哈喽!大家好,我是一位上进心十足,拥有极强学习力的【Java 领域博主】
本博主借助 CSDN 在开发求学之路上将亲身经历与所学心得与知识分享,有兴趣的小伙伴可以关注博主!
也许一个人独行,可以走的很快,但是一群人结伴而行,才能走的更远!让我们在成长的道路上互相学习,共同成长!
如果有对【后端技术】、【前端领域】、【云原生】感兴趣的【小可爱】,欢迎关注【CodeGardenia】💞💞💞

❤️❤️❤️ 感谢各位小伙伴! ❤️❤️❤️
那么,我们开始今天的学习吧!
Spring
Spring认证框架是一个开放源代码的 J2EE 应用程序框架,由Rod Johnson发起,是针对 bean的生命周期 进行管理的轻量级容器(lightweight container)
Spring是Java EE编程领域的一个轻量级开源框架,该框架由一个叫Rod Johnson的程序员在 2002 年最早提出并随后创建,是为了解决企业级编程开发中的复杂性,实现敏捷开发的应用型框架 。
Spring 有两个核心部分:IOC 和 Aop
(1)IOC:控制反转,把创建对象过程交给 Spring 进行管理
(2)Aop:面向切面,不修改源代码进行功能增强
- 轻量级开源的JAVAEE框架
- 可以解决企业复杂的应用
- 拥有IOC,AOP两个核心部分
优点
- IOC 方便解耦,简便开发
- AOP 不改变源代码,增加其功能
- 方便程序测试
- 方便其他程序的整合
- 降低API的开发难度
Spring使用的是基本的JavaBean来完成以前只可能由EJB完成的事情。
然而,Spring的用途不仅仅限于服务器端的开发。
使用
官方文档 : https://spring.io/
下载地址 : https://repo.spring.io/ui/native/release/org/springframework/spring/
下载之后压缩 , 找到 libs文件夹内的 jar 包,导入 spring jar 包即可进行开发
也可以引入依赖 (这里默认使用 Maven 管理 jar 包, 需要手动导入的同学请点击这里下载并导入)
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.3.14</version>
</dependency>
IOC
IOC 概念和原理
- 概念:
控制反转,把对象创建和对象的调用过程交给spring进行管理。
目的:降低耦合度。
底层原理:xml,反射,工厂模式
- Spring提供 IOC 容器两种实现方式(两个接口)
BeanFactory:Spring内部使用的接口,不提倡开发人员使用。特点:加载配置文件时不会创建对象,获取对象时才会创建对象。ApplicationContext:BeanFactory的子接口,提供了更多更强大的功能,一般由开发人员使用。特点:加载配置文件时会把配置文件里的对象进行创建。ApplicationContext两个常用实现类:- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:绝对路径,从盘符开始算起
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:相对路径,从src开始算起

