问题描述
跨境系统新版本上线之后发现凡是通联支付的订单都卡在了准备支付报关这个状态,原因系统拿到的通联支付回抛的支付报关结果全是空(这里取数据是通过流方式读取的,即流中是空的)。
问题查找
由于这个接口已经用了很久,所以开始认为是通联支付那边的问题,找他们的人沟通说确定已经把状态回抛给我们了,而我们拿到的数据又确实为空。问题到底出在哪?通过mock站点自测发现发送的时候有数据,但是到了Controller处理时流中数据为空。现在可以确定是我们自身系统问题了。那究竟是什么原因导致的呢?
第一次遇到这种问题(一个简单的Controller request.getInputStream()无故丢失了),肯定是请求到达Controller之前已经被使用过了,但是具体是什么引起的完全没什么思路。由于通联支付的订单比较少,零星的几单,出问题的这一单离上一正常单已经有段时间了。这期间上了很多版本。现在只能通过逐一排查新功能来查找到底是哪个功能影响到了这里。这一过程是痛苦的~~。最好把目标锁定在了集成oums时使用的spring-session。发现把spring-session禁掉接口变正常了,所以可以确定问题肯定出在这。先看下发送端和接收端的代码以方便下文深入探讨:
/**
* 这是根据对接文档自己写的,可以说明问题
*/
public Result<String> doPost(String content) throws Exception {
HttpEntity resEntity;
try {
HttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault();
HttpPost method = new HttpPost(url);
ByteArrayEntity byteArrayEntity = new ByteArrayEntity(content.getBytes(Constants.DEFAULT_CHARSET));
byteArrayEntity.setContentEncoding(Constants.DEFAULT_CHARSET);
byteArrayEntity.setContentType("application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8");
method.setEntity(byteArrayEntity);
HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(method);
resEntity = response.getEntity();
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error("", e);
return Results.exception();
}
return Results.of(resEntity.toString());
}/**
* 通联支付报关结果
*/
@RequestMapping("/allinpay")
public void allinpay(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
String btResponse;
try {
Result<AllinpayResultParam> statusResult = HttpRequestUtil.getRequestObjectByXml(request, AllinpayResultParam.class);
btResponse = statusResult.isSuccess() ? allinpayRequestService.processOrderDeclareRequest(statusResult.getData()) :
statusResult.getRes().getMsg();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("通联支付报关结果处理失败", e);
btResponse = "系统异常";
}
try {
response.getOutputStream().write(btResponse.getBytes(Constants.DEFAULT_CHARSET));
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
/*主要看这里,很简单的流读取*/
public static String getRequestData(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
ByteArrayOutputStream os = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
InputStream inputStream = null;
String message;
try {
/*流中一直没数据 */
inputStream = request.getInputStream();
int c;
while ((c = inputStream.read()) != -1) {
os.write(c);
}
message = new String(os.toByteArray());
logger.info(String.format("请求链接:%s; 请求内容:%s", request.getRequestURI(), message));
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
throw new RuntimeException("读取数据流失败");
} finally {
os.close();
if (inputStream != null) {
inputStream.close();
}
}
return message;
}spring-session源码解析
在filter中打个断点可以看到filterChain中有一个DelegatingFilterProxy:
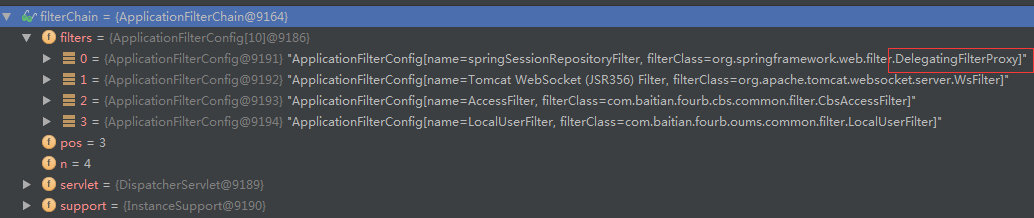
这是一个代理Filter,它代理的实际上是SessionRepositoryFilter,这个Filter是spring-session提供的。它对HttpServletRequest , HttpServletResponse 进行了一层包装来实现自己的功能,引发这个问题的关键点是重写了getSession方法:
@Override
public HttpSession getSession(boolean create) {
if(currentSession != null) {
return currentSession;
}
//关键是这里
String requestedSessionId = getRequestedSessionId();
if(requestedSessionId != null) {
S session = sessionRepository.getSession(requestedSessionId);
if(session != null) {
this.requestedSessionIdValid = true;
currentSession = new HttpSessionWrapper(session, getServletContext());
currentSession.setNew(false);
return currentSession;
}
}
if(!create) {
return null;
}
S session = sessionRepository.createSession();
currentSession = new HttpSessionWrapper(session, getServletContext());
return currentSession;
}其中有一个getRequestSessionId()最终调用到了CookieHttpSessionStrategy的getCurrentSessionAlias()方法:
public String getCurrentSessionAlias(HttpServletRequest request) {
if(sessionParam == null) {
return DEFAULT_ALIAS;
}
//罪魁祸首
String u = request.getParameter(sessionParam);
if(u == null) {
return DEFAULT_ALIAS;
}
if(!ALIAS_PATTERN.matcher(u).matches()) {
return DEFAULT_ALIAS;
}
return u;
}说了这么多,罪魁祸首出来了,就是: request.getParameter(sessionParam)。回过头来看下上图FilterChain中有一个LocalUserFilter,这个Filter是oums中添加。其中有获取session的操作,最终会调用这个request.getParameter()。而request.getParameter()操作会读取流信息,从而导致流被掏空,以致请求到达Controller时没数据可以读取。
request.getParameter()与request.getInputStream()的关系
getParameter方法为什么会读取流中的信息呢?它有没有什么规则呢?继续深究需要研究tomcat源码。我们使用的HttpServletRequest接口的底层承载类是tomcat中的**org.apache.coyote.Request**Parameters类也被封装在这里:
private final Parameters parameters = new Parameters();这里主要看下Parameters是如何赋值的,当第一次调用request.getParamater()的时候会进行一次参数的解析操作,具体逻辑在org.apache.catalina.connector.Request类中的parseParameters()方法中:
protected void parseParameters() {
parametersParsed = true;
Parameters parameters = coyoteRequest.getParameters();
boolean success = false;
try {
//省略不必要的代码
......
......
//解析查询字符串中的参数
parameters.handleQueryParameters();
......
......
String contentType = getContentType();
//如果contentType是multipart/form-data,解析请求中附带的参数
if ("multipart/form-data".equals(contentType)) {
parseParts(false);
success = true;
return;
}
//如果contentType是application/x-www-form-urlencoded类型才继续往下执行,其他类型的contentType到此就解析结束了
if (!("application/x-www-form-urlencoded".equals(contentType))) {
success = true;
return;
}
int len = getContentLength();
if (len > 0) {
......
......
try {
//读取请求体中的内容到缓存中
if (readPostBody(formData, len) != len) {
......
......
return;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
......
}
//解析请求体中的参数
parameters.processParameters(formData, 0, len);
}
......
......
success = true;
} finally {
......
......
}
}从上面的代码可以看出关键点在32行的readPostBody这里,继续看代码:
protected int readPostBody(byte body[], int len) throws IOException {
int offset = 0;
do {
int inputLen = getStream().read(body, offset, len - offset);
if (inputLen <= 0) {
return offset;
}
offset += inputLen;
} while ((len - offset) > 0);
return len;
}
public InputStream getStream() {
if (inputStream == null) {
inputStream = new CoyoteInputStream(inputBuffer);
}
return inputStream;
}看到这里应该就明白了,这里读取的是InputStream中的数据。
更深层次探讨
在上文parseParameters()方法中,不知道你有没有注意到请求体中的数据只有当contentType为application/x-www-form-urlencoded时,才会被解析成Paramater,其他类型的contentType只会解析queryString中的参数。所以最终产生问题的原因还与发送请求时的contentType有关。假如我们指定其他类型的contentType就可以避免这个问题的产生。但是由于调用方是第三方企业,所以我们无法控制。对于这方面的内容Servlet规范中有提及:

