Glide源码学习笔记六:磁盘缓存实现
文章目录
前言
上一章Glide源码学习笔记五:磁盘缓存分析获取磁盘缓存的一些逻辑。在DecodeJob.getNextGenerator()方法中,构建了三种磁盘资源获取方式,这三种方法的实现类都实现了DataFetcherGenerator(资源获取生成器)接口,触发资源获取的方法为DataFetcherGenerator.startNext(),接下来通过分析ResourceCacheGenerator,DataCacheGenerator,SourceGenerator这三个类是实现startNext方法来学习磁盘资源的实现。
在这里帮大家回忆一下这三个类的构建条件:
private DataFetcherGenerator getNextGenerator() {
switch (stage) {
//处理从磁盘缓存获取已处理文件的情况
case RESOURCE_CACHE:
return new ResourceCacheGenerator(decodeHelper, this);
//处理从磁盘缓存获取源文件的情况
case DATA_CACHE:
return new DataCacheGenerator(decodeHelper, this);
//下载成功之后的解码转化操作
case SOURCE:
return new SourceGenerator(decodeHelper, this);
case FINISHED:
return null;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unrecognized stage: " + stage);
}
}
以上三个加载器是顺序遍历的,为了便于理解,我们从最后一个开始倒叙分析,因为一开始肯定是没有缓存的。
SourceGenerator.startNext()
@Override
public boolean startNext() {
//如果有缓存,就直接返回缓存
if (dataToCache != null) {
Object data = dataToCache;
dataToCache = null;
try {
boolean isDataInCache = cacheData(data);
if (!isDataInCache) {
return true;
}
}
}
}
if (sourceCacheGenerator != null && sourceCacheGenerator.startNext()) {
return true;
}
sourceCacheGenerator = null;
loadData = null;
boolean started = false;
//没有缓存,开始下载
while (!started && hasNextModelLoader()) {
loadData = helper.getLoadData().get(loadDataListIndex++);
//loadData不为空并且支持缓存或者有loadpath,就开始下载
if (loadData != null
&& (helper.getDiskCacheStrategy().isDataCacheable(loadData.fetcher.getDataSource())
|| helper.hasLoadPath(loadData.fetcher.getDataClass()))) {
started = true;
startNextLoad(loadData);
}
}
return started;
}
代码中有几个类很眼生,先简单介绍一下:
1.ModelLoader:模块加载器
2.SourceGenerator:实现了DataFetcherGenerator接口,资源生成器
3.DataFetcher:数据抓取
4.LoadData:数据加载
5.LoadPath:加载器可能会有多个LoadPath
6.DecodePath:解码
简单来说,SourceGenerator是一个DataFetcher的生成器,ResourceCacheGenerator和DataCacheGenerator也是。
DataFetcher是一个数据抓取器,存放在LoadData中,而LoadData是在ModelLoader中构造的,以上2 ~ 4构成了Glide数据的转换与获取,5 ~ 6构成Glide的解码过程。
先来分析LoadData是怎么来的。
getLoadData()
List<LoadData<?>> getLoadData() {
//标志位判断,loadData是否设置过
if (!isLoadDataSet) {
isLoadDataSet = true;
loadData.clear();
//获取modelLoaders
List<ModelLoader<Object, ?>> modelLoaders = glideContext.getRegistry().getModelLoaders(model);
//从modelLoaders中获取数据构造loadData
for (int i = 0, size = modelLoaders.size(); i < size; i++) {
ModelLoader<Object, ?> modelLoader = modelLoaders.get(i);
//构造LoadData
LoadData<?> current = modelLoader.buildLoadData(model, width, height, options);
if (current != null) {
loadData.add(current);
}
}
}
return loadData;
}
这里有一个modelLoaders比较关键,这个地方也是之前遗漏没有说过的Glide初始化步骤,
在这里打一个补丁:
glideContext.getRegistry()返回的是一个Registry类,注册。在Glide的构造方法中,除了给Engine,MemoryCache等等一些变量赋值,代码最多的就是这个Registry相关的方法,在这里就把源码po上来了,大家感受一下。
Glide(
@NonNull Context context,
@NonNull Engine engine,
@NonNull MemoryCache memoryCache,
@NonNull BitmapPool bitmapPool,
@NonNull ArrayPool arrayPool,
@NonNull RequestManagerRetriever requestManagerRetriever,
@NonNull ConnectivityMonitorFactory connectivityMonitorFactory,
int logLevel,
@NonNull RequestOptionsFactory defaultRequestOptionsFactory,
@NonNull Map<Class<?>, TransitionOptions<?, ?>> defaultTransitionOptions,
@NonNull List<RequestListener<Object>> defaultRequestListeners,
GlideExperiments experiments) {
this.engine = engine;
this.bitmapPool = bitmapPool;
this.arrayPool = arrayPool;
this.memoryCache = memoryCache;
this.requestManagerRetriever = requestManagerRetriever;
this.connectivityMonitorFactory = connectivityMonitorFactory;
this.defaultRequestOptionsFactory = defaultRequestOptionsFactory;
final Resources resources = context.getResources();
registry = new Registry();
registry.register(new DefaultImageHeaderParser());
// Right now we're only using this parser for HEIF images, which are only supported on OMR1+.