Bean管理是指两个操作:Spring 创建对象 和 Spring 注入属性
Bean管理有两种操作方式:基于xml配置文件方式实现 和 基于注解方式实现
Bean管理(基于xml)
(1)基于xml方式创建对象
xml 配置文件,配置创建的对象
<!-- 配置 类对象 -->
<bean id=" " class=" "></bean>
- bean标签有很多属性,常用属性:
- id:唯一标识 (一般为 首字母小写的类名)
- class:类路径
- 创建对象时,默认执行无参构造函数
(2)基于 xml 方式注入属性
- 第一种方法:使用
set方法进行注入
- 首先需要为类的属性提供
set方法:
public class User {
private String userName;
private String userAge;
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public void setUserAge(String userAge) {
this.userAge = userAge;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public String getUserAge() {
return userAge;
}
}
- 然后在xml配置文件中通过property标签进行属性注入
<!--配置User对象-->
<bean id="user" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.User">
<property name="userName" value="Spring"></property>
<property name="userAge" value="19"></property>
</bean>
- 即可在测试类中查看是否注入成功
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
User user = applicationContext.getBean("user", User.class);
System.out.println(user.getUserName() + " " + user.getUserAge());
- 第二种方法:使用有参构造函数进行注入
- 首先需要提供有参构造方法
public class User {
private String userName;
private String userAge;
public User(String userName, String userAge){
this.userName = userName;
this.userAge = userAge;
}
}
- 再通过 xml 配置文件中通过
constructor-arg标签进行属性注入
<!--配置User对象-->
<bean id="user" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.User">
<constructor-arg name="userName" value="haha"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="userAge" value="18"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
- 第三种方法:
p名称空间注入
-
首先在xml配置文件中添加p名称空间,并且在bean标签中进行操作
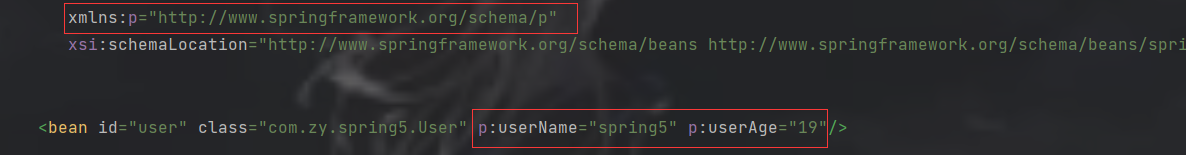
-
提供
set方法
public class User {
private String userName;
private String userAge;
public User() {
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public void setUserAge(String userAge) {
this.userAge = userAge;
}
}
(3)基于 xml 注入其他特殊属性
- 注入 NULL 值
<!--配置User对象-->
<bean id="user" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.User">
<property name="userName"> <null/> </property>
</bean>
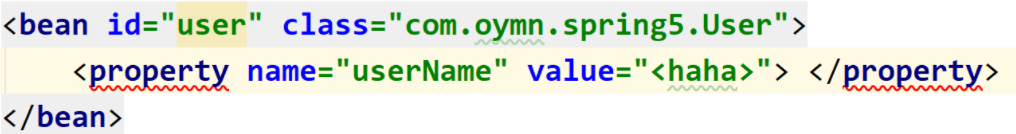
- 属性值包含特殊符号
如果
userName属性需要赋值为 < haha >
如果像上面那样直接在value中声明的话会报错,因为包含特殊符号 <>
通过 <![CDATA[值]]> 来表示:

3. 注入属性——外部 bean
有两个类:UserService和UserDaoImpl,其中UserDaoImpl实现UserDao接口
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao){
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void add(){
System.out.println("add");
}
}
通过 ref 来指定创建userDaoImpl
<bean id="userDaoImpl" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.UserService">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDaoImpl"></property>
</bean>
- 注入属性——内部 bean
不通过ref属性,而是通过嵌套一个bean标签实现
<!--内部 bean-->
<bean id="emp" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.bean.Emp">
<!--设置两个普通属性-->
<property name="ename" value="lucy"></property>
<property name="gender" value="女"></property>
<!--设置对象类型属性-->
<property name="dept">
<bean id="dept" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.bean.Dept">
<property name="dname" value="安保部"></property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
- 注入属性——级联赋值
emp类中有ename和dept两个属性,其中dept有dname属性,写法二需要emp提供dept属性的get方法
<!--级联赋值-->
<bean id="emp" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.bean.Emp">
<!--设置两个普通属性-->
<property name="ename" value="lucy"></property> <property name="gender" value="女"></property>
<!--写法一-->
<property name="dept" ref="dept"></property>
<!--写法二-->
<property name="dept.dname" value="技术部"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="dept" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.bean.Dept">
<property name="dname" value="财务部"></property>
</bean>
- 注入集合属性(数组,List,Map)
假设有一个Student类
public class Student {
private String[] courses;
private List<String> list;
private Map<String,String> map;
private Set<String> set;
public void setCourses(String[] courses) {
this.courses = courses;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public void setMap(Map<String, String> map) {
this.map = map;
}
public void setSet(Set<String> set) {
this.set = set;
}
}
在xml配置文件中对这些集合属性进行注入
<bean id="stu" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.Stu">
<!--数组类型属性注入-->
<property name="courses">
<array>
<value>java课程</value>
<value>数据库课程</value>
</array>
</property>
<!--List类型属性注入-->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>张三</value>
<value>李四</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--Map类型属性注入-->
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="JAVA" value="java"></entry>
<entry key="PHP" value="php"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<!--Set类型属性注入-->
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>Mysql</value>
<value>Redis</value>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
- 注入的集合值为对象
<!--创建多个 course 对象-->
<bean id="course1" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.collectiontype.Course">
<property name="cname" value="Spring5 框架"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="course2" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.collectiontype.Course">
<property name="cname" value="MyBatis 框架"></property>
</bean>
<!--注入 list 集合类型,值是对象-->
<property name="courseList">
<list>
<ref bean="course1"></ref>
<ref bean="course2"></ref>
</list>
</property>
- 集合注入部分提取
使用 util 标签,这样不同的bean都可以使用相同的集合注入
<!--将集合注入部分提取出来-->
<util:list id="booklist">
<value>Spring</value>
<value>Spring5</value>
</util:list>
<bean id="book" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.Book">
<property name="list" ref="booklist"></property>
</bean>
FactoryBean
- Spring有两种Bean
- 一种是普通Bean,另一种是工厂Bean(FactoryBean)
(4)通过外部属性文件来操作 bean
创建外部属性文件,
properties格式文件
引入context名称空间,并通过context标签引入外部属性文件,使用“${}”来获取文件中对应的值


