1. 数据结构
参考博客数据结构
map概述
map的数据结构为key(键)和value(值)键值对的模式。内部原理是基于数组与单向链表的。其操作是对数组和单向链表进行增加、删除、修改、遍历。
HashMap和Hashtable不同之处在于Hashtable允许key或者value为空,再者Hashtable是线程安全的。
2. hashMap结构图(哈希表)
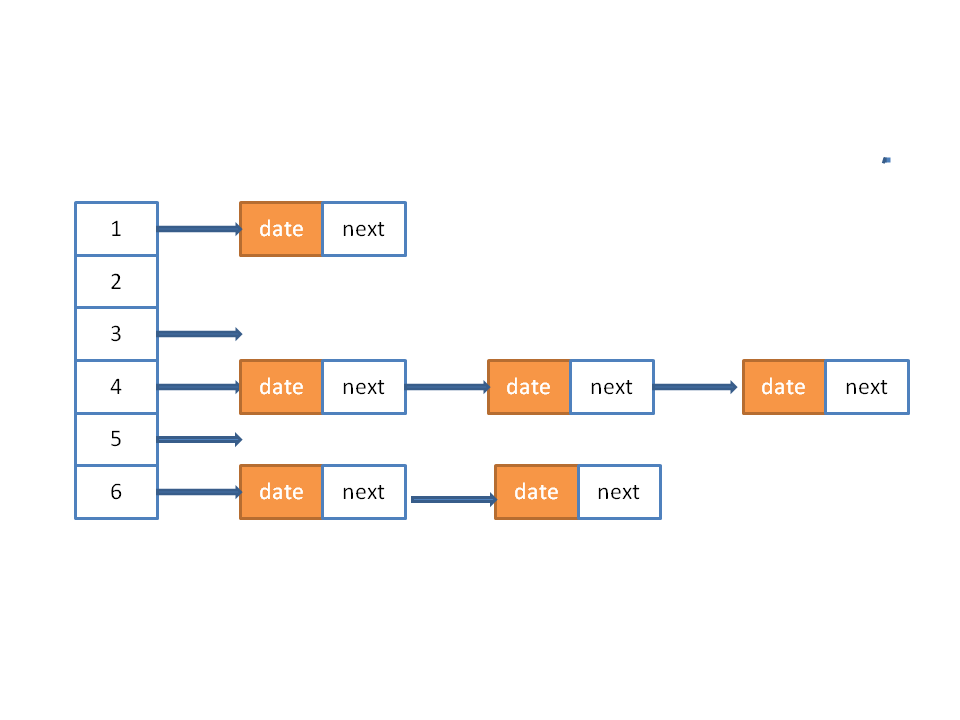
纵向为数组、横向为单向链表
使用场景
1、需要线程安全的,请使用Hashtable。
2、允许key或者value为空请使用Hashtable。
3、追求程序性能的,是使用HahsMap
3. HashMap源码分析
了解源码之前,请先学习一下数据结构中的哈希表以及算列法。
数组的特点是:寻址容易,插入和删除困难;而链表的特点是:寻址困难,插入和删除容易。那么我们能不能综合两者的特性,做出一种寻址容易,插入删除也容易的数据结构?答案是肯定的,这就是我们要提起的哈希表,哈希表有多种不同的实现方法,我接下来解释的是最常用的一种方法——拉链法,我们可以理解为“链表的数组。
HashMap无惨构造方法
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity
* (16) and the default load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashMap() {
//loadFactor 负载因子默认为 0.75f
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
//threshold 临界值 = 默认初始容量 * 负载因子
threshold = (int)(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
//默认初始容量(16)
table = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];
init();
}从源码获取HashMap的容器容量大小为16, 扩容的临界值为12。
hashMap的put方法
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
//key可以为空
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
//取得key的hashCode
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
//取得元素在数组中的位置或者是内存中的位置
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//解决hash冲突,新插入的元素的数组位置如果已经被其他元素占用了,那么就使用单向链表。占用的元素链表下一个指向新插入的元素
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
//修改记录统计
modCount++;
//hash不冲突,新元素则添加到指定的数组位置
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}根据散列法获取数组的位置
/**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
//等同于h%length,但是不等效。h%length需要调用cpu计算。效率更低
return h & (length-1);
}HashMap数组扩容
/**
* Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to
* the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this
* method to resize the table if appropriate.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method.
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
//在指定的数组下标位置添加新元素
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
//判断添加元素后的容器容量大于临界值。则需要数组扩容
if (size++ >= threshold)
//扩容的容器容量= 2 * 数组长度
resize(2 * table.length);
}
/**
* Rehashes the contents of this map into a new array with a
* larger capacity. This method is called automatically when the
* number of keys in this map reaches its threshold.
*
* If current capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY, this method does not
* resize the map, but sets threshold to Integer.MAX_VALUE.
* This has the effect of preventing future calls.
*
* @param newCapacity the new capacity, MUST be a power of two;
* must be greater than current capacity unless current
* capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY (in which case value
* is irrelevant).
*/
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
//扩容后新的数组
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
//将旧的数据内容copy扩容后新的数组
transfer(newTable);
table = newTable;
//重新计算临界值 = 数组长度 * 负载因子
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
}4. map优化点
1、负载因子本身就是在空间和时间之间的折衷。当我使用较小的负载因子时,虽然降低了冲突的可能性,使得单个链表的长度减小了,加快了访问和更新的速度,但是它占用了更多的空间,使得数组中的大部分空间没有得到利用,元素分布比较稀疏,同时由于Map频繁的调整大小,可能会降低性能。但是如果负载因子过大,会使得元素分布比较紧凑,导致产生冲突的可能性加大,从而访问、更新速度较慢。所以我们一般推荐不更改负载因子的值,采用默认值0.75.
HashMap优化代码
暂无,后续添加
























 216
216

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