// If we need this for other file types, we should consider removing this restriction.
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O_MR1) {
registry.register(new ExifInterfaceImageHeaderParser());
}
List<ImageHeaderParser> imageHeaderParsers = registry.getImageHeaderParsers();
ByteBufferGifDecoder byteBufferGifDecoder =
new ByteBufferGifDecoder(context, imageHeaderParsers, bitmapPool, arrayPool);
ResourceDecoder<ParcelFileDescriptor, Bitmap> parcelFileDescriptorVideoDecoder =
VideoDecoder.parcel(bitmapPool);
// TODO(judds): Make ParcelFileDescriptorBitmapDecoder work with ImageDecoder.
Downsampler downsampler =
new Downsampler(
registry.getImageHeaderParsers(), resources.getDisplayMetrics(), bitmapPool, arrayPool);
ResourceDecoder<ByteBuffer, Bitmap> byteBufferBitmapDecoder;
ResourceDecoder<InputStream, Bitmap> streamBitmapDecoder;
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.P
&& experiments.isEnabled(EnableImageDecoderForBitmaps.class)) {
streamBitmapDecoder = new InputStreamBitmapImageDecoderResourceDecoder();
byteBufferBitmapDecoder = new ByteBufferBitmapImageDecoderResourceDecoder();
} else {
byteBufferBitmapDecoder = new ByteBufferBitmapDecoder(downsampler);
streamBitmapDecoder = new StreamBitmapDecoder(downsampler, arrayPool);
}
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.P
&& experiments.isEnabled(EnableImageDecoderForAnimatedWebp.class)) {
registry.append(
Registry.BUCKET_ANIMATION,
InputStream.class,
Drawable.class,
AnimatedWebpDecoder.streamDecoder(imageHeaderParsers, arrayPool));
registry.append(
Registry.BUCKET_ANIMATION,
ByteBuffer.class,
Drawable.class,
AnimatedWebpDecoder.byteBufferDecoder(imageHeaderParsers, arrayPool));
}
ResourceDrawableDecoder resourceDrawableDecoder = new ResourceDrawableDecoder(context);
ResourceLoader.StreamFactory resourceLoaderStreamFactory =
new ResourceLoader.StreamFactory(resources);
ResourceLoader.UriFactory resourceLoaderUriFactory = new ResourceLoader.UriFactory(resources);
ResourceLoader.FileDescriptorFactory resourceLoaderFileDescriptorFactory =
new ResourceLoader.FileDescriptorFactory(resources);
ResourceLoader.AssetFileDescriptorFactory resourceLoaderAssetFileDescriptorFactory =
new ResourceLoader.AssetFileDescriptorFactory(resources);
BitmapEncoder bitmapEncoder = new BitmapEncoder(arrayPool);
BitmapBytesTranscoder bitmapBytesTranscoder = new BitmapBytesTranscoder();
GifDrawableBytesTranscoder gifDrawableBytesTranscoder = new GifDrawableBytesTranscoder();
ContentResolver contentResolver = context.getContentResolver();
registry
.append(ByteBuffer.class, new ByteBufferEncoder())