Bean管理(基于注解)
- 格式:@注解名称(属性名=属性值,属性名=属性值,……)
- 注解可以作用在类,属性,方法
- 使用注解的目的:简化xml配置
(1)基于注解创建对象
spring提供了四种创建对象的注解:
- @Component
- @Service:一般用于Service层
- @Controller:一般用于web层
- @ Repository:一般用于Dao层
- 引入依赖 (这里默认使用 Maven 管理 jar 包, 需要手动导入的同学请点击这里下载并导入)
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-aop -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>5.3.14</version>
</dependency>
- 开启组件扫描:扫描
base-package包下所有有注解的类并为其创建对象
<context:component-scan base-package="<自定义路径>"></context:component-scan>
- com.zy.spring5-8080.Service有一个
studentService类
//这里通过@Component注解来创建对象,括号中value的值等同于之前xml创建对象使用的id,为了后面使用时通过id来获取对象
//括号中的内容也可以省略,默认是类名并且首字母小写
//可以用其他三个注解
@Component(value="studentService")
public class studentService {
public void add(){
System.out.println("addService");
}
}
- 可以通过
getBean方法来获取studentService对象
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean4.xml");
StuService stuService = context.getBean("stuService", StuService.class);
System.out.println(stuService);
stuService.add();
开启组件扫描的细节配置
use-default-fileters设置为 false 表示不使用默认过滤器,通过include-filter来设置只扫描com.zy.spring5-8080包下的所有@Controller修饰的类
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zy.spring5-8080" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
exclude-filter设置哪些注解不被扫描,例子中为@Controller修饰的类不被扫描
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zy.spring5-8080">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
(2)基于注解进行属性注入
- @Autowired:根据属性类型自动装配
创建StudentDao接口和StudentDaoImpl实现类,为StudentDaoImpl添加创建对象注解
public interface StudentDao{
public void add();
}
@Repository
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao{
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("StudentDaoImpl ");
}
}
StudentService 类中添加 StudentDao 属性,为其添加@Autowire注解,spring会自动为StudentDao属性创建StudentDaoImpl对象
@Component(value="studentService")
public class StudentService{
@Autowired
public StudentDao studentDao ;
public void add(){
System.out.println("addService");
studentDao.add();
}
}
测试
@Test
public void test1(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean4.xml");s
StudentService studentService= context.getBean("StudentService", StudentService.class);
System.out.println(studentService);
studentService.add();
}
- @Qualifier:根据属性名称自动装配
当遇到一个接口有很多实现类时,只通过@Autowire是无法完成自动装配的,所以需要再使用@Qualifier通过名称来锁定某个类
@Component(value="studentService")
public class StudentService {
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value="studentDaoImpl") //这样就能显式指定studentDaoImpl这个实现类
public StudentDao studentDao;
public void add(){
System.out.println("addService");
studentDao.add();
}
}
- @Resource:可以根据类型注入,也可以根据名称注入
@Component(value="studentService")
public class StudentService {
//@Resource //根据类型进行注入
@Resource(name="studentDaoImpl") //根据名称进行注入
public StudentDao studentDao;
public void add(){
System.out.println("addService");
studentDao.add();
}
}
- @Value:注入普通类型属性
@Value(value = "spring5")
private String name;
(3)完全注解开发
创建配置类,替代xml配置文件
@Configuration //表明为一个配置类
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.zy.spring5-8080") //开启组件扫描
public class SpringConfig {}
测试类:
@Test
public void test2(){
//创建AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
StudentService studentService = context.getBean("studentService", StudentService.class);
System.out.println(studentService);
studentService.add();
}
Bean的作用域
在Spring中,默认情况下 bean 是单实例对象
 执行结果是相同的
执行结果是相同的
但是可以通过 bean 标签的 scope 属性 来设置单实例还是多实例
Scope属性值:
- singleton:默认值,表示单实例对象。加载配置文件时就会创建单实例对象。
- prototype:表示多实例对象。不是在加载配置文件时创建对象,在调用getBean方法时创建多实例对象。

