SecurityContextPersistenceFilter,为 Spring Security 框架 Filter Chain 过滤器链的第一个 Filter,具有不可或缺的作用。
/**
* Populates the {@link SecurityContextHolder} with information obtained from the
* configured {@link SecurityContextRepository} prior to the request and stores it back in
* the repository once the request has completed and clearing the context holder. By
* default it uses an {@link HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository}. See this class for
* information <tt>HttpSession</tt> related configuration options.
* <p>
*/记得 Spring Security 框架中,可以通过 HttpServletRequest 中的 SPRING_SECURITY_CONTEXT 属性,直接获取当前登录用户的 SecurityContext 吗?其正是由此 Filter 实现的,而此也正是该类的重要使命。
@RequestMapping("/user")
@ResponseBody
public Object user(HttpServletRequest request) {
return request.getSession().getAttribute(HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository.SPRING_SECURITY_CONTEXT_KEY);
}启动系统,正常登录后,访问 http://localhost:8080/springsecuritylearning/user 路径,则能正常展示当前已身份认证成功的 SecurityContext。

下面,将会详细分析此 Filter 的具体功用。
该 Filter 从配置的 SecurityContextRepository(默认为 HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository)中获取信息并在请求完成后将其存储到 SecurityContextHolder 中。
并且,该 Filter 必须在其它任何身份验证处理之前执行,这也就是为什么会是 Spring Security 框架 Filter Chain 过滤器链的第一个 Filter。
/**
* <p>
* This filter MUST be executed BEFORE any authentication processing mechanisms.
* Authentication processing mechanisms (e.g. BASIC, CAS processing filters etc) expect
* the <code>SecurityContextHolder</code> to contain a valid <code>SecurityContext</code>
* by the time they execute.
*/同 FilterSecurityInterceptor 一样,该 Filter 仅会执行一次。
/**
* <p>
* This filter will only execute once per request, to resolve servlet container
* (specifically Weblogic) incompatibilities.
*/
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
......
if (request.getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null) {
// ensure that filter is only applied once per request
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
......
}在其它 Filter 执行之前,会先从 SecurityContextRepository 中获取当前的 SecurityContext,然后再执行后续 Filter。
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
......
HttpRequestResponseHolder holder = new HttpRequestResponseHolder(request,
response);
SecurityContext contextBeforeChainExecution = repo.loadContext(holder);
try {
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(contextBeforeChainExecution);
chain.doFilter(holder.getRequest(), holder.getResponse());
}
......
}从 SecurityContextRepository 中获取当前的 SecurityContext 的逻辑如下。
public SecurityContext loadContext(HttpRequestResponseHolder requestResponseHolder) {
HttpServletRequest request = requestResponseHolder.getRequest();
HttpServletResponse response = requestResponseHolder.getResponse();
HttpSession httpSession = request.getSession(false);
SecurityContext context = readSecurityContextFromSession(httpSession);
if (context == null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No SecurityContext was available from the HttpSession: "
+ httpSession + ". " + "A new one will be created.");
}
context = generateNewContext();
}
......
return context;
}如果 SecurityContext 不存在,则会创建一个新的 SecurityContext 并返回。
待后续 Filter 执行完毕,SecurityContextRepository 会将当前新的 SecurityContext 进行保存,并且情况当前的SecurityContextHolder 中的 SecurityContext。
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
......
try {
......
}
finally {
SecurityContext contextAfterChainExecution = SecurityContextHolder
.getContext();
// Crucial removal of SecurityContextHolder contents - do this before anything
// else.
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
repo.saveContext(contextAfterChainExecution, holder.getRequest(),
holder.getResponse());
