0 引言
图像处理算法有很多种,图像处理算法旨在提高图片质量,或者提取图片信息等。我们在摄像机捕获到图像后,经过图像处理往往能得到更高质量的图片。例如常见的去运动模糊、增强对比等。本次我将实现的是canny边缘检测,除此之外,我还做了直方图均衡,但本篇仅设计canny边缘检测,如果有需要直方图均衡,请私信。
下面进入正题~
1 实验目的
编程实现Canny边缘检测。
2 实验内容
2.1 流程图
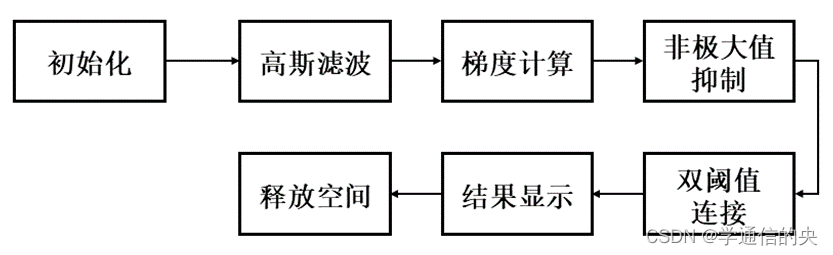
Canny边缘检测主要包括四个步骤:高斯平滑滤波、计算梯度方向和幅度、对梯度幅值应用非最大抑制细化边缘、用双阈值和连接分析检测并连接边缘。
下面我将具体介绍原理。
2.2 实验原理
2.2.1 高斯平滑滤波
边缘检测是一个高通滤波的过程,因为边缘往往位于图像灰度变化剧烈的地方。对图像提取边缘可以通过图像的二阶导数如拉普拉斯算子,或者一阶导数如Sobel,Prewitt,Robert等算子,一般情况下:
(1)一阶导数通常会产生较粗的边缘;
(2)二阶导数对精细细节,如细线、孤立点和噪声有较强的响应;
(3)二阶导数在灰度斜坡和灰度台阶过渡处会产生双边沿响应;
(4)二阶导数的符号可以确定边缘的过渡是从亮到暗还是从暗到亮;
(5)二阶导数对细节更敏感。
由于导数对噪声比较敏感,因此提取边缘之前最好先对图像进行平滑处理,以去除噪声(噪声是高频信号,通过低通滤波去除)。这里我进行了高斯滤波。
对含有加性高斯白噪声的图像,高斯一阶导数近似为最佳台阶边缘检测器。
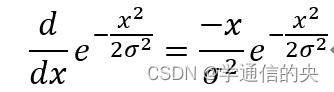
用G(x,y)表示高斯函数:
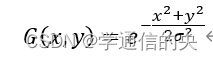
用G和f的卷积形成一幅光滑后的图像
![]()
//Step1. 高斯滤波 Remove noise (apply gaussian)
Mat image;
GaussianBlur(src, image, Size(3, 3), 1.5);2.2.2 计算梯度幅值和方向
计算梯度值和方向,其中:
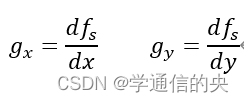
梯度的幅值为:
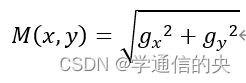
梯度的方向为:

在计算过程中,我使用了Sobel算子:
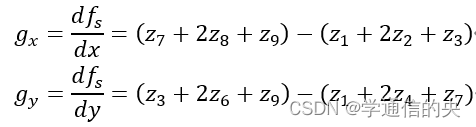
设像素点排列为:
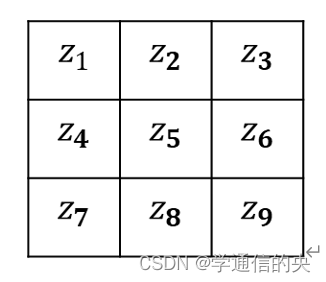
则Sobel算子为:
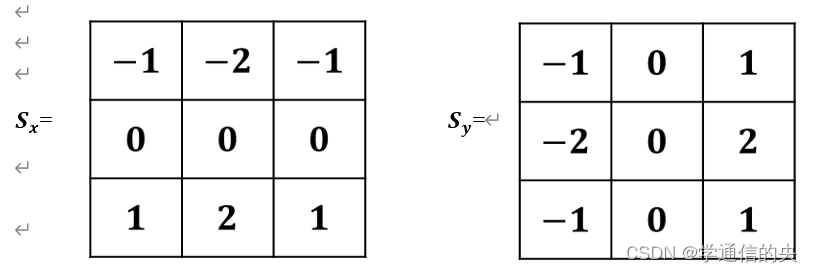
//Step2. 使用sobel计算相应的梯度幅值及方向. Calculate gradient (apply sobel operator)
Mat magX, magY;//X,Y方向的梯度
Sobel(image, magX, CV_32FC1, 1, 0, 3);
Sobel(image, magY, CV_32FC1, 0, 1, 3);
Mat Mag, Ori;//梯度幅值,幅角
cartToPolar(magX, magY, Mag, Ori, true);//幅角0~3602.2.3 对梯度幅值进行非最大抑制细化边缘
非极大值抑制是进行边缘检测的一个重要步骤,通俗意义上是指寻找像素点局部最大值。在每一点上,领域中心x与沿着其对应的梯度方向的两个像素相比,若中心像素为最大值,则保留,否则中心置0,这样可以抑制非极大值,保留局部梯度最大的点,以细化边缘。
