foo and bar are equal\n";
if (foo != bar) std::cout << "foo and bar are not equal\n";
if (foo < bar) std::cout << "foo is less than bar\n";
if (foo > bar) std::cout << "foo is greater than bar\n";
if (foo <= bar) std::cout << "foo is less than or equal to bar\n";
if (foo >= bar) std::cout << "foo is greater than or equal to bar\n";
return 0;
}六、汇总代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//测试string容量相关的接口
//size/clear/resize
void Teststring1()
{
//注意:string类对象支持直接用cin和cout进行输入和输出
string s("hello,sunlang!!!");//用C-siring来构造string类对象
cout << s.size() << endl;//返回字符串有效字符长度
cout << s.length() << endl;//返回字符串有效字符长度
cout << s.capacity() << endl;//返回空间总大小
cout << s << endl;
//将s中的字符串清空,注意清空时只是将size清0,不改变底层空间的大小
s.clear();
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
//将s中有效字符个数增加到10个,多出位置用‘a'进行补充
//"aaaaaaaa"
s.resize(10, 'a');
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
//将s中有效字符个数增加到15个,多出位置用缺省值'\0'进行补充
//"aaaaaaaa\0\0\0\0"
s.resize(15);
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
cout << s << endl;
//将s中有效字符个数缩小到5个
s.resize(5);
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
cout << s << endl;
}
void Teststring2()
{
string s;
//测试reserve是否会改变string中有效元素个数
s.reserve(100);
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
//测试reserve参数小于string的底层空间大小时,是否会将空间缩小
s.reserve(50);
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout<<s.capacity()<<endl;
}
//利用reserve提高插入数据的效率,避免增容带来的开销
void TestPushBack()
{
string s;
size_t sz = s.capacity();
cout << "making s grow:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
s.push_back('c');
if (sz != s.capacity())
{
sz = s.capacity();
cout << "capacity changed:" << sz << '\n';
}
}
}
//构建vector时,如果提前已经知道string中大概要放多少个元素,可以提前将string中空间设置好
void TestPushBackReserve()
{
string s;
s.reserve(100);
size_t sz = s.capacity();
cout << "making s grow:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
s.push_back('c');
if (sz != s.capacity())
{
sz = s.capacity();
cout << "capacity changed:" << sz << '\n';
}
}
}
//string的遍历
//begin()+end() for+[] 范围for
//注意:string遍历时使用最多的还是for+下标或者范围for(C++11后才支持)
//begin()+end()大多数使用在需要使用STL提供的算法操作string时,比如:采用reserve逆置string
void Teststring3()
{
string s1("hello sunlang");
const string s2("Hello sunlang");
cout << s1 << " " << s2 << endl;
cout << s1[0] << " " << s2[0] << endl;
s1[0] = 'H';
cout << s1 << endl;
//s2[0]='h';代码编译失败,因为const类型对象不能修改
}
void Teststring4()
{
string s("hello sunlang");
//以下三种方式除了遍历string对象,还可以遍历修改string中的字符
//第一种使用最多
//for+operator[]
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i)
{
cout << s[i] << endl;
}
//迭代器
string::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << endl;
++it;
}
//string::reserve_iterator rit =s.rbegin();
//C++11之后,直接使用auto定义迭代器,让编译器推到迭代器的类型
//auto rit = s.rbegin();
//while (rit != s.rend())
//{
// cout << *rit << endl;
//}
//范围for
for (auto ch : s)
{
cout << ch << endl;
}
}
//测试string
//1、插入(拼接)方式:push_back append operator+=
//2、正向和反向查找:find()+rfind()
//3、截取子串:substr()
//4、删除:erase
void Teststring5()
{
string str;
str.push_back(' ');//在str后插入空格
str.append("hello");//在str后追加一个字符"hello"
str += 's';//在str后追加一个字符'b'
str += "un";//在str后追加一个字符串"it"
cout << str << endl;
cout << str.c_str() << endl;//以C语言的方式打印字符串
//获取file的后缀
string file("Test.cpp");
size_t pos = file.rfind('.');
string suffix(file.substr(pos, file.size() - pos));
cout << suffix << endl;
//npos是string里面的一个静态成员变量
//static const size_t npos=-1;
//取出ur1中的域名
string ur1("https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/editor/128085730");
cout << ur1 << endl;
size_t start = ur1.find("://");
if (start == string::npos)
{
cout << "invalid url" << endl;
return;
}
start += 3;
size_t finish = url.find('/', start);
string address = url.substr(start, finish - start);
cout << address << endl;
// 删除 url 的协议前缀
pos = url.find("://");
url.erase(0, pos + 3);
cout << url << endl;
}
int main()
{
Teststring1();
Teststring2();
TestPushBack();
TestPushBackReserve();
Teststring3();
Teststring4();
Teststring5();
return 0;
}























 958
958











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