Bean的生命周期
(1)通过构造器创建 bean 实例(无参数构造)
(2)为 bean 的属性设置值和对其他 bean 引用(调用 set 方法)
(3)把 bean 实例传递 bean 后置处理器的方法 postProcessBeforeInitialization
(4)调用 bean 的初始化的方法(需要进行配置初始化的方法)
(5)把 bean 实例传递 bean 后置处理器的方法 postProcessAfterInitialization
(6)bean 可以使用了(对象获取到了)
(7)当容器关闭时候,调用 bean 的销毁的方法(需要进行配置销毁的方法)
- 实体类
public class Orders {
private String orderName;
public Orders() {
System.out.println("第一步:执行无参构造方法创建bean实例");
}
public void setOrderName(String orderName) {
this.orderName = orderName;
System.out.println("第二步:调用set方法设置属性值");
}
//初始化方法
public void initMethod(){
System.out.println("第四步:执行初始化方法");
}
//销毁方法
public void destroyMethod(){
System.out.println("第七步:执行销毁方法");
}
}
- 后置处理器
//实现后置处理器,需要实现BeanPostProcessor接口
public class MyBeanPost implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("第三步:将bean实例传递给bean后置处理器的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("第五步:将bean实例传递给bean后置处理器的postProcessAfterInitialization方法");
return bean;
}
}
- XML 注入实体
<bean id="orders" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.domain.Orders" init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod">
<property name="orderName" value="spring5"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置bean后置处理器,这样配置后整个xml里面的bean用的都是这个后置处理器-->
<bean id="myBeanPost" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.MyBeanPost"></bean>
- 测试
@Test
public void testOrders(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
Orders orders = context.getBean("orders", Orders.class);
System.out.println("第六步:获取bean实例对象");
System.out.println(orders);
//手动让bean实例销毁
context.close();
}

xml自动装配
-
根据指定的装配规则(属性名称或者属性类型),Spring自动将匹配的属性值进行注入
-
根据属性名称自动装配:要求 emp 中属性的名称 dept 和 bean标签的 id 值 dept 一样,才能识别
<!--指定autowire属性值为byName-->
<bean id="emp" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.Emp" autowire="byName"></bean>
<bean id="dept" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.Dept"></bean>
- 根据属性类型自动装配:要求同一个xml文件中不能有两个相同类型的bean,否则无法识别是哪一个
<!--指定autowire属性值为byType-->
<bean id="emp" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.Emp" autowire="byType"></bean>
<bean id="dept" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.Dept"></bean>
AOP
底层原理
-
面向切面编程:利用 AOP 可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。通俗来说就是在不修改代码的情况下添加新的功能。
-
底层通过动态代理来实现:
- 第一种:有接口的情况,使用JDK动态代理:创建接口实现类的代理对象
- 第二种:无接口的情况,使用CGLIB动态代理:创建当前类子类的代理对象
JDK动态代理
- 通过
java.lang.reflect.Proxy类 的newProxyInstance方法 创建代理类 newProxyInstance方法

