在学习数据结构与算法分析过程中,便于使用的ArrayList类的实现是个很好的练手项目,本博文将提供详细的代码,给出一个便于使用的ArrayList泛型类的实现。
为了避免与类库中的类相混淆,我们将其命名为MyArrayList。由于程序较长,也相对简单,不太想逐段分析,我们先将几个注意点指出,后面放出整段程序。
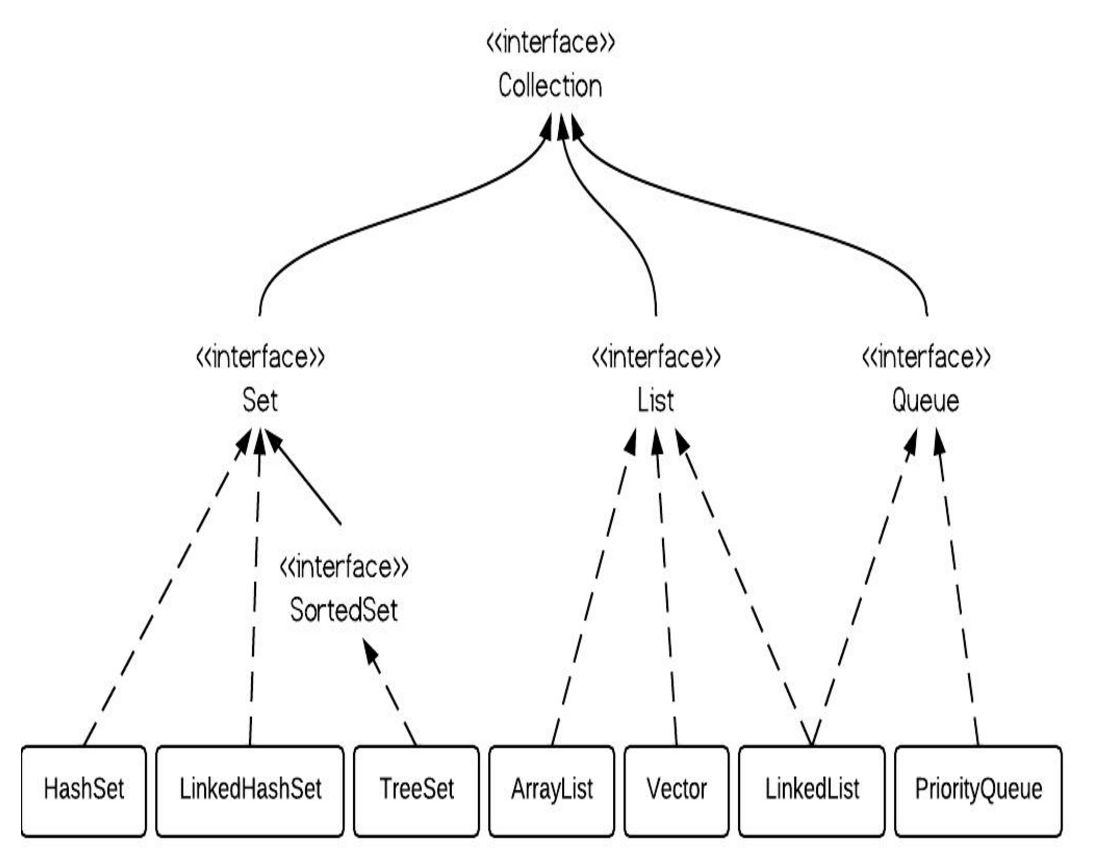
(1)首先,注意Collection和Collections是完全不同的两个概念。
java.util.Collections 是一个包装类(工具类/帮助类)。它包含有各种有关集合操作的静态多态方法。此类不能实例化,就像一个工具类,用于对集合中元素进行排序、搜索以及线程安全等各种操作,服务于Java的Collection框架。
java.util.Collection 是一个集合接口(集合类的一个顶级接口)。它提供了对集合对象进行基本操作的通用接口方法。Collection接口在Java 类库中有很多具体的实现。Collection接口的意义是为各种具体的集合提供了最大化的统一操作方式,其直接继承接口有List与Set。
下面是Collection接口的层次结构:
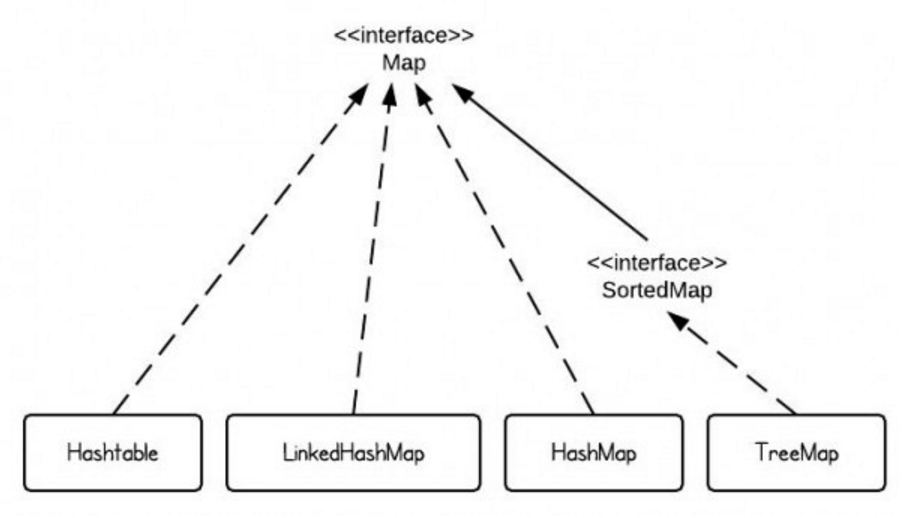
顺便看下Map接口的层次结构:
(2)在ArrayList中有一个容量的概念,表示基础数组的大小,用ensureCapacity进行控制,对应数组的length属性,注意这个容量和表的大小不是一个概念,即size()方法返回的私有域theSize。从我们的例程可以看出,总是要求容量大于等于表的大小。
好,下面是MyArrayList的实现,注意肯定和类库中的ArrayList是有点区别的,主要用于理解数据结构
// Build a ArrayList based on P46 of DSAA
public class MyArrayList<AnyType> implements Iterable<AnyType>
{
//@ Fields
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
private int theSize;
private AnyType[] theItems;
//@ Constructors
public MyArrayList()
{
doClear();
}
//@ Methods
// Returns the number of items in this collection.
public int size()
{
return theSize;
}
// Returns true if the collection is empty
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return size()==0;
}
// Returns the item at position idx
public AnyType get(int idx)
{
if(idx<0 || idx>=size())
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException("Index " + idx + "; size " + size())
return theItems[idx];
}
// Changes the item at position idx
public AnyType set(int idx, AnyType newVal)
{
if(idx<0 || idx>=size()
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException("Index " + idx + "; size " + size())
AnyType oldVal = theItems[idx];
theItems[idx] = newVal;
return oldVal;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void ensureCapacity(int newCapacity)
{
if(newCapacity<theSize)
return;
AnyType[] old = theItems;
