请关注微信公众号:拾荒的小海螺
博客地址:http://lsk-ww.cn/
1、简述
链表是一种常见的数据结构,它通过一系列节点(Node)来表示一个序列。每个节点包含数据和指向下一个节点的引用。链表的种类有很多,包括单向链表、双端链表、有序链表和双向链表。本文将介绍这些链表的基本概念和 Java 实现。
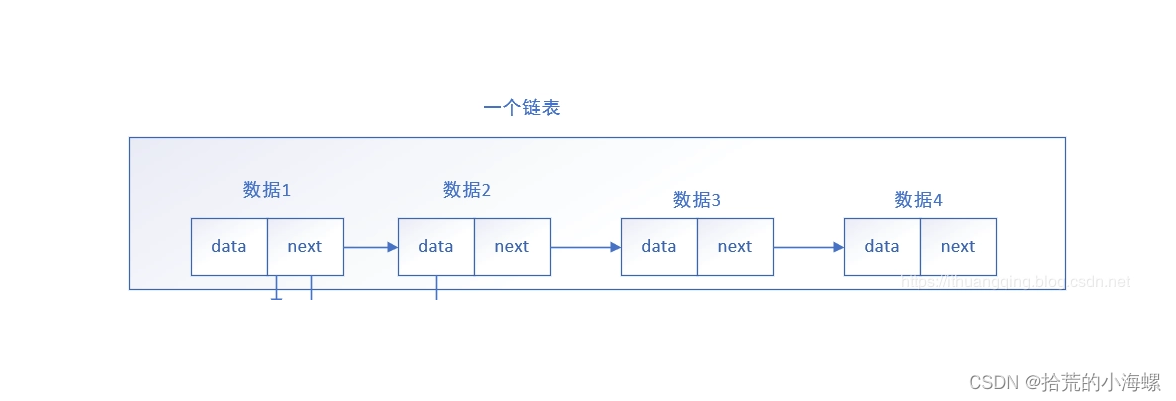
2、单向链表(Singly Linked List)
单向链表是一种最基本的链表结构,每个节点只包含一个指向下一个节点的引用。链表的第一个节点称为头节点(head),最后一个节点的下一个引用指向 null,以下是单向链表的实例:
class SinglyLinkedList {
private Node head;
private static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
public void add(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
} else {
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode;
}
}
public void printList() {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SinglyLinkedList list = new SinglyLinkedList();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.printList(); // 输出: 1 2 3
}
}
3、双端链表(Doubly Ended Linked List)
双端链表是一个扩展的单向链表,它在链表中维护对最后一个节点(尾节点)的引用,以便于在链表末尾进行快速插入操作,以下是双端链表的实例:
class DoublyEndedLinkedList {
private Node head;
private Node tail;
private static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
public void addLast(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (tail == null) {
head = tail = newNode;
} else {
tail.next = newNode;
tail = newNode;
}
}
public void printList() {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyEndedLinkedList list = new DoublyEndedLinkedList();
list.addLast(1);
list.addLast(2);
list.addLast(3);
list.printList(); // 输出: 1 2 3
}
}
4、有序链表(Sorted Linked List)
有序链表是一种链表,其中元素按升序排列。每次插入新元素时,链表会自动将其插入到正确的位置以保持顺序,以下是有序链表的实例:
class SortedLinkedList {
private Node head;
private static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
public void add(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null || head.data >= newNode.data) {
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
} else {
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null && current.next.data < newNode.data) {
current = current.next;
}
newNode.next = current.next;
current.next = newNode;
}
}
public void printList() {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortedLinkedList list = new SortedLinkedList();
list.add(3);
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.printList(); // 输出: 1 2 3
}
}
5、双向链表(Doubly Linked List)
双向链表是一种链表,其中每个节点包含指向前一个节点和后一个节点的引用。这使得在链表中可以向前和向后遍历,以下是双向链表的实例:
class DoublyLinkedList {
private Node head;
private Node tail;
private static class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
}
public void add(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = tail = newNode;
} else {
tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = tail;
tail = newNode;
}
}
public void printList() {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
}
}
public void printListReverse() {
Node current = tail;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " ");
current = current.prev;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList list = new DoublyLinkedList();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.printList(); // 输出: 1 2 3
System.out.println();
list.printListReverse(); // 输出: 3 2 1
}
}
6、总结
本文介绍了四种常见的链表及其 Java 实现:单向链表、双端链表、有序链表和双向链表。每种链表都有其独特的特点和应用场景。单向链表结构简单,适合于基础数据存储;双端链表适合于需要快速在末尾插入的场景;有序链表适用于需要保持顺序的数据集合;双向链表则适合于需要双向遍历的复杂应用。通过这些示例,希望您能更好地理解链表结构及其在 Java 中的实现。























 1715
1715











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










