现代智能手机,基本上都有指纹解锁功能,那他是怎么实现的哦?下面从代码角度来分析下他。
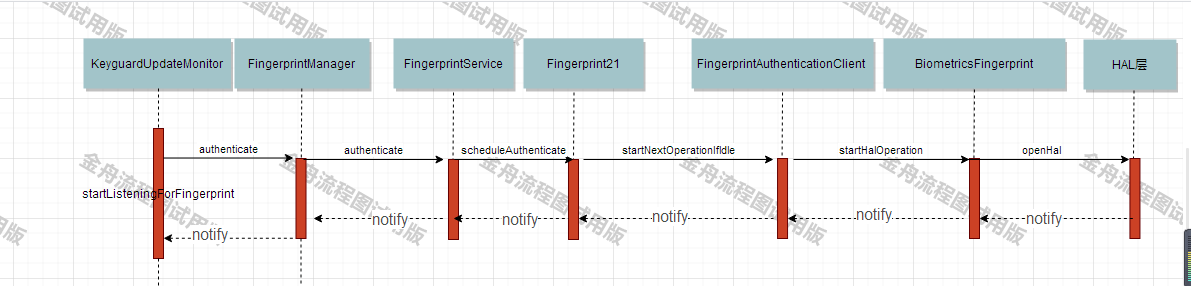
先上流程图
此图是一个指纹注册流程图,以及指纹设别后,如何通知到上层的
既然指纹设别后,要通知到上层,那肯定事先要把相关回调接口对象注册进去。流程图大概如下

指纹解锁,首先要录入(这个有其他博客分析过了),然后指纹服务注册,下面看看如何注册的?
一般从KeyguardUpdate.java类中发起注册的
KeyguardUpdateMonitor.java文件
private void startListeningForFingerprint() {
final int userId = getCurrentUser();
final boolean unlockPossible = isUnlockWithFingerprintPossible(userId);
if (mFingerprintCancelSignal != null) {
Log.e(TAG, "Cancellation signal is not null, high chance of bug in fp auth lifecycle"
+ " management. FP state: " + mFingerprintRunningState
+ ", unlockPossible: " + unlockPossible);
}
if (mFingerprintRunningState == BIOMETRIC_STATE_CANCELLING) {
setFingerprintRunningState(BIOMETRIC_STATE_CANCELLING_RESTARTING);
return;
}
if (mFingerprintRunningState == BIOMETRIC_STATE_CANCELLING_RESTARTING) {
// Waiting for restart via handleFingerprintError().
return;
}
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "startListeningForFingerprint()");
if (unlockPossible) {
mFingerprintCancelSignal = new CancellationSignal();
if (isEncryptedOrLockdown(userId)) {
mFpm.detectFingerprint(mFingerprintCancelSignal, mFingerprintDetectionCallback,
userId);
} else {
mFpm.authenticate(null /* crypto */, mFingerprintCancelSignal,
mFingerprintAuthenticationCallback, null /* handler */,
FingerprintManager.SENSOR_ID_ANY, userId, 0 /* flags */);
}
setFingerprintRunningState(BIOMETRIC_STATE_RUNNING);
}
}第28行,mFingerprintAuthenticationCallback这个是个回调对象,其作用是把这个对象传递到FingerprintManager对象中,然后等待底层设别结果,回传过来
mFingerprintAuthenticationCallback具体代码如下,注意这个回调接口,不涉及到跨进程,所以,不需要继承stub
@VisibleForTesting
final FingerprintManager.AuthenticationCallback mFingerprintAuthenticationCallback
= new AuthenticationCallback() {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailed() {
handleFingerprintAuthFailed();
}
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSucceeded(AuthenticationResult result) {
Trace.beginSection("KeyguardUpdateMonitor#onAuthenticationSucceeded");
handleFingerprintAuthenticated(result.getUserId(), result.isStrongBiometric());
Trace.endSection();
}
@Override
public void onAuthenticationHelp(int helpMsgId, CharSequence helpString) {
handleFingerprintHelp(helpMsgId, helpString.toString());
}
@Override
public void onAuthenticationError(int errMsgId, CharSequence errString) {
handleFingerprintError(errMsgId, errString.toString());
}
@Override
public void onAuthenticationAcquired(int acquireInfo) {
handleFingerprintAcquired(acquireInfo);
}
@Override
public void onUdfpsPointerDown(int sensorId) {
Log.d(TAG, "onUdfpsPointerDown, sensorId: " + sensorId);
}
@Override
public void onUdfpsPointerUp(int sensorId) {
Log.d(TAG, "onUdfpsPointerUp, sensorId: " + sensorId);
}
};
回到KeyguardUpdateMonitor#startListeningForFingerprint方法的第27行,如下部分
mFpm.authenticate(null /* crypto */, mFingerprintCancelSignal,
mFingerprintAuthenticationCallback, null /* handler */,
FingerprintManager.SENSOR_ID_ANY, userId, 0 /* flags */);
这行代码调用到FingerprintManager#authenticate
/**
* Per-user and per-sensor version of authenticate.
* @hide
*/
@RequiresPermission(anyOf = {USE_BIOMETRIC, USE_FINGERPRINT})
public void authenticate(@Nullable CryptoObject crypto, @Nullable CancellationSignal cancel,
@NonNull AuthenticationCallback callback, Handler handler, int sensorId, int userId,
int flags) {
FrameworkStatsLog.write(FrameworkStatsLog.AUTH_DEPRECATED_API_USED,
AUTH_DEPRECATED_APIUSED__DEPRECATED_API__API_FINGERPRINT_MANAGER_AUTHENTICATE,
mContext.getApplicationInfo().uid,
mContext.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion);
if (callback == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Must supply an authentication callback");
}
if (cancel != null && cancel.isCanceled()) {
Slog.w(TAG, "authentication already canceled");
return;
}
final boolean ignoreEnrollmentState = flags == 0 ? false : true;
if (mService != null) {
try {
useHandler(handler);
mAuthenticationCallback = callback;
mCryptoObject = crypto;
final long operationId = crypto != null ? crypto.getOpId() : 0;
final long authId = mService.authenticate(mToken, operationId, sensorId, userId,
mServiceReceiver, mContext.getOpPackageName(), ignoreEnrollmentState);
if (cancel != null) {
cancel.setOnCancelListener(new OnAuthenticationCancelListener(authId));
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Remote exception while authenticating: ", e);
// Though this may not be a hardware issue, it will cause apps to give up or try
// again later.