解决方案
- 1 修改contentType
- 2 不使用spring-session
- 3 重写HttpServletRequest
我们知道可以通过修改contentType来避免这个问题,但是由于请求是第三方发送的,所以我们只能在接收端做手脚,怎么解决呢?最终选择了一个比较挫的方法。我们是通过请求到达LocalUserFilter之前对HttpServletRequest做一个封装,将流改造成可以重复读取的,不多说了,看代码吧:
public class MultiReadHttpServletRequest extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
private ByteArrayOutputStream cachedBytes;
public MultiReadHttpServletRequest(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
super(request);
cacheInputStream();
}
//每次获取流都创建一个从cachedBytes读取数据的流
@Override
public ServletInputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return new CachedServletInputStream();
}
@Override
public BufferedReader getReader() throws IOException {
return new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(getInputStream()));
}
//将流中的内容缓存起来
private void cacheInputStream() throws IOException {
cachedBytes = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
IOUtils.copy(super.getInputStream(), cachedBytes);
}
public class CachedServletInputStream extends ServletInputStream {
private ByteArrayInputStream input;
public CachedServletInputStream() {
input = new ByteArrayInputStream(cachedBytes.toByteArray());
}
......
......
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
return input.read();
}
}
}这个方法可以解决当前的问题,但是会引发其他问题,因为getInpustream和getParamater是相互影响的,这里把流用掉了,getParamater()就取不到了。所以只能用在特殊的接口上,在Filter中使用的时候只对需要的请求进行包装。谁有什么更好的方法欢迎提出来。






















 1037
1037

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