.append(InputStream.class, new StreamEncoder(arrayPool))
/* Bitmaps */
.append(Registry.BUCKET_BITMAP, ByteBuffer.class, Bitmap.class, byteBufferBitmapDecoder)
.append(Registry.BUCKET_BITMAP, InputStream.class, Bitmap.class, streamBitmapDecoder);
if (ParcelFileDescriptorRewinder.isSupported()) {
registry.append(
Registry.BUCKET_BITMAP,
ParcelFileDescriptor.class,
Bitmap.class,
new ParcelFileDescriptorBitmapDecoder(downsampler));
}
registry
.append(
Registry.BUCKET_BITMAP,
ParcelFileDescriptor.class,
Bitmap.class,
parcelFileDescriptorVideoDecoder)
.append(
Registry.BUCKET_BITMAP,
AssetFileDescriptor.class,
Bitmap.class,
VideoDecoder.asset(bitmapPool))
.append(Bitmap.class, Bitmap.class, UnitModelLoader.Factory.<Bitmap>getInstance())
.append(Registry.BUCKET_BITMAP, Bitmap.class, Bitmap.class, new UnitBitmapDecoder())
.append(Bitmap.class, bitmapEncoder)
/* BitmapDrawables */
.append(
Registry.BUCKET_BITMAP_DRAWABLE,
ByteBuffer.class,
BitmapDrawable.class,
new BitmapDrawableDecoder<>(resources, byteBufferBitmapDecoder))
.append(
Registry.BUCKET_BITMAP_DRAWABLE,
InputStream.class,
BitmapDrawable.class,
new BitmapDrawableDecoder<>(resources, streamBitmapDecoder))
.append(
Registry.BUCKET_BITMAP_DRAWABLE,
ParcelFileDescriptor.class,
BitmapDrawable.class,
new BitmapDrawableDecoder<>(resources, parcelFileDescriptorVideoDecoder))
.append(BitmapDrawable.class, new BitmapDrawableEncoder(bitmapPool, bitmapEncoder))
/* GIFs */
.append(
Registry.BUCKET_ANIMATION,
InputStream.class,
GifDrawable.class,
new StreamGifDecoder(imageHeaderParsers, byteBufferGifDecoder, arrayPool))
.append(
Registry.BUCKET_ANIMATION, ByteBuffer.class, GifDrawable.class, byteBufferGifDecoder)
.append(GifDrawable.class, new GifDrawableEncoder())
/* GIF Frames */
// Compilation with Gradle requires the type to be specified for UnitModelLoader here.
.append(
GifDecoder.class, GifDecoder.class, UnitModelLoader.Factory.<GifDecoder>getInstance())
.append(
Registry.BUCKET_BITMAP,
GifDecoder.class,
Bitmap.class,
new GifFrameResourceDecoder(bitmapPool))
/* Drawables */
.append(Uri.class, Drawable.class, resourceDrawableDecoder)
.append(
Uri.class, Bitmap.class, new ResourceBitmapDecoder(resourceDrawableDecoder, bitmapPool))
/* Files */
.register(new ByteBufferRewinder.Factory())
.append(File.class, ByteBuffer.class, new ByteBufferFileLoader.Factory())
.append(File.class, InputStream.class, new FileLoader.StreamFactory())
.append(File.class, File.class, new FileDecoder())
.append(File.class, ParcelFileDescriptor.class, new FileLoader.FileDescriptorFactory())
// Compilation with Gradle requires the type to be specified for UnitModelLoader here.
