一、学习目标
学习进程控制中fork()函数
运用fork()函数实践案例创建进程
二、fork()函数
1.基本知识
①引入
#include <unistd.h>
pid_t fork(void);
②功能
创建进程;函数执行后,系统会创建一个与原进程几乎相同的进程,之后父子进程都继续执行
③返回值说明
- 成功:返回两个值,子进程创建成功后,原程序会被复制,就有了两个fork函数。父进程的fork函数会返回子进程的pid,子进程的fork函数会返回0.
- 不成功:若子进程创建失败,原程序不会复制,父进程的fork函数返回-1。
④案例创建进程
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
pid_t tempPid;
tempPid = fork();
if(tempPid == -1){
perror("fork error");
}else if(tempPid > 0){//parent
printf("parent process, pid = %d, ppid = %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
}else{//child
printf("child process, pid = %d, ppid = %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
}//of if
printf("......finish......");
return 0;
}//of main
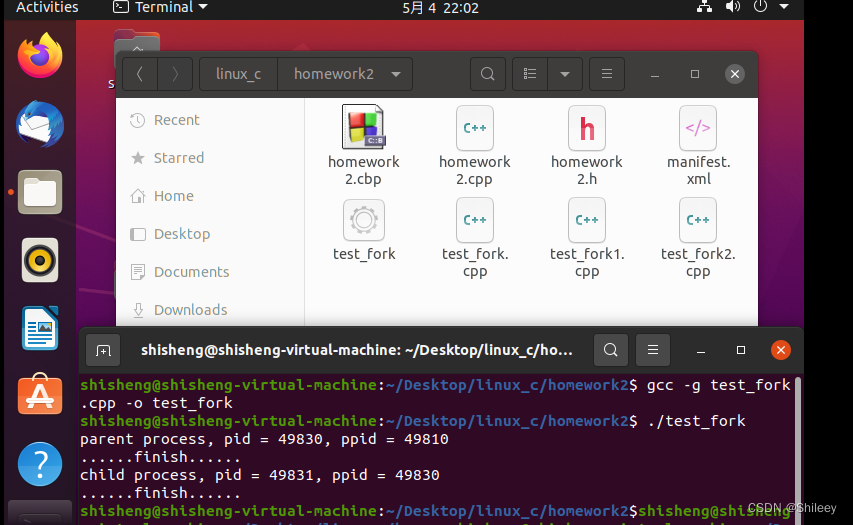
【思考】多次执行test_fork会发现,child process后输出的ppid不等于parent process的pid,而等于1。
因为父进程先于子进程终止,子进程变成“孤儿进程”,后面由init进程来接收。
2.创建多个进程
①方法
使用for循环
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 2; i ++){
tempPid = fork();
}//of for i
【注意】:每一次循环,进程的总数是当前进程数量的两倍,2次循环则为2² = 4个进程。
【解决方法】:如果只希望父进程可以创建新进程,则在for循环中添加一个判断:若当前进程不是父进程,则跳出循环。
②案例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
pid_t tempPid;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 2; i ++){
if((tempPid = fork()) == 0){
break;
}//of if
}//of for i
if(tempPid == -1){
perror("fork error");
}else if(tempPid > 0){//parent
printf("parent process, pid = %d, ppid = %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
}else{//child
printf("I am child process = %d, pid = %d, ppid = %d\n", i + 1, getpid(), getppid());
}//of if
printf("......finish......\n");
return 0;
}//of main
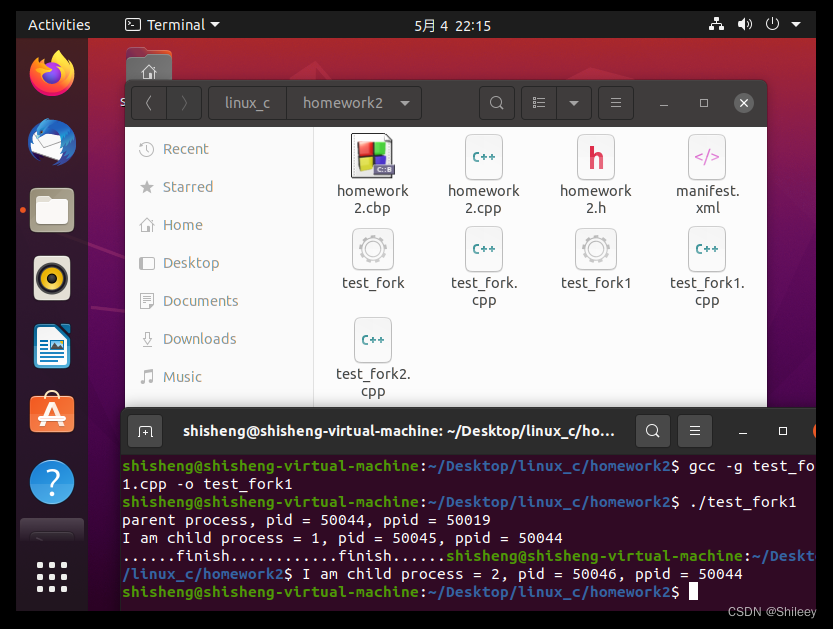
【思考】
(1)为什么子进程的编号不是递增的?
