Ice 出自ZeroC名门之下 , Ice 是一种面向对象的中间件平台。从根本上说,这意味着Ice 为构建面向对象的客户-服务器应用提供了工具、API 和库支持。Ice 应用适合于异构平台环境中使用:客户和服务器可以采用不同的编程语言,可以运行在不同的操作系统和机器架构上,并且可以使用多种网络技术进行通信。无论部署环境如何,这些应用的源码都是可移植的。
Zeroc ICE ( Internet Communications Engine )中间件号称标准统一,开源,跨平台,跨语言,分布式,安全,服务透明,负载均衡,面向对象,性能优越,防火期穿透,通讯屏蔽。因此相比 Corba,DCOM,SOAP,J2EE等的中间件技术,自然是集众多优点于一身,而却没有他们的缺点。
其采用C/S 模式结构,支持同步调用方式和异步调用方式,异步派发调用方式。支持跨语言的对象调用。多种语言之间采用共同的Slice(Specification Language for Ice)进行沟通。支持ice到C,JAVA,C#,VB,Python,Ruby,PHP等多种语言的映射。 Ice具有丰富的特性,其性能远是基于jms 所不能比的。
下面记录一个基于java的ice应用过程
1 下载最新安装包;
http://www.zeroc.com/download.html 根据操作系统和需要选择
我这里安装的是ice-3.3.0
2 安装之后的Ice相关路径:
slice2cpp,slice2java在/bin/下
Ice.jar 存储于/lib/java2/下
相关的Ice的库存储于/lib下.
3.创建ice文件
model.ice
#ifndef _MODEL
#define _MODEL
module com
{
module alan
{
module generated
{
module model
{
/**定义整型数组**/
sequence<int> IntegerArray;
/**自定义Map类型**/
dictionary<string, string> CustomMap;
/**消息类型**/
enum MessageType {ERROR,INFO,WARNING};
/**消息的操作类型**/
enum ActionType {Add,Modifiy,Remove,Stop,Start,Pause};
/** 消息结构 **/
["java:getset"]
struct Message {
/**消息类型**/
MessageType type;
/**消息类型**/
ActionType action;
/**相关id**/
IntegerArray relatedIds;
/**扩展属性**/
CustomMap extention;
};
};
};
};
};
#endif
service.ice
#ifndef _GENERATED
#define _GENERATED
#include <model.ice>
module com
{
module alan
{
module generated
{
interface MessageServiceIce
{
/**
* 向ice服务发送信息
* @param message 消息内容
* @return true 成功 false 失败
*/
string sendMessage(model::Message msg);
};
};
};
};
#endif
4.dos环境下执行(可以搞成.bat文件)
cd E:/workspace/ICETest/slice
E:/Ice-3.3.0/bin/slice2java -I. --output-dir=../src *.ice //生产代码
E:/Ice-3.3.0/bin/slice2html -I. --output-dir=doc *.ice//生产doc文档,可以忽略
5.代码生产后结构(实际应用中可以吧generted 打包放置到client和server端)
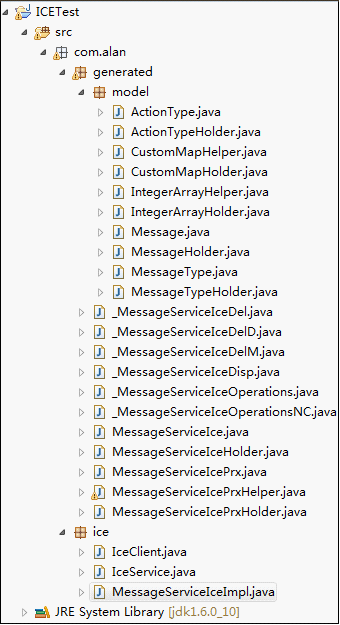
导入ice.jar编写代码,MessageServiceIceImpl .java代码:
public class MessageServiceIceImpl extends _MessageServiceIceDisp {
public String sendMessage(Message msg, Current __current) {
String str = msg.getType() +" "+ msg.getAction()+" " + Arrays.toString(msg.getRelatedIds());
return str;
}
}
服务器端代码:
public class IceService {
public static void main(String[] args){
int status = 0;
Communicator ic = null;
try{
ic = Util.initialize(args);
ObjectAdapter adapter = ic.createObjectAdapterWithEndpoints("testAdapter", "tcp -h localhost -p 10000");
ObjectImpl object = new MessageServiceIceImpl();
adapter.add(object, ic.stringToIdentity("testAdapter"));
adapter.activate();
ic.waitForShutdown();
} catch (Ice.LocalException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
status = 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
status = 1;
}
if (ic != null) {
try {
ic.destroy();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
status = 1;
}
}
System.exit(status);
}
客户端代码:
public class IceClient {
public static void main(String[] args){
int status = 0;
Communicator ic = null;
try{
ic = Ice.Util.initialize(args);
Ice.ObjectPrx base = ic.stringToProxy("testAdapter:tcp -h localhost -p 10000");
MessageServiceIcePrx client = MessageServiceIcePrxHelper.checkedCast(base);
if (client == null)
throw new Error("Invalid proxy");
Map<String ,String > map = new HashMap<String, String>();
Message msg = new Message(MessageType.INFO, ActionType.Add,new int[]{1},map);
System.out.println(client.sendMessage(msg));//这里调用了Service端方法
} catch (Ice.LocalException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
status = 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
status = 1;
}
if (ic != null) {
try {
ic.destroy();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
status = 1;
}
}
System.exit(status);
}
}
6.最后我们开始运行Server,再运行Client,看到控制台输出INFO Add [1],一个基本的ice应用就完成了!
关于ICE 更多请关注下篇:http://blog.csdn.net/liuzhoulong/article/details/6228333



























 1135
1135

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