在John Canny提出Canny算子的论文中,非极大值抑制时,他采用了近似处理的方法.将各点的梯度方向近似量化到0°、90°、45°、135°四个梯度方向上进行,每个像素点梯度方向按照距离这四个方向的相近程度用这四个方向来代替。通过量化,意味着图像中各点的梯度方向只能沿着0°、90°、45°、135°四个方向中的某一个。
如下图所示为选择的4个量化方向,每个方向对应邻域内的两个点,4个方向正好将邻域内的8个点应用完毕。
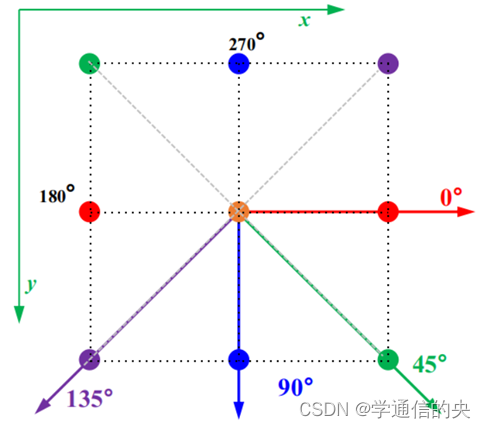
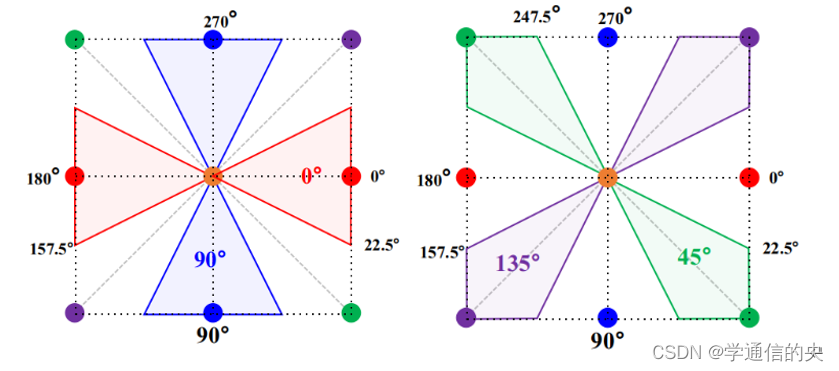
//Step3.Non-maximum supression 非极大值抑制
nonMaximumSuppression(Mag, Ori);
void nonMaximumSuppression(Mat& magnitudeImage, const Mat& directionImage)
{
Mat edgeMag_noMaxsup = Mat::zeros(magnitudeImage.size(), CV_32FC1);
//根据输入的角度,判断该点梯度方向位于位于那个区间
//[0,45,90,135]
auto judgeDir = [](float angle)->int {
if ((0 <= angle && angle < 22.5) || (157.5 <= angle && angle < 202.5) || (337.5 <= angle && angle < 360))//梯度方向为水平方向
return 0;
else if ((22.5 <= angle && angle < 67.5) || (202.5 <= angle && angle < 247.5))//45°方向
return 45;
else if ((67.5 <= angle && angle < 112.5) || ((247.5 <= angle && angle < 292.5)))
return 90;
else /*if( (112.5<=angle&&angle<157.5) || ((292.5<=angle&&angle<337.5)) )*/
return 135;
};
for (int r = 1; r < magnitudeImage.rows - 1; ++r)
{
for (int c = 1; c < magnitudeImage.cols - 1; ++c)
{
const float mag = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r, c);//当前位置梯度幅值
//将其量化到4个方向中进行计算
const float angle = directionImage.at<float>(r, c);
const int nDir = judgeDir(angle);
//非极大值抑制,8邻域的点进行比较,但只比较梯度方向
//或者采用线性插值的方式,在亚像素层面进行比较
//由于图像的y轴向下,x轴向右,因此注意这里的45°和135°
switch (nDir)
{
case 0://梯度方向为水平方向-邻域内左右比较
{
float left = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r, c - 1);
float right = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r, c + 1);
if (mag > left && mag >= right)
edgeMag_noMaxsup.at<float>(r, c) = mag;
break;
}
case 135://即我们平常认为的45°.邻域内右上 左下比较.
