题目:
输入整数n(1≤n≤10)和n个整数存入数组,要求定义一个函数voidsort(int *list,int n),使用选择排序法对指针list所指数组进行升序排列,n为list所指向数组的元素个数。在main函数中调用sort函数实现排序,最后输出排序后的结果。
选择排序法:
选择排序(Selection sort)是一种简单直观的排序算法。它的工作原理是:第一次从待排序的数据元素中选出最小(或最大)的一个元素,存放在序列的起始位置,然后再从剩余的未排序元素中寻找到最小(大)元素,然后放到已排序的序列的末尾。以此类推,直到全部待排序的数据元素的个数为零。
选择排序法代码传送门:https://blog.csdn.net/lbcbjtlhmjq/article/details/128741011
代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 10
void swap(int* a, int* b)//两数交换函数
{
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
void sort(int* list, int n)//选择排序函数
{
int j, i,min,max;
for (j = 0; j < n / 2; j++)
{
min = j;
max = n - j - 1;
for (i = j; i < n - j; i++)//筛选出最大值与最小值
{
if (list[i] < list[min])
min = i;
if (list[i] > list[max])
max = i;
}
swap(&list[j], &list[min]);
if (max == j)//考虑最大值位置与未排序数组最左端重合的情况
swap(&list[n - j - 1], &list[min]);
else
swap(&list[n - j - 1], &list[max]);
}
}
int main()
{
int n,i;
int list[N]={ };
printf("输入整数n(1≤n≤10):");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("输入n个整数:");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &list[i]);
sort(list, n);//调用函数
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", list[i]);
return 0;
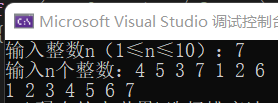
}运行结果:





















 7296
7296











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