- 参数一:类加载器
- 参数二:所增强方法所在的类,这个类实现的接口,支持多个接口
- 参数三:实现InvocationHandle接口,重写invoke方法来添加新的功能
代码举例:
public interface UserDao {
public int add(int a, int b);
public int multi(int a, int b);
}
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a+b;
}
@Override
public int multi(int a, int b) {
return a*b;
}
}
public class Main {
@Test
public void test1(){
//所需代理的类实现的接口,支持多个接口
Class[] interfaces = {UserDao.class};
UserDao userDao = new UserDaoImpl();
//调用newProxyInstance方法来创建代理类
UserDao userDaoProxy = (UserDao) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Main.class.getClassLoader(), interfaces, new UserDaoProxy(userDao));
int result = userDaoProxy.add(1, 2);
System.out.println(result);
}
//创建内部类,实现InvocationHandler接口,重写invoke方法,添加新功能
class UserDaoProxy implements InvocationHandler {
Object obj;
//通过有参构造函数将所需代理的类传过来
public UserDaoProxy(Object obj){
this.obj = obj;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("进入" + method.getName() + "方法,这是新增的代码,参数有" + Arrays.toString(args));
//执行原有的代码
Object invoke = method.invoke(obj, args);
System.out.println("方法原先的内容执行完了");
return invoke;
}
}
}
运行结果:

基于 AspectJ 实现AOP操作
(1)AOP相关术语:
- 连接点:类中可以被增强的方法,称为连接点
- 切入点:实际被增强的方法,称为切入点
- 通知:增强的那一部分逻辑代码。
- 前置通知:增强部分代码在原代码前面
- 后置通知:增强部分代码在原代码后面
- 环绕通知:增强部分代码既有在原代码前面,也有在原代码后面
- 异常通知:原代码发生异常后才会执行
- 最终通知:类似与finally那一部分
- 切面:指把通知应用到切入点这一个动作
(2)切入点表达式
- 语法:execution([权限修饰符] [返回类型] [类全路径] [方法名称] [参数列表])
- 举例:对 com.zy.spring5-8080.dao.BookDao 类里面的 add 进行增强
execution(* com.zy.spring5-8080.dao.BookDao.add(..)) - 举例:对 com.zy.spring5-8080.dao.BookDao 类里面的所有的方法进行增强
execution(* com.zy.spring5-8080.dao.BookDao.*(..)) - 举例 :对 com.zy.spring5-8080.dao 包里面所有类,类里面所有方法进行增强
execution(* com.zy.spring5-8080.dao.*.* (..))
基于注解方式
(1)栗子
@Component
public class User {
public void add(){
System.out.println("User.add()");
}
}
@Component
@Aspect //使用Aspect注解
public class UserProxy {
//前置通知
@Before(value="execution(* com.zy.spring5-8080.User.add(..))")
public void before(){
System.out.println("UserProxy.before()");
}
//后置通知
@AfterReturning(value="execution(* com.zy.spring5-8080.User.add(..))")
public void afterReturning(){
System.out.println("UserProxy.afterReturning()");
}
//最终通知
@After(value="execution(* com.zy.spring5-8080.User.add(..))")
public void After(){
System.out.println("UserProxy.After()");
}
//异常通知
@AfterThrowing(value="execution(* com.zy.spring5-8080.User.add(..))")
public void AfterThrowing(){
System.out.println("UserProxy.AfterThrowing()");
}
//环绕通知
@Around(value="execution(* com.zy.spring5-8080.User.add(..))")
public void Around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("UserProxy.Around() _1");
//调用proceed方法执行原先部分的代码
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("UserProxy.Around() _2");
}
}
配置xml文件
<!--开启组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zy.spring5-8080"></context:component-scan>
<!--开启AspectJ生成代理对象-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
测试
@Test
public void test2(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
User user = context.getBean("user", User.class);
user.add();
}
运行结果

