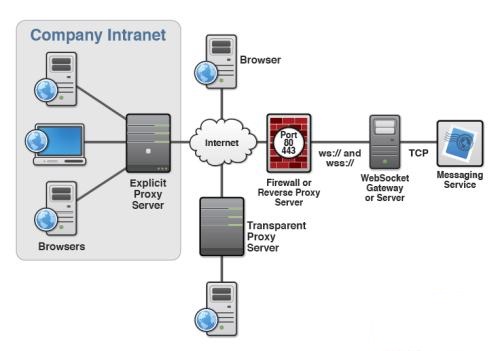
WebSocket是HTML5开始提供的一种在单个 TCP 连接上进行全双工通讯的协议。
在WebSocket API中,浏览器和服务器只需要做一个握手的动作,然后,浏览器和服务器之间就形成了一条快速通道。两者之间就直接可以数据互相传送。
浏览器通过 JavaScript 向服务器发出建立 WebSocket 连接的请求,连接建立以后,客户端和服务器端就可以通过 TCP 连接直接交换数据。
当你获取 Web Socket 连接后,你可以通过 send() 方法来向服务器发送数据,并通过 onmessage 事件来接收服务器返回的数据。
以下 API 用于创建 WebSocket 对象。
var Socket = new WebSocket(url, [protocol] );
Websocket Python3 Server实例
#!/usr/bin/env python
import asyncio
import websockets
import json
with open("web_so_cfg.json",'r') as load_f:
global load_dict
load_dict = json.load(load_f)
ipaddr=load_dict['server_url']
port=load_dict['server_port']
data_file=load_dict['data_file']
help_cmd=load_dict['help_cmd']
load_f.close()
print("ipaddr=",ipaddr)
print("port=",port)
print("data_file=",data_file)
file_name = data_file
top_items_name = ''
with open(file_name, 'r') as load_f:
global load_dict_2
load_dict_2 = json.load(load_f)
print('-----------------------------------')
for item in load_dict_2:
top_items_name=top_items_name+item+'\n'
print(item,'=',load_dict_2[item])
print('-----------------------------------')
async def ift_command_line(websocket, path):
name = await websocket.recv()
print("< {}".format(name))
ift_message = "ift_command_line: {}".format(name)
ift_message_str=ift_message+" test msg"
'''
await websocket.send(ift_message_str)
print("> {}".format(ift_message_str))
'''
print (name)
if name == 'help':
with open("web_so_cfg.json",'r') as load_f:
load_dict = json.load(load_f)
help_cmd=load_dict['help_cmd']
load_f.close()
help_name='the command help: '+help_cmd
ift_message = "ift_command_line: {}!".format(help_name)
await websocket.send(ift_message)
elif name == 'get-json-topitem':
ift_message = "ift_command_line(from server): {}!".format(top_items_name)
await websocket.send(ift_message)
elif 'get-json-value-of' in name:
str_array=name.split('of')
item=str_array[1].strip()
print (item)
if item in load_dict_2:
value=load_dict_2[item]
else:
value='null'
print(value)
ift_message = "ift_command_line(from server): {}!".format(value)
await websocket.send(ift_message)
else:
error_infor=name +' is not a command!'
ift_message = "ift_command_line(from server): {}!".format(error_infor)
await websocket.send(ift_message)
start_server = websockets.serve(ift_command_line, ipaddr, port)
asyncio.get_event_loop().run_until_complete(start_server)
asyncio.get_event_loop().run_forever()
Websocket server配置文件web_so_cfg.json
{
"server_url": "192.168.8.102",
"server_port": "8765",
"data_file": "Handbetrieb_Maske_b.JSON",
"help_cmd":"get-json-topitem,get-json-value-of <itemname>,get-data,get-name,add-user,mod-user,mod-user-pwd,mod-user-service,create-json-with-name:value,parse-json-with-\"jsonstr\""
}
Demo中使用的Json文件:Handbetrieb_Maske_b.JSON
{
"current_tester": "SSTM",
"current_materdata": "D:\\SVN\\Weishaupt_E01600\\image\\daten\\sw\\M1.sw",
"specimen_type": "1 Ph",
"selected_axis": "1",
"current_power_supply_unit": "Sinamics NT 3Ph 600V/120A",
"power_supply_controls": {
"setpoint_voltage": {
"current_value": 50,
"unit": "V",
"min_value": 0,
"max_value": 600,
"supported_precision": 0.1
},
"setpoint_frequency": {
"current_value": 45.0,
"unit": "Hz",
"min_value": 45.0,
"max_value": 75.0,
"supported_precision": 0.1
}
},
"load_machine_controls": {
"setpoint_speed": {
"current_value": 0,
"unit": "rpm",
"min_value": 0,
"max_value": 1000,
"supported_precision": 0.1
},
"setpoint_current_limit_torque": {
"current_value": 0,
"unit": "Nmm",
"min_value": 0,
"max_value": 100,
"supported_precision": 1
},
"setpoint_load_active": {
"current_value": false
}
},
"specimen_controls": {
"setpoint_rotation_direction": {
"current_value": "clockwise",
"possible_values": [
"clockwise",
"counter clockwise"
]
},
"setpoint_speciment_power_supply_active": {
"current_value": false
},
"setpoint_1uf_condensator_connected": {
"current_value": false