因为当子进程被创建后,它与它的父进程及其它进程共同竞争系统资源,所以父子进程执行的顺序是不确定的,终止的先后顺序也是不确定的。
(2)为什么终端提示符后面仍然有子进程信息打印,而命令提示符在最后一行的开头闪烁?
Shell命令提示符也是1个进程,它需要和新建进程一起竞争CPU。
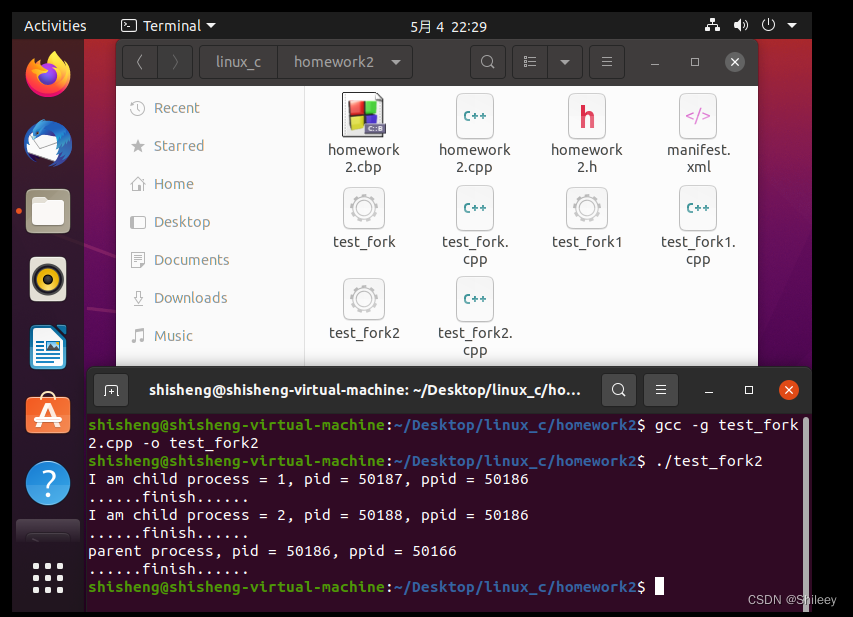
3.进程的执行顺序:利用sleep函数,暂缓进程执行
①案例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
pid_t tempPid;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 2; i ++){
if((tempPid = fork()) == 0){
break;
}//of if
}//of for i
if(tempPid == -1){
perror("fork error");
}else if(tempPid > 0){//parent
sleep(2);
printf("parent process, pid = %d, ppid = %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
}else{//child
sleep(i);
printf("I am child process = %d, pid = %d, ppid = %d\n", i + 1, getpid(), getppid());
}//of if
printf("......finish......\n");
return 0;
}//of main
三、总结
了解了fork()函数的知识,对于进程管理有了初步认识
对C语言代码有些遗忘生疏,需要自己复习并动手规范敲代码





















 112
112











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