// the warning here should be suppressed
theItems = (AnyType[]) new Object[newCapacity];
for(int i=0; i<size(); i++)
theItems[i] = old[i];
}
// Adds an item to this collection at the end
public boolean add(AnyType x)
{
add(size(),x);
return true;
}
// Adds an item to this collection at the specified index
public void add(int idx, AnyType x)
{
if(theItems.length == size())
ensureCapacity(size()*2+1);
for (int i=theSize; i>idx; i--)
theItems[i] = theItems[i-1];
theItems[idx] = x;
theSize++;
}
// Removes an item from this collection
public AnyType remove(int idx)
{
AnyType removedItem = theItems[idx];
for (int i=idx; i<size()-1; i++)
theItems[i] = theItems[i+1];
theSize--;
return removedItem;
}
// Changes the size of the collection to zero
public void clear()
{
doClear();
}
private void doClear()
{
theSize = 0;
ensureCapacity(DEFAULT_CAPACITY);
}
// Obtains an Iterator object used to traverse the collection
public java.util.Iterator<AnyType> iterator()
{
return new ArrayListIterator();
}
/**
* This is the implementation of the ArrayListIterator.
* It maintains a notion of a current position and
* the implicit reference to the MyArrayList.
**/
private class ArrayListIterator implements java.util.Iterator<AnyType>
{
private int current = 0;
private boolean okToRemove = false;
public boolean hasNest()
{
return current<size();
}
public AnyType next()
{
if(!hasNext())
throw new java.util.NoSuchElementException();
okToRemove = true;
return theItems[current++];
}
public void remove()
{
if(!okToRemove)
throw new IllegalStateException();
MyArrayList.this.remove(--current);
okToRemove = false;
}
}
// Returns a String representation of this collection
public String toString()
{
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
for(AnyType x: this)
sb.append(x+" ");
sb.append("]");
return new String(sb);
}
}





















 4597
4597

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