callback.onAuthenticationError(FINGERPRINT_ERROR_HW_UNAVAILABLE,
getErrorString(mContext, FINGERPRINT_ERROR_HW_UNAVAILABLE,
0 /* vendorCode */));
}
}
}第29行,mAuthenticationCallback = callback 这个地方很重要,后面指纹设别结果,最终会回调到这里,然后告知给上层用户。
第32行,mService对象实例对象是在哪儿实现的?看下面代码
registerService(Context.FINGERPRINT_SERVICE, FingerprintManager.class,
new CachedServiceFetcher<FingerprintManager>() {
@Override
public FingerprintManager createService(ContextImpl ctx) throws ServiceNotFoundException {
final IBinder binder;
if (ctx.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
binder = ServiceManager.getServiceOrThrow(Context.FINGERPRINT_SERVICE);
} else {
binder = ServiceManager.getService(Context.FINGERPRINT_SERVICE);
}
IFingerprintService service = IFingerprintService.Stub.asInterface(binder);
return new FingerprintManager(ctx.getOuterContext(), service);
}});在第11行实现的,他最终会跨进程调用到FingerprintService.java的相关方法 。
再看第12行,把远程对象FingerprintService实例和系统服务对象FingerprintManager进行绑定。
然后在FingerprintManager#authenticate方法中,就可以使用了mService变量了,调用到FingerprintService#authenticate方法,如下
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
@Override // Binder call
public long authenticate(final IBinder token, final long operationId,
final int sensorId, final int userId, final IFingerprintServiceReceiver receiver,
final String opPackageName, boolean ignoreEnrollmentState) {
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUserId = UserHandle.getCallingUserId();
if (!canUseFingerprint(opPackageName, true /* requireForeground */, callingUid,
callingPid, callingUserId)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Authenticate rejecting package: " + opPackageName);
return -1;
}
// Keyguard check must be done on the caller's binder identity, since it also checks
// permission.
final boolean isKeyguard = Utils.isKeyguard(getContext(), opPackageName);
// Clear calling identity when checking LockPatternUtils for StrongAuth flags.
long identity = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (isKeyguard && Utils.isUserEncryptedOrLockdown(mLockPatternUtils, userId)) {
// If this happens, something in KeyguardUpdateMonitor is wrong.
// SafetyNet for b/79776455
EventLog.writeEvent(0x534e4554, "79776455");
Slog.e(TAG, "Authenticate invoked when user is encrypted or lockdown");
return -1;
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(identity);
}
final boolean restricted = getContext().checkCallingPermission(MANAGE_FINGERPRINT)
!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED;
final int statsClient = isKeyguard ? BiometricsProtoEnums.CLIENT_KEYGUARD
: BiometricsProtoEnums.CLIENT_FINGERPRINT_MANAGER;
final Pair<Integer, ServiceProvider> provider;
if (sensorId == FingerprintManager.SENSOR_ID_ANY) {
provider = getSingleProvider();
} else {
Utils.checkPermission(getContext(), USE_BIOMETRIC_INTERNAL);
provider = new Pair<>(sensorId, getProviderForSensor(sensorId));
}
if (provider == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Null provider for authenticate");
return -1;
}
final FingerprintSensorPropertiesInternal sensorProps =
provider.second.getSensorProperties(sensorId);
if (!isKeyguard && !Utils.isSettings(getContext(), opPackageName)
&& sensorProps != null && sensorProps.isAnyUdfpsType()) {
identity = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
return authenticateWithPrompt(operationId, sensorProps, userId, receiver,
ignoreEnrollmentState);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(identity);
}
}
return provider.second.scheduleAuthenticate(provider.first, token, operationId, userId,
0 /* cookie */, new ClientMonitorCallbackConverter(receiver), opPackageName,
restricted, statsClient, isKeyguard);
}注意代码第63行,provider.second实际上就是Fingerprint21对象实例,(生物解锁--指纹服务注册流程_liujun3512159的博客-CSDN博客)
另外参数
new ClientMonitorCallbackConverter(receiver)也是很重要的,后面会分析到
往下看Fingerprint21#scheduleAuthenticate
@Override
public void scheduleAuthenticate(int sensorId, @NonNull IBinder token, long operationId,
int userId, int cookie, @NonNull ClientMonitorCallbackConverter listener,
@NonNull String opPackageName, long requestId, boolean restricted, int statsClient,
boolean allowBackgroundAuthentication) {
mHandler.post(() -> {
scheduleUpdateActiveUserWithoutHandler(userId);
final boolean isStrongBiometric = Utils.isStrongBiometric(mSensorProperties.sensorId);
final FingerprintAuthenticationClient client = new FingerprintAuthenticationClient(
mContext, mLazyDaemon, token, requestId, listener, userId, operationId,
restricted, opPackageName, cookie, false /* requireConfirmation */,
mSensorProperties.sensorId, isStrongBiometric, statsClient,
mTaskStackListener, mLockoutTracker,
mUdfpsOverlayController, mSidefpsController,
allowBackgroundAuthentication, mSensorProperties);
mScheduler.scheduleClientMonitor(client, mFingerprintStateCallback);
});
}第17行,mScheduler对象实例是从哪儿定义的,直接上代码,在FingerprintService下会调用的
Fingerprint21#newInstance
public static Fingerprint21 newInstance(@NonNull Context context,
@NonNull FingerprintStateCallback fingerprintStateCallback,
@NonNull FingerprintSensorPropertiesInternal sensorProps,
@NonNull LockoutResetDispatcher lockoutResetDispatcher,
@NonNull GestureAvailabilityDispatcher gestureAvailabilityDispatcher) {
final Handler handler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper());
final BiometricScheduler scheduler =
new BiometricScheduler(TAG,
BiometricScheduler.sensorTypeFromFingerprintProperties(sensorProps),
gestureAvailabilityDispatcher);
final HalResultController controller = new HalResultController(sensorProps.sensorId,
context, handler,
scheduler);
return new Fingerprint21(context, fingerprintStateCallback, sensorProps, scheduler, handler,
lockoutResetDispatcher, controller);
}通过第8行得知,
mScheduler.scheduleClientMonitor(client, mFingerprintStateCallback);调用到哪边了。
另外第11行的HalResultController也很重要,先记下来。
public void scheduleClientMonitor(@NonNull BaseClientMonitor clientMonitor,
@Nullable BaseClientMonitor.Callback clientCallback) {
// If the incoming operation should interrupt preceding clients, mark any interruptable
// pending clients as canceling. Once they reach the head of the queue, the scheduler will
// send ERROR_CANCELED and skip the operation.
if (clientMonitor.interruptsPrecedingClients()) {
for (Operation operation : mPendingOperations) {
if (operation.mClientMonitor instanceof Interruptable
&& operation.mState != Operation.STATE_WAITING_IN_QUEUE_CANCELING) {
Slog.d(getTag(), "New client incoming, marking pending client as canceling: "
+ operation.mClientMonitor);
operation.mState = Operation.STATE_WAITING_IN_QUEUE_CANCELING;
}
}
}
mPendingOperations.add(new Operation(clientMonitor, clientCallback));
Slog.d(getTag(), "[Added] " + clientMonitor
+ ", new queue size: " + mPendingOperations.size());
// If the new operation should interrupt preceding clients, and if the current operation is
// cancellable, start the cancellation process.