request.removeAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED);
......
}
}最后,SecurityContextRepository 会保存新的 SecurityContext,并清空 FILTER_APPLIED 标识。SecurityContextRepository 保存新的 SecurityContext 逻辑如下。
public void saveContext(SecurityContext context, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
SaveContextOnUpdateOrErrorResponseWrapper responseWrapper = WebUtils
.getNativeResponse(response,
SaveContextOnUpdateOrErrorResponseWrapper.class);
if (responseWrapper == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot invoke saveContext on response "
+ response
+ ". You must use the HttpRequestResponseHolder.response after invoking loadContext");
}
// saveContext() might already be called by the response wrapper
// if something in the chain called sendError() or sendRedirect(). This ensures we
// only call it
// once per request.
if (!responseWrapper.isContextSaved()) {
responseWrapper.saveContext(context);
}
}方法开头所获取的 SaveContextOnUpdateOrErrorResponseWrapper(SaveToSessionResponseWrapper 父类),正是在 Filter 执行开始时,loadContext 方法所设置的 response。
public SecurityContext loadContext(HttpRequestResponseHolder requestResponseHolder) {
HttpServletRequest request = requestResponseHolder.getRequest();
HttpServletResponse response = requestResponseHolder.getResponse();
HttpSession httpSession = request.getSession(false);
......
SaveToSessionResponseWrapper wrappedResponse = new SaveToSessionResponseWrapper(
response, request, httpSession != null, context);
requestResponseHolder.setResponse(wrappedResponse);
......
return context;
}最后,新的 SecurityContext 的保存逻辑,会落到 SaveContextOnUpdateOrErrorResponseWrapper 的子类上,即内部类 HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository.SaveToSessionResponseWrapper。
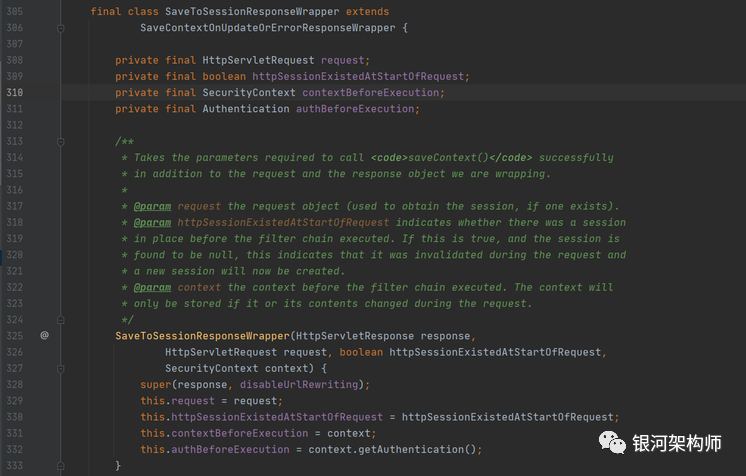
保存 SecurityContext 逻辑如下。
protected void saveContext(SecurityContext context) {
final Authentication authentication = context.getAuthentication();
HttpSession httpSession = request.getSession(false);
// See SEC-776
if (authentication == null || trustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("SecurityContext is empty or contents are anonymous - context will not be stored in HttpSession.");
}
if (httpSession != null && authBeforeExecution != null) {
// SEC-1587 A non-anonymous context may still be in the session
// SEC-1735 remove if the contextBeforeExecution was not anonymous
httpSession.removeAttribute(springSecurityContextKey);
}
return;
}
if (httpSession == null) {
httpSession = createNewSessionIfAllowed(context);
}
// If HttpSession exists, store current SecurityContext but only if it has
// actually changed in this thread (see SEC-37, SEC-1307, SEC-1528)
if (httpSession != null) {
// We may have a new session, so check also whether the context attribute
// is set SEC-1561
if (contextChanged(context)
|| httpSession.getAttribute(springSecurityContextKey) == null) {
httpSession.setAttribute(springSecurityContextKey, context);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("SecurityContext '" + context
+ "' stored to HttpSession: '" + httpSession);
}
}
}
}其实,就是在判断当前的 SecurityContext 有无变化,或者其中的 Authentication 有无变化,来清除或者设置HttpSession 中的 SPRING_SECURITY_CONTEXT 属性。比如,身份认证成功、身份认证失败等。
身份认证成功后,系统会设置 SPRING_SECURITY_CONTEXT 属性值到 HttpSession 中。这也是为什么我们可以通过 Request 来获取 SPRING_SECURITY_CONTEXT 标识值,也即 SecurityContext 的原因。
其它详细源码,请参考文末源码链接,可自行下载后阅读。
我是银河架构师,十年饮冰,难凉热血,愿历尽千帆,归来仍是少年!
如果文章对您有帮助,请举起您的小手,轻轻【三连】,这将是笔者持续创作的动力源泉。当然,如果文章有错误,或者您有任何的意见或建议,请留言。感谢您的阅读!
源码
github
https://github.com/liuminglei/SpringSecurityLearning/tree/master/40
gitee
https://gitee.com/xbd521/SpringSecurityLearning/tree/master/40























 298
298











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