.append(File.class, File.class, UnitModelLoader.Factory.<File>getInstance())
/* Models */
.register(new InputStreamRewinder.Factory(arrayPool));
if (ParcelFileDescriptorRewinder.isSupported()) {
registry.register(new ParcelFileDescriptorRewinder.Factory());
}
registry
.append(int.class, InputStream.class, resourceLoaderStreamFactory)
.append(int.class, ParcelFileDescriptor.class, resourceLoaderFileDescriptorFactory)
.append(Integer.class, InputStream.class, resourceLoaderStreamFactory)
.append(Integer.class, ParcelFileDescriptor.class, resourceLoaderFileDescriptorFactory)
.append(Integer.class, Uri.class, resourceLoaderUriFactory)
.append(int.class, AssetFileDescriptor.class, resourceLoaderAssetFileDescriptorFactory)
.append(Integer.class, AssetFileDescriptor.class, resourceLoaderAssetFileDescriptorFactory)
.append(int.class, Uri.class, resourceLoaderUriFactory)
.append(String.class, InputStream.class, new DataUrlLoader.StreamFactory<String>())
.append(Uri.class, InputStream.class, new DataUrlLoader.StreamFactory<Uri>())
.append(String.class, InputStream.class, new StringLoader.StreamFactory())
.append(String.class, ParcelFileDescriptor.class, new StringLoader.FileDescriptorFactory())
.append(
String.class, AssetFileDescriptor.class, new StringLoader.AssetFileDescriptorFactory())
.append(Uri.class, InputStream.class, new AssetUriLoader.StreamFactory(context.getAssets()))
.append(
Uri.class,
AssetFileDescriptor.class,
new AssetUriLoader.FileDescriptorFactory(context.getAssets()))
.append(Uri.class, InputStream.class, new MediaStoreImageThumbLoader.Factory(context))
.append(Uri.class, InputStream.class, new MediaStoreVideoThumbLoader.Factory(context));
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.Q) {
registry.append(
Uri.class, InputStream.class, new QMediaStoreUriLoader.InputStreamFactory(context));
registry.append(
Uri.class,
ParcelFileDescriptor.class,
new QMediaStoreUriLoader.FileDescriptorFactory(context));
}
registry
.append(Uri.class, InputStream.class, new UriLoader.StreamFactory(contentResolver))
.append(
Uri.class,
ParcelFileDescriptor.class,
new UriLoader.FileDescriptorFactory(contentResolver))
.append(
Uri.class,
AssetFileDescriptor.class,
new UriLoader.AssetFileDescriptorFactory(contentResolver))
.append(Uri.class, InputStream.class, new UrlUriLoader.StreamFactory())
.append(URL.class, InputStream.class, new UrlLoader.StreamFactory())
.append(Uri.class, File.class, new MediaStoreFileLoader.Factory(context))
.append(GlideUrl.class, InputStream.class, new HttpGlideUrlLoader.Factory())
.append(byte[].class, ByteBuffer.class, new ByteArrayLoader.ByteBufferFactory())
.append(byte[].class, InputStream.class, new ByteArrayLoader.StreamFactory())
.append(Uri.class, Uri.class, UnitModelLoader.Factory.<Uri>getInstance())
.append(Drawable.class, Drawable.class, UnitModelLoader.Factory.<Drawable>getInstance())
.append(Drawable.class, Drawable.class, new UnitDrawableDecoder())
/* Transcoders */
.register(Bitmap.class, BitmapDrawable.class, new BitmapDrawableTranscoder(resources))
.register(Bitmap.class, byte[].class, bitmapBytesTranscoder)
.register(
Drawable.class,
byte[].class,
new DrawableBytesTranscoder(
bitmapPool, bitmapBytesTranscoder, gifDrawableBytesTranscoder))
.register(GifDrawable.class, byte[].class, gifDrawableBytesTranscoder);
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.M) {
ResourceDecoder<ByteBuffer, Bitmap> byteBufferVideoDecoder =
VideoDecoder.byteBuffer(bitmapPool);
registry.append(ByteBuffer.class, Bitmap.class, byteBufferVideoDecoder);
registry.append(
ByteBuffer.class,
BitmapDrawable.class,
new BitmapDrawableDecoder<>(resources, byteBufferVideoDecoder));
}
ImageViewTargetFactory imageViewTargetFactory = new ImageViewTargetFactory();
glideContext =
new GlideContext(
context,
arrayPool,
registry,
imageViewTargetFactory,
defaultRequestOptionsFactory,
defaultTransitionOptions,
defaultRequestListeners,
engine,
experiments,
logLevel);
}
在这里,registry的append方法虽然很多,但是都是有迹可循的。一句话总结就是,首先构建了不同的编码器和解码器,将各种类型对应的编码器和解码器。
Glide的加载,可以归纳为如下几个阶段:
model(数据源)–>data(转换数据)–>decode(解码)–>transformed(缩放)–>transcoded(转码)–>encoded(编码保存到本地)。
看完上面的代码,就可以理解为什么获取的LoadData是一个List了,举例传入的是一个String类型的Url,上面代码中就有针对这种情况的好几种解码器:
.append(String.class, InputStream.class, new DataUrlLoader.StreamFactory<String>())
.append(String.class, InputStream.class, new StringLoader.StreamFactory())
.......