if (clientMonitor.interruptsPrecedingClients()
&& mCurrentOperation != null
&& mCurrentOperation.mClientMonitor instanceof Interruptable
&& mCurrentOperation.mState == Operation.STATE_STARTED) {
Slog.d(getTag(), "[Cancelling Interruptable]: " + mCurrentOperation);
cancelInternal(mCurrentOperation);
}
startNextOperationIfIdle();
}第31行代码,继续往下看
protected void startNextOperationIfIdle() {
if (mCurrentOperation != null) {
Slog.v(getTag(), "Not idle, current operation: " + mCurrentOperation);
return;
}
if (mPendingOperations.isEmpty()) {
Slog.d(getTag(), "No operations, returning to idle");
return;
}
mCurrentOperation = mPendingOperations.poll();
final BaseClientMonitor currentClient = mCurrentOperation.mClientMonitor;
Slog.d(getTag(), "[Polled] " + mCurrentOperation);
// If the operation at the front of the queue has been marked for cancellation, send
// ERROR_CANCELED. No need to start this client.
if (mCurrentOperation.mState == Operation.STATE_WAITING_IN_QUEUE_CANCELING) {
Slog.d(getTag(), "[Now Cancelling] " + mCurrentOperation);
if (!(currentClient instanceof Interruptable)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Mis-implemented client or scheduler, "
+ "trying to cancel non-interruptable operation: " + mCurrentOperation);
}
final Interruptable interruptable = (Interruptable) currentClient;
interruptable.cancelWithoutStarting(getInternalCallback());
// Now we wait for the client to send its FinishCallback, which kicks off the next
// operation.
return;
}
if (mGestureAvailabilityDispatcher != null
&& mCurrentOperation.mClientMonitor instanceof AcquisitionClient) {
mGestureAvailabilityDispatcher.markSensorActive(
mCurrentOperation.mClientMonitor.getSensorId(),
true /* active */);
}
// Not all operations start immediately. BiometricPrompt waits for its operation
// to arrive at the head of the queue, before pinging it to start.
final boolean shouldStartNow = currentClient.getCookie() == 0;
if (shouldStartNow) {
if (mCurrentOperation.isUnstartableHalOperation()) {
final HalClientMonitor<?> halClientMonitor =
(HalClientMonitor<?>) mCurrentOperation.mClientMonitor;
// Note down current length of queue
final int pendingOperationsLength = mPendingOperations.size();
final Operation lastOperation = mPendingOperations.peekLast();
Slog.e(getTag(), "[Unable To Start] " + mCurrentOperation
+ ". Last pending operation: " + lastOperation);
// For current operations, 1) unableToStart, which notifies the caller-side, then
// 2) notify operation's callback, to notify applicable system service that the
// operation failed.
halClientMonitor.unableToStart();
if (mCurrentOperation.mClientCallback != null) {
mCurrentOperation.mClientCallback.onClientFinished(
mCurrentOperation.mClientMonitor, false /* success */);
}
// Then for each operation currently in the pending queue at the time of this
// failure, do the same as above. Otherwise, it's possible that something like
// setActiveUser fails, but then authenticate (for the wrong user) is invoked.
for (int i = 0; i < pendingOperationsLength; i++) {
final Operation operation = mPendingOperations.pollFirst();
if (operation == null) {
Slog.e(getTag(), "Null operation, index: " + i
+ ", expected length: " + pendingOperationsLength);
break;
}
if (operation.isHalOperation()) {
((HalClientMonitor<?>) operation.mClientMonitor).unableToStart();
}
if (operation.mClientCallback != null) {
operation.mClientCallback.onClientFinished(operation.mClientMonitor,
false /* success */);
}
Slog.w(getTag(), "[Aborted Operation] " + operation);
}
// It's possible that during cleanup a new set of operations came in. We can try to
// run these. A single request from the manager layer to the service layer may
// actually be multiple operations (i.e. updateActiveUser + authenticate).
mCurrentOperation = null;
startNextOperationIfIdle();
} else {
Slog.d(getTag(), "[Starting] " + mCurrentOperation);
currentClient.start(getInternalCallback());
mCurrentOperation.mState = Operation.STATE_STARTED;
}
} else {
try {
mBiometricService.onReadyForAuthentication(currentClient.getCookie());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.e(getTag(), "Remote exception when contacting BiometricService", e);
}
Slog.d(getTag(), "Waiting for cookie before starting: " + mCurrentOperation);
mCurrentOperation.mState = Operation.STATE_WAITING_FOR_COOKIE;
}
}第87行currentClient.start(getInternalCallback());
currentClient 就是对象实例FingerprintAuthenticationClient
(见先前的代码mPendingOperations.add(new Operation(clientMonitor, clientCallback));)
public void start(@NonNull Callback callback) {
super.start(callback);
if (mSensorProps.isAnyUdfpsType()) {
// UDFPS requires user to touch before becoming "active"
mState = STATE_STARTED_PAUSED;
} else {
mState = STATE_STARTED;
}
}第2行代码super.start(callback); 继续往下看,找到AuthenticationClient 类下的start方法
@Override
public void start(@NonNull Callback callback) {
super.start(callback);
final @LockoutTracker.LockoutMode int lockoutMode =
mLockoutTracker.getLockoutModeForUser(getTargetUserId());
if (lockoutMode != LockoutTracker.LOCKOUT_NONE) {
Slog.v(TAG, "In lockout mode(" + lockoutMode + ") ; disallowing authentication");
int errorCode = lockoutMode == LockoutTracker.LOCKOUT_TIMED
? BiometricConstants.BIOMETRIC_ERROR_LOCKOUT
: BiometricConstants.BIOMETRIC_ERROR_LOCKOUT_PERMANENT;
onError(errorCode, 0 /* vendorCode */);
return;
}
if (mTaskStackListener != null) {
mActivityTaskManager.registerTaskStackListener(mTaskStackListener);
}
Slog.d(TAG, "Requesting auth for " + getOwnerString());
mStartTimeMs = System.currentTimeMillis();
mAuthAttempted = true;
startHalOperation();
}第24行startHalOperation(),实际上就是调用到FingerprintAuthenticationClient 类下的
@Override
protected void startHalOperation() {
mSensorOverlays.show(getSensorId(), getShowOverlayReason(), this);
try {
// GroupId was never used. In fact, groupId is always the same as userId.
getFreshDaemon().authenticate(mOperationId, getTargetUserId());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Remote exception when requesting auth", e);
onError(BiometricFingerprintConstants.FINGERPRINT_ERROR_HW_UNAVAILABLE,
0 /* vendorCode */);
mSensorOverlays.hide(getSensorId());
mCallback.onClientFinished(this, false /* success */);
}
}第7行,getFreshDaemon().authenticate 就是进行指纹服务注册,后面会继续分析相关底层。
继续往下分析getFreshDaemon()
//HalClientMonitor 文件
getFreshDaemon()
public T getFreshDaemon() {
//应该调用到Fingerprint21 类下的getDaemon方法
return mLazyDaemon.getDaemon();
}
//Fingerprint21 文件
mLazyDaemon = Fingerprint21.this::getDaemon;显然,要去Fingerprint21类下去找getDaemon
@VisibleForTesting
synchronized IBiometricsFingerprint getDaemon() {
if (mTestHalEnabled) {
final TestHal testHal = new TestHal(mContext, mSensorId);
testHal.setNotify(mHalResultController);
return testHal;
}
if (mDaemon != null) {
return mDaemon;
}
Slog.d(TAG, "Daemon was null, reconnecting, current operation: "
+ mScheduler.getCurrentClient());
try {
mDaemon = IBiometricsFingerprint.getService();
} catch (java.util.NoSuchElementException e) {
// Service doesn't exist or cannot be opened.