(2)实现异常环绕
使结果出现异常通知,在 add 方法中添加
int i = 1/0
public void add(){
int i = 1/0;
System.out.println("User.add()");
}
After最终通知有执行,而 AfterReturning 后置通知并没有执行。

(3)抽取切入点
有很多通知的切入点都是相同的方法,因此,可以将该切入点进行抽取,通过
@Pointcut注解
@Pointcut(value="execution(* com.zy.spring5-8080.User.add(..))")
public void pointDemo(){
}
//前置通知
@Before(value="pointDemo()")
public void before(){
System.out.println("UserProxy.before()");
}
- 设置增强类优先级
有多个增强类对同一方法进行增强时,可以通过
@Order(数字值)来设置增强类的优先级,数字越小优先级越高
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(1)
public class PersonProxy
- 完全注解开发
可以通过配置类来彻底摆脱 xml 配置文件
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.zy.spring5-8080")
// @EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解相当于上面xml文件中配置的
// <aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
public class Config {}
基于 xml 方式
此种方式开发中不常使用,了解即可
- 创建 Book 和 BookProxy 类
public class Book {
public void buy(){
System.out.println("buy()");
}
}
public class BookProxy {
public void before(){
System.out.println("before()");
}
}
- 配置 xml 文件
<!--创建对象-->
<bean id="book" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.Book"></bean>
<bean id="bookProxy" class="com.zy.spring5-8080.BookProxy"></bean>
<aop:config>
<!--切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="p" expression="execution(* com.zy.spring5-8080.Book.buy(..))"/>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:aspect ref="bookProxy">
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="p"/> <!--将bookProxy中的before方法配置为切入点的前置通知-->
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
事务管理
事务是数据库操作最基本单元,逻辑上一组操作,要么都成功,如果有一个失败所有操作都失败
事务四个特性(ACID)
(1)原子性 (要没成功要么失败)
(2)一致性 (数据保持一致)
(3)隔离性 (互相不干扰)
(4)持久性
事务操作
事务添加到 JavaEE 三层结构里面 Service 层(业务逻辑层)
在 Spring 进行事务管理操作
有两种方式:编程式事务管理和声明式事务管理(使用)
声明式事务管理
(1)基于注解方式(使用)
(2)基于 xml 配置文件方式
在 Spring 进行声明式事务管理,底层使用 AOP 原理
Spring 事务管理 API
提供一个接口,代表事务管理器,这个接口针对不同的框架提供不同的实现类
注解声明式事务管理
- 配置事务管理器
<!--创建事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!--注入数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
- 开启事务注解 - 引入名称空间
tx
<!--开启事务注解-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven>
- 使用
@Transactionl
在 service 类上面(或者 service 类里面方法上面)添加事务注解
(1)@Transactional,这个注解添加到类上面,也可以添加方法上面
(2)如果把这个注解添加类上面,这个类里面所有的方法都添加事务
(3)如果把这个注解添加方法上面,为这个方法添加事务
@Service
@Transactional
public class UserService {
声明式事务管理的参数配置
- propagation:事务传播行为,总共有7种
- isolation:事务隔离级别
有三个读问题:脏读,不可重复读,虚读(幻读)- 脏读:一个未提交事务读取到另一个未提交事务的数据(事件回滚,导致A读取B还未提交的事务,应该读取原始数据)
- 不可重复读:一个未提交的事务,获取到了一个已经提交修改的事务(A读取B提交的事务,正常来说都提交了才能读取)
- 幻读:一个未提交的数据获取到了另一个事务添加数据
设置隔离级别,解决读问题
级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 虚读
-------- | ----- | ------ | ------ | -------
READ UNCOMMITED(读未提交) | 有 | 有 | 有
READ COMMITED(读已提交) | 无 | 有 | 有
REPEATABLE READ(可重复读) | 无 | 无 | 有
SERIALIZABLE(串行化) | 无 | 无| 无
- timeout:超时时间
- 事务需要在一定时间内进行提交,超过时间后回滚
- 默认值是-1,设置时间以秒为单位
- readOnly:是否只读
- 默认值为false,表示可以查询,也可以增删改
- 设置为true,只能查询
- rollbackFor:回滚,设置出现哪些异常进行事务回滚
- noRollbackFor:不回滚,设置出现哪些异常不进行事务回滚
@Service
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED)
public class AccountService {
完全注解实现声明式事务管理
- 配置类
@Configuration //配置类
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.zy.spring5-8080") //开启组件扫描
@EnableTransactionManagement //开启事务
public class Config {
//创建数据库连接池
@Bean
public DruidDataSource getDruidDataSource(){
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
druidDataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
druidDataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/study");
druidDataSource.setUsername("root");
druidDataSource.setPassword("root");
return druidDataSource;
}
//创建JdbcTemplate对象
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource){
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
return jdbcTemplate;
}
//创建事务管理器
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager getDataSourceTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
}
xml 实现声明式事务管理
- 配置数据库信息
<!-- 组件扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zy"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 数据库连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://study" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="root" />
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
</bean>
<!-- JdbcTemplate对象 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!--注入 dataSource 数据库连接池 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
- 配置事务管理器
<!--1 创建事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!--注入数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
- 配置通知
<!--2 配置通知-->
<tx:advice id="txadvice">
<!--配置事务参数-->
<tx:attributes>
<!--指定哪种规则的方法上面添加事务-->
<tx:method name="accountMoney" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<!--<tx:method name="account*"/>-->
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
- 配置切入点和切面
<!--3 配置切入点和切面-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="execution(* com.zy.spring5-8080.service.UserService.*(..))"/>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txadvice" pointcut-ref="pt"/>
</aop:config>
配置切入点 切入面id要一样吻合,expression表明函数的位置以及方法
切面的ref是事务的通知,两者衔接在一起
Spring5新特性
日志封装
Spring5移除了
Log4jConfigListener,官方建议使用Log4j2
整合 Log4j2
- 引入 jar 包