.......
而这个append方法,就是添加到ModelLoaders中去。
再看看modelLoader.buildLoadData是如何构建LoadData的。
modelLoader.buildLoadData(还是以Model是String类型的Url举例)
//StringLoader
@Override
public LoadData<Data> buildLoadData(
@NonNull String model, int width, int height, @NonNull Options options) {
//将String转成Uri
Uri uri = parseUri(model);
if (uri == null || !uriLoader.handles(uri)) {
return null;
}
return uriLoader.buildLoadData(uri, width, height, options);
}
//HttpGlideUrlLoader
@Override
public LoadData<InputStream> buildLoadData(
@NonNull GlideUrl model, int width, int height, @NonNull Options options) {
// GlideUrls memoize parsed URLs so caching them saves a few object instantiations and time
// spent parsing urls.
GlideUrl url = model;
if (modelCache != null) {
url = modelCache.get(model, 0, 0);
if (url == null) {
modelCache.put(model, 0, 0, model);
url = model;
}
}
int timeout = options.get(TIMEOUT);
//新建一个HttpUrlFetcher类型的DataFetcher
return new LoadData<>(url, new HttpUrlFetcher(url, timeout));
}
buildLoadData就是根据各种情况,在这里Model是String,对应的DataFetcher就是HttpUrlFetcher。
在这里,就已经构造出LoadData了,现在就可以开始下载新资源。再回到SourceGenerator的startNextLoad方法中,开始下载!
startNextLoad()
private void startNextLoad(final LoadData<?> toStart) {
loadData.fetcher.loadData(
helper.getPriority(),
new DataCallback<Object>() {
@Override
public void onDataReady(@Nullable Object data) {
if (isCurrentRequest(toStart)) {
onDataReadyInternal(toStart, data);
}
}
@Override
public void onLoadFailed(@NonNull Exception e) {
if (isCurrentRequest(toStart)) {
onLoadFailedInternal(toStart, e);
}
}
});
}
这里的代码很简单,DataFetch调用loadData方法之后,在回调中处理成功或失败的情况。如果下载成功,回通过一个很长的回调,将资源缓存到内存缓存的activeResources中。、
DataCacheGenerator和ResourceCacheGenerator的原理与SourceGenerator基本是一致的,只不过一个用来加载原始的本地缓存图,另一个用来加载处理过的本地缓存。在这里就不分析了。
总结
这是Glide系列的最后一篇文章,解码和下载过程就省略了。
这是我第一次写博客,肯定有许多不足,希望大家帮我提一点意见,多交流交流,感谢!
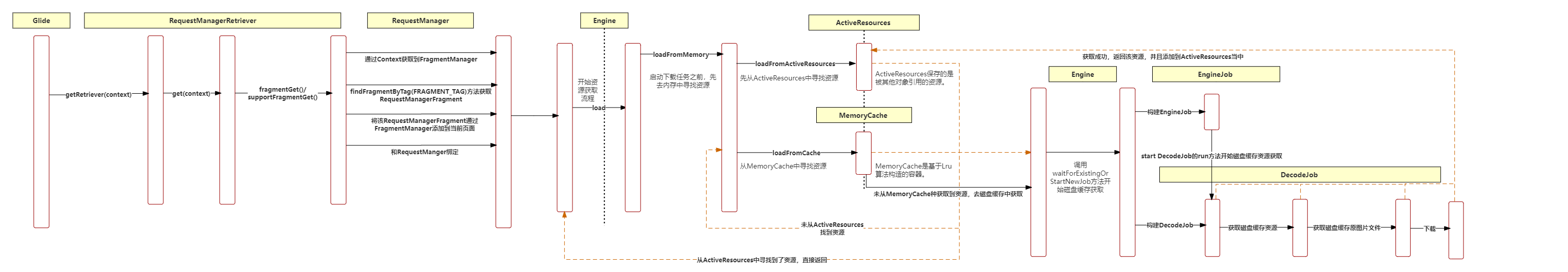
这个是我总结的整个Glide加载流程,请点击大图查看。






















 928
928











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