Slog.w(TAG, "NoSuchElementException", e);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failed to get fingerprint HAL", e);
}
if (mDaemon == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Fingerprint HAL not available");
return null;
}
mDaemon.asBinder().linkToDeath(this, 0 /* flags */);
// HAL ID for these HIDL versions are only used to determine if callbacks have been
// successfully set.
long halId = 0;
try {
halId = mDaemon.setNotify(mHalResultController);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failed to set callback for fingerprint HAL", e);
mDaemon = null;
}
Slog.d(TAG, "Fingerprint HAL ready, HAL ID: " + halId);
if (halId != 0) {
scheduleLoadAuthenticatorIds();
scheduleInternalCleanup(ActivityManager.getCurrentUser(), null /* callback */);
} else {
Slog.e(TAG, "Unable to set callback");
mDaemon = null;
}
return mDaemon;
}第16行,mDaemon = IBiometricsFingerprint.getService(),就是hidl调用获取到对应的对象。
IBiometricsFingerprint.getService() 最终的信息在BiometricsFingerprint.cpp中有描述
IBiometricsFingerprint.hal文件,这里就涉及到hal层的使用了。另外第35行,很重要,后面会分析。
直接看BiometricsFingerprint实例化方法中,有openHal(),会往hal层调用。
//BiometricsFingerprint.cpp 文件
BiometricsFingerprint::BiometricsFingerprint() : mClientCallback(nullptr), mDevice(nullptr) {
sInstance = this; // keep track of the most recent instance
mDevice = openHal();
if (!mDevice) {
ALOGE("Can't open HAL module");
}
}见第4行,调用openHal(),见代码
//这个方法最终会访问到底层了,比如我们熟悉的hw_get_module
fingerprint_device_t* BiometricsFingerprint::openHal() {
int err;
const hw_module_t *hw_mdl = nullptr;
ALOGD("Opening fingerprint hal library...");
if (0 != (err = hw_get_module(FINGERPRINT_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, &hw_mdl))) {
ALOGE("Can't open fingerprint HW Module, error: %d", err);
return nullptr;
}
if (hw_mdl == nullptr) {
ALOGE("No valid fingerprint module");
return nullptr;
}
fingerprint_module_t const *module =
reinterpret_cast<const fingerprint_module_t*>(hw_mdl);
if (module->common.methods->open == nullptr) {
ALOGE("No valid open method");
return nullptr;
}
hw_device_t *device = nullptr;
if (0 != (err = module->common.methods->open(hw_mdl, nullptr, &device))) {
ALOGE("Can't open fingerprint methods, error: %d", err);
return nullptr;
}
if (kVersion != device->version) {
// enforce version on new devices because of HIDL@2.1 translation layer
ALOGE("Wrong fp version. Expected %d, got %d", kVersion, device->version);
return nullptr;
}
fingerprint_device_t* fp_device =
reinterpret_cast<fingerprint_device_t*>(device);
if (0 != (err =
fp_device->set_notify(fp_device, BiometricsFingerprint::notify))) {
ALOGE("Can't register fingerprint module callback, error: %d", err);
return nullptr;
}
return fp_device;
}第25行,就是打开具体厂商指纹模组了。
第40行,设置回调到底软 ,其目的是指纹解锁后,信息往上回传,后面会分析的。
回到getFreshDaemon().authenticate ,实际上就是调用BiometricsFingerprint.cpp#authenticate
Return<RequestStatus> BiometricsFingerprint::authenticate(uint64_t operationId,
uint32_t gid) {
return ErrorFilter(mDevice->authenticate(mDevice, operationId, gid));
}第3行的mDevice就是具体厂商返回的。
搜索上文的module->common.methods->open ,在源码的第25行,会获取到具体厂商的device
这个open方法主要是将厂商指纹模组模块的算法识别逻辑结果和HAL层进行绑定(一般是fingerprint.default.so文件),设置回调通知,这个文件一般都不开源,不过Android原生也是有这部分代码的(当然只是看看,并不能使用)
例如,文件Fingerprint.c文件。
static int fingerprint_open(const hw_module_t* module, const char __unused *id,
hw_device_t** device)
{
if (device == NULL) {
ALOGE("NULL device on open");
return -EINVAL;
}
fingerprint_device_t *dev = malloc(sizeof(fingerprint_device_t));
memset(dev, 0, sizeof(fingerprint_device_t));
dev->common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
dev->common.version = FINGERPRINT_MODULE_API_VERSION_2_0;
dev->common.module = (struct hw_module_t*) module;
dev->common.close = fingerprint_close;
dev->pre_enroll = fingerprint_pre_enroll;
dev->enroll = fingerprint_enroll;
dev->get_authenticator_id = fingerprint_get_auth_id;
dev->cancel = fingerprint_cancel;
dev->remove = fingerprint_remove;
dev->set_active_group = fingerprint_set_active_group;
dev->authenticate = fingerprint_authenticate;
dev->set_notify = set_notify_callback;
dev->notify = NULL;
*device = (hw_device_t*) dev;
return 0;
}
static struct hw_module_methods_t fingerprint_module_methods = {
.open = fingerprint_open,
};
fingerprint_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.module_api_version = FINGERPRINT_MODULE_API_VERSION_2_0,
.hal_api_version = HARDWARE_HAL_API_VERSION,
.id = FINGERPRINT_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "Demo Fingerprint HAL",
.author = "The Android Open Source Project",
.methods = &fingerprint_module_methods,
},
};至此,指纹服务注册分析完毕。
现在分析指纹按压的时候,如何把信息返回到上层的。
从上文,搜索下代码
fp_device->set_notify(fp_device, BiometricsFingerprint::notify)))
这个 BiometricsFingerprint::notify就是把这个回调设置到hal层,接受指纹hal层指纹设别结果的回传。BiometricsFingerprint::notify的具体代码实现如下。
void BiometricsFingerprint::notify(const fingerprint_msg_t *msg) {
BiometricsFingerprint* thisPtr = static_cast<BiometricsFingerprint*>(
BiometricsFingerprint::getInstance());
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(thisPtr->mClientCallbackMutex);
if (thisPtr == nullptr || thisPtr->mClientCallback == nullptr) {
ALOGE("Receiving callbacks before the client callback is registered.");
return;
}
const uint64_t devId = reinterpret_cast<uint64_t>(thisPtr->mDevice);
switch (msg->type) {
case FINGERPRINT_ERROR: {
int32_t vendorCode = 0;
FingerprintError result = VendorErrorFilter(msg->data.error, &vendorCode);
ALOGD("onError(%d)", result);
if (!thisPtr->mClientCallback->onError(devId, result, vendorCode).isOk()) {
ALOGE("failed to invoke fingerprint onError callback");
}
}
break;
case FINGERPRINT_ACQUIRED: {
int32_t vendorCode = 0;
FingerprintAcquiredInfo result =
VendorAcquiredFilter(msg->data.acquired.acquired_info, &vendorCode);
ALOGD("onAcquired(%d)", result);
if (!thisPtr->mClientCallback->onAcquired(devId, result, vendorCode).isOk()) {
ALOGE("failed to invoke fingerprint onAcquired callback");
