临时对象通常产生于3种情况:
1、类型转换
2、按值传递
3、按值返回
- 类型转换
通常是为了让函数调用成功而产生的临时对象:传递某对象给一个函数,而其类型与它绑定的参数类型不同。
例如:
void test(const string& str);
char buffer[] = "buffer";
test(buffer);//此刻发生类型转换编译器类型转换:产生一个类型为string的临时对象,该对象以buffer为参数调用string constructor,当test函数返回时,临时对象会自动销毁。
注意:对于引用(reference)参数而言,只有当对象被传递给一个reference-to-const参数时,转换才发生。如果对象参数传递给一个reference-to-non-const对象,则不会发生转换。
例如:
void upper(string& str);
char buffer[] = "buffer";
test(buffer);//编译出错- 按值传递:通常是为了让函数调用成功而产生临时对象。
例如:
void foo(X x0);
X xx;
foo(xx);此时编译器产生的伪代码:
//编译器产生的临时对象
X _temp0;
//编译器对拷贝构造的调用
_temp0.X::X(xx);
foo(_temp0);又如例:
class CTemp
{
public:
int a;
int b;
CTemp(CTemp& t){cout << "copy function " << endl; a = t.a; b = t.b;};
CTemp(int m = 0, int n = 0);
virtual ~CTemp(){};
int GetSum(CTemp ts);
};
CTemp::CTemp(int m, int n)
{
cout << "construct function " << endl;
a = m;
b = n;
cout << a << endl;
cout << b << endl;
}
int CTemp::GetSum(CTemp ts)
{
int tmp = ts.a + ts.b;
ts.a = 100;
return tmp;
}
void main()
{
CTemp tm(10, 20);
cout << tm.GetSum(tm) << endl;
cout << tm.a << endl;
}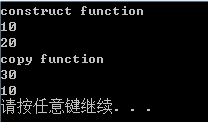
1,调用拷贝构造函数来创建一个副本为GetSum函数体内所用。
2,在GetSum函数体内对tm副本进行的修改并没有影响到tm本身。
int CTemp::GetSum(CTemp& ts)
{
int tmp = ts.a + ts.b;
ts.a = 1000; //此时通过ts这个引用参考(refer to)对象本身
return tmp;
}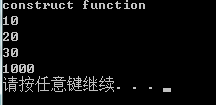
通过引用,减少了一次临时对象的创建。
如程序改为:
void main()
{
CTemp tm(10, 20),sum;
sum = 1000; 调用CTemp(int m = 0,int n = 0)构造函数
cout << tm.GetSum(sum) << endl;
}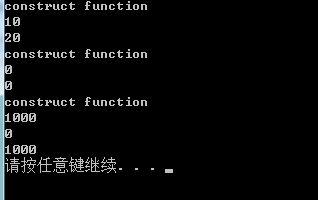
输出调用了3次构造函数:sum = 1000. 1000和sum类型不符,但编译器为了通过编译以1000为参数调用构造函数创建了临时对象。
解决方法:
void main()
{
CTemp tm(10, 20);
CTemp sum = 1000;
cout << tm.GetSum(sum) << endl;
}只作了稍稍改动,就减少了一次临时对象的创建。
1,此时的“=”号由原本的赋值变为了构造。
2,对Sum的构造推迟了。当我们定义CTmep sum时,在main的栈中为sum对象创建了一个预留的空间。而我们用1000调用构造时,此时的构造是在为sum预留的空间中进行的。因此也减少了一次临时对象的创建。
- 函数返回一个对象
当函数需要返回一个对象,会在栈中创建一个临时对象,存储函数的返回值。、
例如:
class CTemp
{
public:
int a;
CTemp(CTemp& t)
{
cout << "Copy ctor" << endl;
a = t.a;
}
CTemp& operator=(CTemp& t)
{
cout << "Assignment copy ctor" << endl;
a = t.a;
return *this;
}
CTemp(int m = 0);
virtual ~CTemp(){};
};
CTemp::CTemp(int m)
{
cout << "Construct function" << endl;
a = m;
}
CTemp Double(CTemp& ts)
{
CTemp tmp;
tmp.a = ts.a * 2;
return tmp;
}
void main()
{
CTemp tm(10), sum;
sum = Double(tm);
cout << sum.a << endl;
}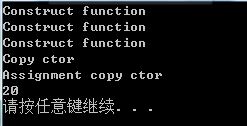
对于 sum = Double(tm);语句生成了两个对象:
1、创建一个tmp临时对象 CTmp tmp;
2、将tmp对象返回,返回过程中调用Copy cotr创建一个返回对象:return tmp;
3、将返回结果通过调用赋值拷贝函数,赋给sum:sum = 函数返回值;//该步没有创建对象
解决方案:
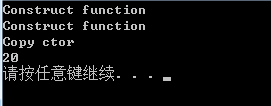
void main()
{
CTemp tm(10);
CTemp sum = Double(tm);
cout << sum.a << endl;
}
若修改为
CTemp Double(CTemp& ts)
{
return ts.a * 2;
}减少一次构造函数调用(tmp),一次拷贝构造函数(tmp拷贝给返回对象)调用和一次赋值拷贝函数调用
原因:返回对象直接使用为sum预留的空间,减少了返回临时对象的生成
参考:
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-10533652-id-2949402.html
http://blog.csdn.net/imyfriend/article/details/12886577






















 1068
1068

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








