import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
e0 = 1
e1 = 1
e2 = 1
alpha = 0.01
theta0 = np.random.uniform(0, 1)
theta1 = np.random.uniform(0, 1)
theta2 = np.random.uniform(0, 1)
theta = np.array([theta1, theta2])
eps = 1e-4
x = np.array([[2, 3], [4, 6], [7, 8], [12, 15]])
t = np.array([5, 8, 14, 17])
cnt = 0 # 迭代次数
while (abs(e0) >= eps or abs(e1) >= eps or abs(e2) >= eps): # 这里用绝对值小于eps进行判定 如果不用绝对值的话如果有数据小于0的话会直接跳出循环
cnt += 1
i = np.random.randint(0,4) #随机一个整数作为本次的训练数据
e0 = (np.sum((x[i] * theta)) + theta0 * 1 - t[i])
e1 = (np.sum((x[i] * theta)) + theta0 * 1 - t[i]) * x[i][0]
e2 = (np.sum((x[i] * theta)) + theta0 * 1 - t[i]) * x[i][1]
i = np.random.randint(0,4)
e0 += (np.sum((x[i] * theta)) + theta0 * 1 - t[i])
e1 += (np.sum((x[i] * theta)) + theta0 * 1 - t[i]) * x[i][0]
e2 += (np.sum((x[i] * theta)) + theta0 * 1 - t[i]) * x[i][1]
# 上面是求导公式
e0 /= 5
e1 /= 5
e2 /= 5
theta0 = theta0 - alpha * e0 # 公式
theta1 = theta1 - alpha * e1
theta2 = theta2 - alpha * e2
theta = np.array([theta1, theta2]) # 每次都要对theta进行更新以便进行下次迭代
print(cnt)
print(theta0, theta1, theta2)
# 至此我们已经得到了三个常数的近似值 下面绘制3D图
fig = plt.figure()
ax = Axes3D(fig)
a = np.arange(0, 20) # 设置两个坐标轴的长度
b = np.arange(0, 20)
A, B = np.meshgrid(a, b) # 生成网络格
Z = theta0 + theta1 * A + theta2 * B # 把得到的theta值带入h(x)函数
plt.xlabel('x1')
plt.ylabel('x2')
ax.plot_surface(A, B, Z, rstride=3, cstride=3, cmap='rainbow') # 设置跨度为3 映射颜色为彩虹色
plt.show()
得到的结果
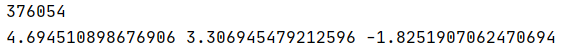
生成的图























 496
496











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