}
}
break;
case FINGERPRINT_TEMPLATE_ENROLLING:
ALOGD("onEnrollResult(fid=%d, gid=%d, rem=%d)",
msg->data.enroll.finger.fid,
msg->data.enroll.finger.gid,
msg->data.enroll.samples_remaining);
if (!thisPtr->mClientCallback->onEnrollResult(devId,
msg->data.enroll.finger.fid,
msg->data.enroll.finger.gid,
msg->data.enroll.samples_remaining).isOk()) {
ALOGE("failed to invoke fingerprint onEnrollResult callback");
}
break;
case FINGERPRINT_TEMPLATE_REMOVED:
ALOGD("onRemove(fid=%d, gid=%d, rem=%d)",
msg->data.removed.finger.fid,
msg->data.removed.finger.gid,
msg->data.removed.remaining_templates);
if (!thisPtr->mClientCallback->onRemoved(devId,
msg->data.removed.finger.fid,
msg->data.removed.finger.gid,
msg->data.removed.remaining_templates).isOk()) {
ALOGE("failed to invoke fingerprint onRemoved callback");
}
break;
case FINGERPRINT_AUTHENTICATED:
if (msg->data.authenticated.finger.fid != 0) {
ALOGD("onAuthenticated(fid=%d, gid=%d)",
msg->data.authenticated.finger.fid,
msg->data.authenticated.finger.gid);
const uint8_t* hat =
reinterpret_cast<const uint8_t *>(&msg->data.authenticated.hat);
const hidl_vec<uint8_t> token(
std::vector<uint8_t>(hat, hat + sizeof(msg->data.authenticated.hat)));
if (!thisPtr->mClientCallback->onAuthenticated(devId,
msg->data.authenticated.finger.fid,
msg->data.authenticated.finger.gid,
token).isOk()) {
ALOGE("failed to invoke fingerprint onAuthenticated callback");
}
} else {
// Not a recognized fingerprint
if (!thisPtr->mClientCallback->onAuthenticated(devId,
msg->data.authenticated.finger.fid,
msg->data.authenticated.finger.gid,
hidl_vec<uint8_t>()).isOk()) {
ALOGE("failed to invoke fingerprint onAuthenticated callback");
}
}
break;
case FINGERPRINT_TEMPLATE_ENUMERATING:
ALOGD("onEnumerate(fid=%d, gid=%d, rem=%d)",
msg->data.enumerated.finger.fid,
msg->data.enumerated.finger.gid,
msg->data.enumerated.remaining_templates);
if (!thisPtr->mClientCallback->onEnumerate(devId,
msg->data.enumerated.finger.fid,
msg->data.enumerated.finger.gid,
msg->data.enumerated.remaining_templates).isOk()) {
ALOGE("failed to invoke fingerprint onEnumerate callback");
}
break;
}
}第63行,指纹设别成功
thisPtr在第2行有定义,即是BiometricsFingerprint对象实例。继续,看看mClientCallback 是如何定义的,原来是其他地方传过来的,其实就是后面的HalResultController
前面,我应该说,我们要留意下代码
halId = mDaemon.setNotify(mHalResultController);就是这里,
mDaemon是远程对象实例BiometricsFingerprint
把mHalResultController设置到程对象实例BiometricsFingerprint。继续往前面找,最终可以找到定义的位置
final HalResultController controller = new HalResultController(sensorProps.sensorId,
context, handler,
scheduler);
HalResultController 源码如下,注意下他的继承类有stub,其作用是为跨进程的,即Binder调用。注意,这里必须要继承stub,要不,就没法跨进程通信了。至于为什么,可以参考下罗升阳的书籍android系统代码情景分析,第5章有详细介绍。
另外下面的博客,也有介绍。
android机制系列之六 Binder/AIDL回调callback机制原理_liujun3512159的博客-CSDN博客
第63行代码
!thisPtr->mClientCallback->onAuthenticated,实际上就是调用到下面的onAuthenticated
public static class HalResultController extends IBiometricsFingerprintClientCallback.Stub {
/**
* Interface to sends results to the HalResultController's owner.
*/
public interface Callback {
/**
* Invoked when the HAL sends ERROR_HW_UNAVAILABLE.
*/
void onHardwareUnavailable();
}
private final int mSensorId;
@NonNull private final Context mContext;
@NonNull final Handler mHandler;
@NonNull final BiometricScheduler mScheduler;
@Nullable private Callback mCallback;
HalResultController(int sensorId, @NonNull Context context, @NonNull Handler handler,
@NonNull BiometricScheduler scheduler) {
mSensorId = sensorId;
mContext = context;
mHandler = handler;
mScheduler = scheduler;
}
public void setCallback(@Nullable Callback callback) {
mCallback = callback;
}
@Override
public void onEnrollResult(long deviceId, int fingerId, int groupId, int remaining) {
mHandler.post(() -> {
final BaseClientMonitor client = mScheduler.getCurrentClient();
if (!(client instanceof FingerprintEnrollClient)) {
Slog.e(TAG, "onEnrollResult for non-enroll client: "
+ Utils.getClientName(client));
return;
}
final int currentUserId = client.getTargetUserId();
final CharSequence name = FingerprintUtils.getLegacyInstance(mSensorId)
.getUniqueName(mContext, currentUserId);
final Fingerprint fingerprint = new Fingerprint(name, groupId, fingerId, deviceId);
final FingerprintEnrollClient enrollClient = (FingerprintEnrollClient) client;
enrollClient.onEnrollResult(fingerprint, remaining);
});
}
@Override
public void onAcquired(long deviceId, int acquiredInfo, int vendorCode) {
onAcquired_2_2(deviceId, acquiredInfo, vendorCode);
}
@Override
public void onAcquired_2_2(long deviceId, int acquiredInfo, int vendorCode) {
mHandler.post(() -> {
final BaseClientMonitor client = mScheduler.getCurrentClient();
if (!(client instanceof AcquisitionClient)) {
Slog.e(TAG, "onAcquired for non-acquisition client: "
+ Utils.getClientName(client));
return;
}
final AcquisitionClient<?> acquisitionClient = (AcquisitionClient<?>) client;
acquisitionClient.onAcquired(acquiredInfo, vendorCode);
});
}
@Override
public void onAuthenticated(long deviceId, int fingerId, int groupId,
ArrayList<Byte> token) {
mHandler.post(() -> {
final BaseClientMonitor client = mScheduler.getCurrentClient();
if (!(client instanceof AuthenticationConsumer)) {
Slog.e(TAG, "onAuthenticated for non-authentication consumer: "
+ Utils.getClientName(client));
return;
}
final AuthenticationConsumer authenticationConsumer =
(AuthenticationConsumer) client;
final boolean authenticated = fingerId != 0;
final Fingerprint fp = new Fingerprint("", groupId, fingerId, deviceId);
authenticationConsumer.onAuthenticated(fp, authenticated, token);
});
}
@Override
public void onError(long deviceId, int error, int vendorCode) {
mHandler.post(() -> {
final BaseClientMonitor client = mScheduler.getCurrentClient();
Slog.d(TAG, "handleError"
+ ", client: " + Utils.getClientName(client)
+ ", error: " + error
+ ", vendorCode: " + vendorCode);
if (!(client instanceof ErrorConsumer)) {