- 创建
log4j2.xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--日志级别以及优先级排序: OFF > FATAL > ERROR > WARN > INFO > DEBUG > TRACE > ALL -->
<!--Configuration后面的status用于设置log4j2自身内部的信息输出,可以不设置,当设置成trace时,可以看到log4j2内部各种详细输出-->
<configuration status="INFO">
<!--先定义所有的appender-->
<appenders>
<!--输出日志信息到控制台-->
<console name="Console" target="SYSTEM_OUT">
<!--控制日志输出的格式-->
<PatternLayout pattern="%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%t] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n"/>
</console>
</appenders>
<!--然后定义logger,只有定义了logger并引入的appender,appender才会生效-->
<!--root:用于指定项目的根日志,如果没有单独指定Logger,则会使用root作为默认的日志输出-->
<loggers>
<root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="Console"/>
</root>
</loggers>
</configuration>
@Nullable 注解
@Nullable注解可以用在方法上,属性上,参数上,表示方法返回值可以为空,属性可以为空,参数可以为空
@Nullable //表示方法返回值可以为空
public int getId();
@Nullable //表示参数可以为空
public void setId(@Nullable int Id);
@Nullable //表示属性可以为空
public int id;
支持函数式风格编程
由于
java 8新增了lamda表达式
@Test
public void test() {
//1 创建 GenericApplicationContext 对象
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
//2 调用 context 的方法对象注册
context.refresh();
context.registerBean("user1",User.class,() -> new User());
//3 获取在 spring 注册的对象
// User user = (User)context.getBean("com.zy.spring5-8080.test.User");
User user = (User)context.getBean("user1");
System.out.println(user);
}
整合JUnit5
- 整合
JUnit5, 引入 jar 包
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.quarkus/quarkus-junit5 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.quarkus</groupId>
<artifactId>quarkus-junit5</artifactId>
<version>2.6.1.Final</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
- 测试
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:bean4.xml")
public class JUnit5Test {
@Autowired
public User user;
@Test
public void test(){
System.out.println(user);
}
}
// 使用一个复合注解代替上述两个
@SpringJUnitConfig(locations = "classpath:bean1.xml")
public class JUnit5Test {
@Autowired
public User user;
@Test
public void test(){
System.out.println(user);
}
}























 1080
1080











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










