2018 CVPR Anatomical Priors in Convolutional Networks for Unsupervised Biomedical Segmentation 每日论文阅读1
2021.05.24 工作快三年,越来越脱离学习,开始每日论文阅读,希望两三年之后在无监督图像分割领域,特别是医疗图像领域有一定的了解和建树
摘要
We consider the problem of segmenting a biomedical image into anatomical regions of interest. We specifically address the frequent scenario where we have no paired training data that contains images and their manual segmentations.
Instead, we employ unpaired segmentation images that we use to build an anatomical prior. Critically these segmentations can be derived from imaging data from a different dataset and imaging modality than the current task.
主要针对的是没有标签的医疗图像分割问题,通过采用无标签图像,建立解剖结构的先验知识
We introduce a generative probabilistic model that employs the learned prior through a convolutional neural network to compute segmentations in an unsupervised setting.
这篇文章介绍了一种生成概率模型,该模型利用卷积神经网络,采用解剖结构的先验知识,去完成分割任务。
主要的贡献点
To our knowledge, there has not been a theoretically rigorous effort to integrate rich probabilistic anatomical priors with a CNN-based segmentation model in a computationally effective manner.
据我们了解,还没有工作将rich probabilistic anatomical priors与CNN分割模型进行计算效率较高的融合。
We introduce a generative model for biomedical segmentation that employs an anatomical prior. We describe a principled theoretical derivation that follows directly from our generative model.
我们介绍了一种包含解剖学先验的生成式的模型。并且,通过该生成式模型,进行了原理上的推导
We demonstrate that this yields intuitive cost functions and simpler models. We use an auto-encoding variational CNN to characterize the anatomical prior, and an encoder-decoder CNN to provide fast segmentation of medical images in unsupervised settings.
最终,产出了一种直观上可以理解的cost function和简单的模型,我们使用auto-encoding variational CNN来描述anatomical prior,和编码解码形式的CNN实现快速的非监督学习
1. 生成式模型

x表示3D volume,也就是我们可以观测到的图像强度,s是3D的anatomical segmentation map。x[j]和y[j]表示图像在像素j处的强度和对应的标签。
下面构建生成式的模型,构建生成式模型分为2步,第一步是 由z到s的过程,即从隐变量到分割结果的模型,第二步是由分割结果,到图片的过程(也可以反着理解,一样)
- 我们这里认为的先验只是是空间部分和解破学形状,用latent variable z来表示。同时,我们对z进行建模,认为其符合标准正态分布,即:
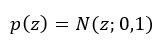
假设s是由低维度z生成的(即z为s 的压缩结果),即:
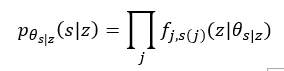
其中,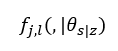 表示,在像素j处,为label l的概率
表示,在像素j处,为label l的概率 - 再我们获得了s后,由s到x 的建模为:
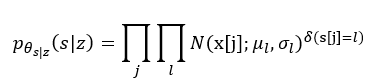
这里,其实就是认为每一类label都符合一种正态分布,拥有自己的均值和方差,其中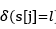 为一个indicator function,即加入有5类,当像素j属于第3类的时候,则为(0,0,1,0,0),指示当前像素属于某一类的函数
为一个indicator function,即加入有5类,当像素j属于第3类的时候,则为(0,0,1,0,0),指示当前像素属于某一类的函数
最后,文章使用MAP estimation:
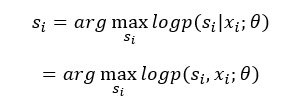
这里,等式之所以成立的原因,是因为 p(x)是保持不变的
2. 基于模型的训练过程
在不假设像素独立性的情况下,去做p(s|x)是非常困难的,因为里面包括了对z的积分。同时,p(z|x,s)也很难,让EM算法无法实现,
所以这里使用 varitional autoencoder bayes来生成对p(z|x,s)的近似,整个推导过程与VAE相似:

所以求q(z|x,s)与p(z|s,x)的近似,其实就是求下式的最小,即可以用VAE来求解
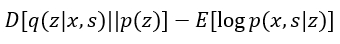
2.1 Anatomical prior learning
本节主要介绍了如何获得label 的一些概率属性
直接获得p(s)是困难的,所以这里希望获得 p(z|s),同样是VAE的方式,用q(z|s)去近似p(z|s)
这里的优势是,s可以从任意数据集去获得,而不用必须是训练数据集的label,相对获得容易很多
2.2 非监督学习
假如我们有paired data的时候,即train data拥有标签的时候,文章中的优化公式为:
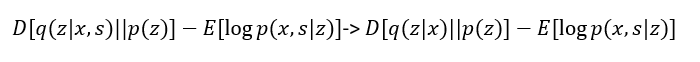
这里KL项的p(z|x,s)变成了p(z|x),然后有:
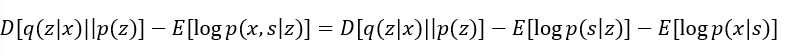
三项分别是kl散度,和VAE一样,第二项直接用Anatomical prior learning的decoder部分得到,第三部分也是s经过神经网络,得到x
具体公式可以看论文
当我们没有paired data 的时候,即第二项和第三项计算不了,这个时候,可以将绝对的label值,变成由p(s|z)生成的概率值,
这里用对s的积分求得了该loss,但是具体为何可以进行这个推导,我认为并没有很严格的推导

最后的(14)式,将原来的indicator function变成了概率
这篇论文提供了代码,等看完源码再来分享






















 1839
1839











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