Slog.e(TAG, "onError for non-error consumer: " + Utils.getClientName(client));
return;
}
final ErrorConsumer errorConsumer = (ErrorConsumer) client;
errorConsumer.onError(error, vendorCode);
if (error == BiometricConstants.BIOMETRIC_ERROR_HW_UNAVAILABLE) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Got ERROR_HW_UNAVAILABLE");
if (mCallback != null) {
mCallback.onHardwareUnavailable();
}
}
});
}
@Override
public void onRemoved(long deviceId, int fingerId, int groupId, int remaining) {
mHandler.post(() -> {
Slog.d(TAG, "Removed, fingerId: " + fingerId + ", remaining: " + remaining);
final BaseClientMonitor client = mScheduler.getCurrentClient();
if (!(client instanceof RemovalConsumer)) {
Slog.e(TAG, "onRemoved for non-removal consumer: "
+ Utils.getClientName(client));
return;
}
final Fingerprint fp = new Fingerprint("", groupId, fingerId, deviceId);
final RemovalConsumer removalConsumer = (RemovalConsumer) client;
removalConsumer.onRemoved(fp, remaining);
});
}
@Override
public void onEnumerate(long deviceId, int fingerId, int groupId, int remaining) {
mHandler.post(() -> {
final BaseClientMonitor client = mScheduler.getCurrentClient();
if (!(client instanceof EnumerateConsumer)) {
Slog.e(TAG, "onEnumerate for non-enumerate consumer: "
+ Utils.getClientName(client));
return;
}
final Fingerprint fp = new Fingerprint("", groupId, fingerId, deviceId);
final EnumerateConsumer enumerateConsumer = (EnumerateConsumer) client;
enumerateConsumer.onEnumerationResult(fp, remaining);
});
}
}第86行
authenticationConsumer.onAuthenticated(fp, authenticated, token);
实际上是调用FingerprintAuthenticationClient #onAuthenticated
@Override
public void onAuthenticated(BiometricAuthenticator.Identifier identifier,
boolean authenticated, ArrayList<Byte> token) {
super.onAuthenticated(identifier, authenticated, token);
if (authenticated) {
mState = STATE_STOPPED;
mSensorOverlays.hide(getSensorId());
} else {
mState = STATE_STARTED_PAUSED_ATTEMPTED;
}
}第4行代码比较关键,他实际上是调用的AuthenticationClient下的onAuthenticated方法。
@Override
public void onAuthenticated(BiometricAuthenticator.Identifier identifier,
boolean authenticated, ArrayList<Byte> hardwareAuthToken) {
super.logOnAuthenticated(getContext(), authenticated, mRequireConfirmation,
getTargetUserId(), isBiometricPrompt());
final ClientMonitorCallbackConverter listener = getListener();
if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "onAuthenticated(" + authenticated + ")"
+ ", ID:" + identifier.getBiometricId()
+ ", Owner: " + getOwnerString()
+ ", isBP: " + isBiometricPrompt()
+ ", listener: " + listener
+ ", requireConfirmation: " + mRequireConfirmation
+ ", user: " + getTargetUserId()
+ ", clientMonitor: " + toString());
final PerformanceTracker pm = PerformanceTracker.getInstanceForSensorId(getSensorId());
if (isCryptoOperation()) {
pm.incrementCryptoAuthForUser(getTargetUserId(), authenticated);
} else {
pm.incrementAuthForUser(getTargetUserId(), authenticated);
}
if (mAllowBackgroundAuthentication) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Allowing background authentication,"
+ " this is allowed only for platform or test invocations");
}
// Ensure authentication only succeeds if the client activity is on top.
boolean isBackgroundAuth = false;
if (!mAllowBackgroundAuthentication && authenticated
&& !Utils.isKeyguard(getContext(), getOwnerString())
&& !Utils.isSystem(getContext(), getOwnerString())) {
final List<ActivityManager.RunningTaskInfo> tasks =
mActivityTaskManager.getTasks(1);
if (tasks == null || tasks.isEmpty()) {
Slog.e(TAG, "No running tasks reported");
isBackgroundAuth = true;
} else {
final ComponentName topActivity = tasks.get(0).topActivity;
if (topActivity == null) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Unable to get top activity");
isBackgroundAuth = true;
} else {
final String topPackage = topActivity.getPackageName();
if (!topPackage.contentEquals(getOwnerString())) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Background authentication detected, top: " + topPackage
+ ", client: " + getOwnerString());
isBackgroundAuth = true;
}
}
}
}
// Fail authentication if we can't confirm the client activity is on top.
if (isBackgroundAuth) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failing possible background authentication");
authenticated = false;
// SafetyNet logging for exploitation attempts of b/159249069.
final ApplicationInfo appInfo = getContext().getApplicationInfo();
EventLog.writeEvent(0x534e4554, "159249069", appInfo != null ? appInfo.uid : -1,
"Attempted background authentication");
}
if (authenticated) {
// SafetyNet logging for b/159249069 if constraint is violated.
if (isBackgroundAuth) {
final ApplicationInfo appInfo = getContext().getApplicationInfo();
EventLog.writeEvent(0x534e4554, "159249069", appInfo != null ? appInfo.uid : -1,
"Successful background authentication!");
}
markAlreadyDone();
if (mTaskStackListener != null) {
mActivityTaskManager.unregisterTaskStackListener(mTaskStackListener);
}
final byte[] byteToken = new byte[hardwareAuthToken.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < hardwareAuthToken.size(); i++) {
byteToken[i] = hardwareAuthToken.get(i);
}
if (mIsStrongBiometric) {
mBiometricManager.resetLockoutTimeBound(getToken(),
getContext().getOpPackageName(),
getSensorId(), getTargetUserId(), byteToken);
}
final CoexCoordinator coordinator = CoexCoordinator.getInstance();
coordinator.onAuthenticationSucceeded(SystemClock.uptimeMillis(), this,
new CoexCoordinator.Callback() {
@Override
public void sendAuthenticationResult(boolean addAuthTokenIfStrong) {
if (addAuthTokenIfStrong && mIsStrongBiometric) {
final int result = KeyStore.getInstance().addAuthToken(byteToken);
Slog.d(TAG, "addAuthToken: " + result);
} else {
Slog.d(TAG, "Skipping addAuthToken");
}
if (listener != null) {
try {
// Explicitly have if/else here to make it super obvious in case the
// code is touched in the future.