},
"setpoint_2uf_condensator_connected": {
"current_value": false
},
"setpoint_4uf_condensator_connected": {
"current_value": false
},
"setpoint_7uf_condensator_connected": {
"current_value": false
},
"setpoint_10uf_condensator_connected": {
"current_value": false
},
"setpoint_20uf_condensator_connected": {
"current_value": false
},
"setpoint_40uf_condensator_connected": {
"current_value": false
}
},
"measurement_setup_controls": {
"setpoint_sample_rate": {
"current_value": "20 Hz",
"possible_values": [
"20 Hz",
"10 Hz",
"1 Hz"
]
},
"setpoint_poweranalyzer_mode_set_to_local": {
"current_value": false
},
"setpoint_countinous_measurement_recording_active": {
"current_value": false
}
},
"actions": [
"shutdown_measurement",
"start_resistance_measurement",
"store_current_sample"
],
"actual_values": [
{
"label": "time",
"current_value": null,
"unit": "s"
},
{
"label": "angle",
"current_value": null,
"unit": "°"
},
{
"label": "speed",
"current_value": null,
"unit": "rpm"
},
{
"label": "torque",
"current_value": null,
"unit": "Nmm"
},
{
"label": "p_mech",
"current_value": null,
"unit": "kW"
},
{
"label": "frequency",
"current_value": null,
"unit": "Hz"
},
{
"label": "voltage",
"current_value": null,
"unit": "V"
},
{
"label": "current",
"current_value": null,
"unit": "A"
},
{
"label": "p_electric",
"current_value": null,
"unit": "kW"
},
{
"label": "Q_1",
"current_value": null,
"unit": "kVAR"
},
{
"label": "S_1",
"current_value": null,
"unit": "kVA"
},
{
"label": "cos_phi",
"current_value": null,
"unit": ""
},
{
"label": "ETA_M",
"current_value": null,
"unit": ""
},
{
"label": "Temp_1",
"current_value": null,
"unit": "°C"
},
{
"label": "Temp_2",
"current_value": null,
"unit": "°C"
},
{
"label": "Temp_3",
"current_value": null,
"unit": "°C"
}
]
}
Websocket Python3 Client实例
#!/usr/bin/env python
import asyncio
import websockets
import json
with open("web_so_cfg.json",'r') as load_f:
load_dict = json.load(load_f)
ipaddr=load_dict['server_url']
port=load_dict['server_port']
data_file=load_dict['data_file']
print("ipaddr=",ipaddr)
print("port=",port)
print("data_file=",data_file)
connect_addr_port='ws://'+ipaddr+':'+port
print("connect_addr_port=",connect_addr_port)
async def web_so_op():
async with websockets.connect(connect_addr_port) as websocket:
name = input("Enter the cmd--->> ")
await websocket.send(name)
print("> {}".format(name))
greeting = await websocket.recv()
print("< {}".format(greeting))
while True:
asyncio.get_event_loop().run_until_complete(web_so_op())
Websocket JavaScript client实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<html>
<h1>WebSocket Test</h1>
<head>
<script>
var wsocket;
var flag=0;
var ws_link;
function Connect(){
var url_port=document.getElementById("msg").value;
if(flag==0){
ws_link='ws://'+url_port;
flag=1;
}
document.getElementById("receive_msg").innerHTML=ws_link;
try{
//wsocket=new WebSocket('ws://192.168.8.101:8765/');
wsocket=new WebSocket(ws_link);
}catch(e){
alert('error');
return;
}
wsocket.onopen = sOpen;
wsocket.onerror = sError;
wsocket.onmessage= sMessage;
wsocket.onclose= sClose;
}
function sOpen(){
alert('connect success!');
}
function sError(e){
alert("error " + e);
document.getElementById("receive_msg").innerHTML=e.data;
}
function sMessage(e){
alert('server says:' + e.data);
document.getElementById("receive_msg").innerHTML='server says:' + e.data;
;
}
function sClose(e){
alert("connect closed:" + e.code);
}
function Send(){
wsocket.send(document.getElementById("msg").value);
}
function Close(){
wsocket.close();
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input id="msg" type="text">
<button id="connect" οnclick="Connect();">Connect</button>
<button id="send" οnclick="Send();">Send</button>
<div id="receive_msg"></div>
</body>
</html>
























 3万+
3万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








