由于工作需要,最近在研究梯度下降法,并附上代码。
1.梯度下降法实现描述:
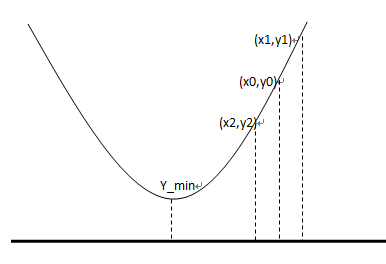
以曲线最低点作为分界线,在其中一边任意选取两点(x0,y0),(x1,y1)。选取初始值x0,x1时,保证y0小于y1。设置大于0的任意初始步长,用作梯度。
2.描述的不是太清楚,还是直接贴代码。
代码已调试运行过,可以快速找到最低点,可自己设定初始值运行(参考设定(x0,y0,step_size)=(100,200,50))。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int func(int x)
{
return x*x;
}
/*fine tuning*/
int fine_tuning(int X)
{
int Y_L,Y_R,Y_MID;
int Y_TMP,Y_MIN;
int X_L=0,X_R=0,X_MIN=0;
int num=0;
int step=2;
printf("Entry fine tuning\n");
//init
X_L=X;X_R=X;
X_L = X-step;
X_R = X+step;
Y_L = func( X_L);
Y_MID = func( X);
Y_R = func( X_R);
if(fabs(Y_L-Y_MID) < 1 &&
fabs(Y_R-Y_MID) < 1 &&
fabs(Y_L-Y_R) < 1){
return X;
}
printf("(X_L,Y_L) (%d,%d);(X,Y) (%d,%d) (X_R,Y_R) (%d,%d)\n\n",X_L,Y_L,X,Y_MID,X_R,Y_R);
//for(num = 0; num < 20; num++)
while(1){
/*calc min val*/
Y_TMP=(Y_L > Y_MID) ? Y_MID : Y_L; //GET Y min value
Y_MIN=(Y_TMP<Y_R) ? Y_TMP: Y_R; // GET MIN Y value
if(fabs(Y_L-Y_MID)< 1 &&
fabs(Y_R-Y_MID)< 1 &&
fabs(Y_L-Y_R)< 1){
return X;
}
if(Y_MIN==Y_MID){
/*if min_val=mid_val,reduce step size*/
step=step>>1;
if(0==step)
break;
X_R=X_R-step;
X_L=X_L+step;
Y_L = func( X_L);
Y_R = func( X_R);
}else if(Y_MIN==Y_R){
/*curve rightward heeling*/
Y_L=Y_MID;
Y_MID=Y_R;
X_L=X;
X=X_R;
X_R=X_R+step;
Y_R = func( X_R);
printf("(X_R,Y_R) (%d,%d)\n",X_R,Y_R);
}else{
/*curve lefttward heeling*/
Y_R=Y_MID;
Y_MID=Y_L;
X_R=X;
X=X_L;
X_L=X_L-step;
Y_L = func( X_L);
printf("(X_L,Y_L) (%d,%d)\n",X_L,Y_L);
}
}
printf("Exit x %d\n",X);
return X;
}
/*addtional y0 <y1*/
int gradient_descent(int x0,int x1,int step)
{
int x2,y0,y1,y2;
y0=func(x0);
y1=func(x1);
printf("\n\n");
printf("(x0,y0) (%d,%d)\n",x0,y0);
printf("(x1,y1) (%d,%d)\n\n",x1,y1);
if(y0>=y1){
printf("Pls renew input x0,x1(need y0< y1)\n");
return -1;
}
while(1){
if(y0<y1)
x2=x0-step;
else
x2=x0+step;
y2=func(x2);
printf("(x2,y2) (%d,%d)\n",x2,y2);
if(y2<y0 && y2<y1){
x0=x2;
y1=y0;//downward move (x1,y1)
y0=y2;
printf("Y2<Y0 (x2,y2) =>[ (x0,y0) (%d,%d)]\n",x0,y0);
}else{
/*y2>=y0*/
step=step>>1;
printf("step %d\n",step);
if(step==1){
return fine_tuning(x0);
//return x0;
}
}
sleep(1);
}
}
int main(int argc,char **argv)
{
int i=0;
int cnt=0;
int res=0;
int x0,x1,step;
#if 0
for(i=-255;i<=255;i++){
if(cnt==10){
printf("\n");
cnt=0;
}
cnt++;
printf("(%3d,%6d) ",i,func(i));
}
printf("\n\n");
#endif
printf("Pls input x0: \n");
scanf("%d",&x0);
printf("Pls input x1: \n");
scanf("%d",&x1);
printf("Pls input step: \n");
scanf("%d",&step);
res=gradient_descent(x0,x1,step);
printf("(x,y) = (%d ,%d)\n",res,func(res));
}
3.用途:
预先知道数据运动趋势(符合类似二次曲线),在不遍历所有数据情况下,一种能快速找到最小值的算法。适用于符合二次曲线走势的大数据,最小值查找。






















 815
815

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