if (!mIsRestricted) {
listener.onAuthenticationSucceeded(getSensorId(),
identifier,
byteToken,
getTargetUserId(),
mIsStrongBiometric);
} else {
listener.onAuthenticationSucceeded(getSensorId(),
null /* identifier */,
byteToken,
getTargetUserId(),
mIsStrongBiometric);
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Unable to notify listener", e);
}
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "Client not listening");
}
}
@Override
public void sendHapticFeedback() {
if (listener != null && mShouldVibrate) {
vibrateSuccess();
}
}
@Override
public void handleLifecycleAfterAuth() {
AuthenticationClient.this.handleLifecycleAfterAuth(true /* authenticated */);
}
@Override
public void sendAuthenticationCanceled() {
sendCancelOnly(listener);
}
});
} else {
// Allow system-defined limit of number of attempts before giving up
final @LockoutTracker.LockoutMode int lockoutMode =
handleFailedAttempt(getTargetUserId());
if (lockoutMode != LockoutTracker.LOCKOUT_NONE) {
markAlreadyDone();
}
final CoexCoordinator coordinator = CoexCoordinator.getInstance();
coordinator.onAuthenticationRejected(SystemClock.uptimeMillis(), this, lockoutMode,
new CoexCoordinator.Callback() {
@Override
public void sendAuthenticationResult(boolean addAuthTokenIfStrong) {
if (listener != null) {
try {
listener.onAuthenticationFailed(getSensorId());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Unable to notify listener", e);
}
}
}
@Override
public void sendHapticFeedback() {
if (listener != null && mShouldVibrate) {
vibrateError();
}
}
@Override
public void handleLifecycleAfterAuth() {
AuthenticationClient.this.handleLifecycleAfterAuth(false /* authenticated */);
}
@Override
public void sendAuthenticationCanceled() {
sendCancelOnly(listener);
}
});
}
}第109行listener实际上就是
FingerprintService#authenticate方法中,即new ClientMonitorCallbackConverter(receiver) 对象实例
所以,listener.onAuthenticationSucceeded调用的是ClientMonitorCallbackConverter#onAuthenticationSucceeded,代码如下
public class ClientMonitorCallbackConverter {
private IBiometricSensorReceiver mSensorReceiver; // BiometricService
private IFaceServiceReceiver mFaceServiceReceiver; // FaceManager
private IFingerprintServiceReceiver mFingerprintServiceReceiver; // FingerprintManager
public ClientMonitorCallbackConverter(IBiometricSensorReceiver sensorReceiver) {
mSensorReceiver = sensorReceiver;
}
public ClientMonitorCallbackConverter(IFaceServiceReceiver faceServiceReceiver) {
mFaceServiceReceiver = faceServiceReceiver;
}
public ClientMonitorCallbackConverter(IFingerprintServiceReceiver fingerprintServiceReceiver) {
mFingerprintServiceReceiver = fingerprintServiceReceiver;
}
// The following apply to all clients
void onAcquired(int sensorId, int acquiredInfo, int vendorCode) throws RemoteException {
if (mSensorReceiver != null) {
mSensorReceiver.onAcquired(sensorId, acquiredInfo, vendorCode);
} else if (mFaceServiceReceiver != null) {
mFaceServiceReceiver.onAcquired(acquiredInfo, vendorCode);
} else if (mFingerprintServiceReceiver != null) {
mFingerprintServiceReceiver.onAcquired(acquiredInfo, vendorCode);
}
}
void onAuthenticationSucceeded(int sensorId, BiometricAuthenticator.Identifier identifier,
byte[] token, int userId, boolean isStrongBiometric) throws RemoteException {
if (mSensorReceiver != null) {
mSensorReceiver.onAuthenticationSucceeded(sensorId, token);
} else if (mFaceServiceReceiver != null) {
mFaceServiceReceiver.onAuthenticationSucceeded((Face) identifier, userId,
isStrongBiometric);
} else if (mFingerprintServiceReceiver != null) {
mFingerprintServiceReceiver.onAuthenticationSucceeded((Fingerprint) identifier, userId,
isStrongBiometric);
}
}
void onAuthenticationFailed(int sensorId) throws RemoteException {
if (mSensorReceiver != null) {
mSensorReceiver.onAuthenticationFailed(sensorId);
} else if (mFaceServiceReceiver != null) {
mFaceServiceReceiver.onAuthenticationFailed();
} else if (mFingerprintServiceReceiver != null) {
mFingerprintServiceReceiver.onAuthenticationFailed();
}
}
public void onError(int sensorId, int cookie, int error, int vendorCode)
throws RemoteException {
if (mSensorReceiver != null) {
mSensorReceiver.onError(sensorId, cookie, error, vendorCode);
} else if (mFaceServiceReceiver != null) {
mFaceServiceReceiver.onError(error, vendorCode);
} else if (mFingerprintServiceReceiver != null) {
mFingerprintServiceReceiver.onError(error, vendorCode);
}
}
// The following only apply to IFingerprintServiceReceiver and IFaceServiceReceiver
public void onDetected(int sensorId, int userId, boolean isStrongBiometric)
throws RemoteException {
if (mFaceServiceReceiver != null) {
mFaceServiceReceiver.onFaceDetected(sensorId, userId, isStrongBiometric);
} else if (mFingerprintServiceReceiver != null) {
mFingerprintServiceReceiver.onFingerprintDetected(sensorId, userId, isStrongBiometric);
}
}
void onEnrollResult(BiometricAuthenticator.Identifier identifier, int remaining)
throws RemoteException {
if (mFaceServiceReceiver != null) {
mFaceServiceReceiver.onEnrollResult((Face) identifier, remaining);
} else if (mFingerprintServiceReceiver != null) {
mFingerprintServiceReceiver.onEnrollResult((Fingerprint) identifier, remaining);
}
}
void onRemoved(BiometricAuthenticator.Identifier identifier, int remaining)
throws RemoteException {
if (mFaceServiceReceiver != null) {
mFaceServiceReceiver.onRemoved((Face) identifier, remaining);
} else if (mFingerprintServiceReceiver != null) {
mFingerprintServiceReceiver.onRemoved((Fingerprint) identifier, remaining);
}
}
/** Called when a challenged has been generated. */
public void onChallengeGenerated(int sensorId, int userId, long challenge)
throws RemoteException {
if (mFaceServiceReceiver != null) {
mFaceServiceReceiver.onChallengeGenerated(sensorId, userId, challenge);
} else if (mFingerprintServiceReceiver != null) {
mFingerprintServiceReceiver.onChallengeGenerated(sensorId, userId, challenge);
}
}
public void onFeatureSet(boolean success, int feature) throws RemoteException {
if (mFaceServiceReceiver != null) {
mFaceServiceReceiver.onFeatureSet(success, feature);
}
}
public void onFeatureGet(boolean success, int[] features, boolean[] featureState)
throws RemoteException {
if (mFaceServiceReceiver != null) {
mFaceServiceReceiver.onFeatureGet(success, features, featureState);
}
}
// Fingerprint-specific callbacks for FingerprintManager only
public void onUdfpsPointerDown(int sensorId) throws RemoteException {
if (mFingerprintServiceReceiver != null) {
mFingerprintServiceReceiver.onUdfpsPointerDown(sensorId);
}
}
public void onUdfpsPointerUp(int sensorId) throws RemoteException {
if (mFingerprintServiceReceiver != null) {
mFingerprintServiceReceiver.onUdfpsPointerUp(sensorId);
}
}
// Face-specific callbacks for FaceManager only
/**
* Called each time a new frame is received during face authentication.
