策略模式:
将动作等变化的东西抽离出来变成行为。这样具体的不变化的事物中会有行为的接口引用,当具体调用的时候可以动态设置他的接口实现类从而动态的改变行为。
要点:
封装变化;多用组合,少用继承;针对接口(不单单是接口可以包含抽象类等)编程,不针对实现编程。
编写排序类DataSorter:
为了测试,我们编写Cat类,在Cat类中继承Comparable接口重写compareTo方法:
编写Cat类的比较器类CatHeightComparator:
最后是测试类Test:
将动作等变化的东西抽离出来变成行为。这样具体的不变化的事物中会有行为的接口引用,当具体调用的时候可以动态设置他的接口实现类从而动态的改变行为。
要点:
封装变化;多用组合,少用继承;针对接口(不单单是接口可以包含抽象类等)编程,不针对实现编程。
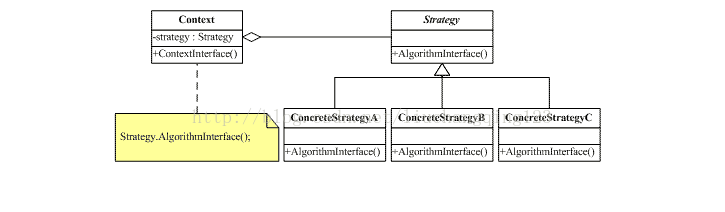
类图:
把会变化的内容取出并封装起来,以便以后可以轻易地改动或扩充部分,而不影响不需要变化的其他部分;
Java是面向对象的语言,所以利用面向对象的思维去编写程序实现功能,重要的一点莫过于使用Java的封装和多态的概念。以下是编写的是实现排序功能的类,在排序类DataSorter中的排序的方法对于不同的场合,其排序的规则是不同的,所以将排序规则进行抽象,抽象出Comparable接口。在对不同的对象进行排序时,该对象必须继承Comparable接口,并且重写compareTo()方法,这样在对该对象进行排序时,就可以依照提供的比较规则进行排序。同样在抽象出Comparable接口之后我们会发现在重写compareTo()方法时,其中的代码也是比较固定的,这样如果有多种比较规则就会显得耦合度较高,所以我们也可以抽象出比较器comparator接口,这样就会大大提高程序的灵活性。以上便是我们解决对不同的对象进行排序的思路。
在以上的分析中我们可以看到我们将对象比较的方法和比较的规则进行了封装和抽象,使之变成一个接口,这样在具体的实现时分别编写不同的实现,而排序方法中则不用变化,从而将对其的影响降到最低,达到了比较好的效果。
首先编写Comparable接口:
package com.lcq.strategy;
/**
* 创建比较接口
* @author lcq
*
*/
public interface Comparable {
public int compareTo(Object o);
}
package com.lcq.strategy;
public interface Comparator {
int compare(Object o1, Object o2);
}
编写排序类DataSorter:
package com.lcq.strategy;
public class DataSorter {
/**
* 编写冒泡排序方法
*
* @param a
*/
public static void sort(int[] a) {
for (int i = a.length; i > 0; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j < i - 1; j++) {
if (a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
swap(a, j, j + 1);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 交换两个数的值
*
* @param a
* @param x
* @param y
*/
private static void swap(int[] a, int x, int y) {
int temp;
temp = a[x];
a[x] = a[y];
a[y] = temp;
}
/**
* 打印出数组的值
*
* @param a
*/
public static void print(int[] a) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
}
/**
* 打印出数组的值
*
* @param a
*/
public static void print(Object[] a) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
}
/**
* 编写可以对任意对象进行排序的方法
* @param a
*/
public static void sort(Object[] a) {
for (int i = a.length; i > 0; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j < i - 1; j++) {
Comparable o1 = (Comparable) a[j];
Comparable o2 = (Comparable) a[j + 1];
if (o1.compareTo(o2) == 1) {
swap(a, j, j + 1);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 交换任意对象
* @param a
* @param x
* @param y
*/
private static void swap(Object[] a, int x, int y) {
Object temp;
temp = a[x];
a[x] = a[y];
a[y] = temp;
}
}
为了测试,我们编写Cat类,在Cat类中继承Comparable接口重写compareTo方法:
package com.lcq.strategy;
/**
* 创建测试的工具类,并且继承Comparable接口,实现compareTo方法
*
* @author lcq
*
*/
public class Cat implements Comparable {
private int height;
private int weight;
private Comparator comparator = new CatHeightComparator();
public Comparator getComparator() {
return comparator;
}
public void setComparator(Comparator comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
public Cat(int height, int weight) {
super();
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.getHeight() + "|" + this.getWeight();
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
// if (o instanceof Cat) {
// Cat c = (Cat) o;
// if (this.getHeight() > c.getHeight())
// return 1;
// else if (this.getHeight() < c.getHeight())
// return -1;
// else
// return 0;
// }
// return -100;
return this.comparator.compare(this, o);
}
}
编写Cat类的比较器类CatHeightComparator:
package com.lcq.strategy;
public class CatHeightComparator implements Comparator {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
Cat c1 = (Cat)o1;
Cat c2 = (Cat)o2;
if(c1.getHeight() > c2.getHeight()) return 1;
else if(c1.getHeight() < c2.getHeight()) return -1;
return 0;
}
}
最后是测试类Test:
package com.lcq.strategy;
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int[] a = {4,5,9,2,3,7};
Cat[] a = {new Cat(1,1),new Cat(4,4),new Cat(2,2)};
DataSorter.sort(a);
DataSorter.print(a);
}
}
























 8615
8615

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