*
* @param frame Information about the current frame.
*
* @throws RemoteException If the binder call to {@link IFaceServiceReceiver} fails.
*/
public void onAuthenticationFrame(@NonNull FaceAuthenticationFrame frame)
throws RemoteException {
if (mFaceServiceReceiver != null) {
mFaceServiceReceiver.onAuthenticationFrame(frame);
}
}
/**
* Called each time a new frame is received during face enrollment.
*
* @param frame Information about the current frame.
*
* @throws RemoteException If the binder call to {@link IFaceServiceReceiver} fails.
*/
public void onEnrollmentFrame(@NonNull FaceEnrollFrame frame) throws RemoteException {
if (mFaceServiceReceiver != null) {
mFaceServiceReceiver.onEnrollmentFrame(frame);
}
}
}
(指纹解锁结果如何回传到上层的_liujun3512159的博客-CSDN博客)
第33行的mSensorReceiver就是 receiever对象实例
这里关键参数receiver是通过aidl传到FingerprintService下的authenticate方法中
显然,这里是通过调用FingerprintManager类的authenticate传进来的
/**
* Per-user and per-sensor version of authenticate.
* @hide
*/
@RequiresPermission(anyOf = {USE_BIOMETRIC, USE_FINGERPRINT})
public void authenticate(@Nullable CryptoObject crypto, @Nullable CancellationSignal cancel,
@NonNull AuthenticationCallback callback, Handler handler, int sensorId, int userId,
int flags) {
FrameworkStatsLog.write(FrameworkStatsLog.AUTH_DEPRECATED_API_USED,
AUTH_DEPRECATED_APIUSED__DEPRECATED_API__API_FINGERPRINT_MANAGER_AUTHENTICATE,
mContext.getApplicationInfo().uid,
mContext.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion);
if (callback == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Must supply an authentication callback");
}
if (cancel != null && cancel.isCanceled()) {
Slog.w(TAG, "authentication already canceled");
return;
}
final boolean ignoreEnrollmentState = flags == 0 ? false : true;
if (mService != null) {
try {
useHandler(handler);
mAuthenticationCallback = callback;
mCryptoObject = crypto;
final long operationId = crypto != null ? crypto.getOpId() : 0;
final long authId = mService.authenticate(mToken, operationId, sensorId, userId,
mServiceReceiver, mContext.getOpPackageName(), ignoreEnrollmentState);
if (cancel != null) {
cancel.setOnCancelListener(new OnAuthenticationCancelListener(authId));
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Remote exception while authenticating: ", e);
// Though this may not be a hardware issue, it will cause apps to give up or try
// again later.
callback.onAuthenticationError(FINGERPRINT_ERROR_HW_UNAVAILABLE,
getErrorString(mContext, FINGERPRINT_ERROR_HW_UNAVAILABLE,
0 /* vendorCode */));
}
}
}注意这里的第29行,上层的回调接口对象。
搜索前面的代码
mFingerprintServiceReceiver.onAuthenticationSucceeded((Fingerprint) identifier, userId,isStrongBiometric);
这行代码执行的就是下面的对应的onAuthenticationSucceeded方法。
第32行参数mServiceReceiver就是这个了
private IFingerprintServiceReceiver mServiceReceiver = new IFingerprintServiceReceiver.Stub() {
@Override // binder call
public void onEnrollResult(Fingerprint fp, int remaining) {
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_ENROLL_RESULT, remaining, 0, fp).sendToTarget();
}
@Override // binder call
public void onAcquired(int acquireInfo, int vendorCode) {
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_ACQUIRED, acquireInfo, vendorCode).sendToTarget();
}
@Override // binder call
public void onAuthenticationSucceeded(Fingerprint fp, int userId,
boolean isStrongBiometric) {
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_AUTHENTICATION_SUCCEEDED, userId, isStrongBiometric ? 1 : 0,
fp).sendToTarget();
}
@Override
public void onFingerprintDetected(int sensorId, int userId, boolean isStrongBiometric) {
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_FINGERPRINT_DETECTED, sensorId, userId, isStrongBiometric)
.sendToTarget();
}
@Override // binder call
public void onAuthenticationFailed() {
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED).sendToTarget();
}
@Override // binder call
public void onError(int error, int vendorCode) {
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_ERROR, error, vendorCode).sendToTarget();
}
@Override // binder call
public void onRemoved(Fingerprint fp, int remaining) {
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_REMOVED, remaining, 0, fp).sendToTarget();
}
@Override // binder call
public void onChallengeGenerated(int sensorId, int userId, long challenge) {
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_CHALLENGE_GENERATED, sensorId, userId, challenge)
.sendToTarget();
}
@Override // binder call
public void onUdfpsPointerDown(int sensorId) {
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_UDFPS_POINTER_DOWN, sensorId, 0).sendToTarget();
}
@Override // binder call
public void onUdfpsPointerUp(int sensorId) {
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_UDFPS_POINTER_UP, sensorId, 0).sendToTarget();
}
}这里,我们看第16行代码
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_AUTHENTICATION_SUCCEEDED, userId, isStrongBiometric ? 1 : 0,fp).sendToTarget();
会触发到下面的地方
case MSG_AUTHENTICATION_SUCCEEDED:
sendAuthenticatedSucceeded((Fingerprint) msg.obj, msg.arg1 /* userId */,
msg.arg2 == 1 /* isStrongBiometric */); private void sendAuthenticatedSucceeded(Fingerprint fp, int userId, boolean isStrongBiometric) {
if (mAuthenticationCallback != null) {
final AuthenticationResult result =
new AuthenticationResult(mCryptoObject, fp, userId, isStrongBiometric);
mAuthenticationCallback.onAuthenticationSucceeded(result);
}
}第5行,变量mAuthenticationCallback 是从哪儿来的?
见博客
生物解锁--指纹服务注册流程_liujun3512159的博客-CSDN博客
实际上,就是KeyguardUpdateMonitor#authenticate 方法中传入了这个对象。
mFpm.authenticate(null /* crypto */, mFingerprintCancelSignal,
mFingerprintAuthenticationCallback, null /* handler */,
FingerprintManager.SENSOR_ID_ANY, userId, 0 /* flags */);实际上就是mFingerprintAuthenticationCallback 对象实例。其代码就是文章开头部分的
FingerprintManager.AuthenticationCallback mFingerprintAuthenticationCallback
至此,指纹解锁结果,回调到最上层了
从这里,我们发现,底软那边解锁成功,一步步的回调到这里,告知上层用户,解锁成功,分析结束。























 1248
1248











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