{
float right_top = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r - 1, c + 1);
float left_down = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r + 1, c - 1);
if (mag > right_top && mag >= left_down)
edgeMag_noMaxsup.at<float>(r, c) = mag;
break;
}
case 90://梯度方向为垂直方向-邻域内上下比较
{
float top = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r - 1, c);
float down = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r + 1, c);
if (mag > top && mag >= down)
edgeMag_noMaxsup.at<float>(r, c) = mag;
break;
}
case 45://邻域内右下 左上比较
{
float left_top = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r - 1, c - 1);
float right_down = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r + 1, c + 1);
if (mag > left_top && mag >= right_down)
edgeMag_noMaxsup.at<float>(r, c) = mag;
break;
}
default:
break;
}
}//每列
}//每行
edgeMag_noMaxsup.copyTo(magnitudeImage);
}2.2.4 双阈值和连接分析检测连接边缘
在施加非极大值抑制之后,剩余的像素可以更准确地表示图像中的实际边缘.然而,仍然存在由于噪声和颜色变化引起的一些边缘像素。为了解决这些杂散响应,必须用弱梯度值过滤边缘像素,并保留具有高梯度值的边缘像素,可以通过选择高低阈值来实现。
使用两个阈值,一个低阈值![]() 和一个高阈值
和一个高阈值![]() 。高低阈值的比率为2:1或3:1。
。高低阈值的比率为2:1或3:1。
如果某一像素位置的梯度幅值超过高阈值,该像素被保留为边缘像素。
如果某一像素位置的梯度幅值小于低阈值,该像素被排除。
如果某一像素位置的梯度幅值在两个阈值之间,则根据连通性来分类为边缘或者非边缘:该像素与确定为边缘的像素点邻接,则判定为边缘;否则为非边缘。
//Step4. 双阈值检测和边缘连接 Double thresholding
edgeDetect(Mag, TU, TL, edges);
void edgeDetect(const Mat& magnitude, int TU, int TL, Mat& edges)
{
int rows = magnitude.rows;
int cols = magnitude.cols;
edges = Mat(magnitude.size(), CV_8UC1, Scalar(0));
for (int y = 0; y < rows; y++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < cols; x++)
{
// 梯度幅值判断.//大于高阈值,为确定边缘点
if (magnitude.at<float>(y, x) >= TU)
{
followEdges(x, y, magnitude, TU, TL, edges);
}
}
}
}
void followEdges(int x, int y, const Mat& magnitude, int TU,
int TL, Mat& edges)
{
edges.at<uchar>(y, x) = 255;//该点与强边缘点邻接,故确定其为边缘点
for (int i = -1; i < 2; i++)//8邻域: (i,j) ∈ [-1 0 1].一共8个点,要去掉自身
{
for (int j = -1; j < 2; j++)
{
if (i == 0 && j == 0)//去除自身点
continue;
// 边界限制
if ((x + i >= 0) && (y + j >= 0) &&
(x + i < magnitude.cols) && (y + j < magnitude.rows))
{
// 梯度幅值边缘判断及连接
if ((magnitude.at<float>(y + j, x + i) > TL)
&& (edges.at<uchar>(y + j, x + i) != 255))//大于低阈值,且该点尚未被确定为边缘点
{
followEdges(x + i, y + j, magnitude, TU, TL, edges);
}
}
}
}
}3 实现结果
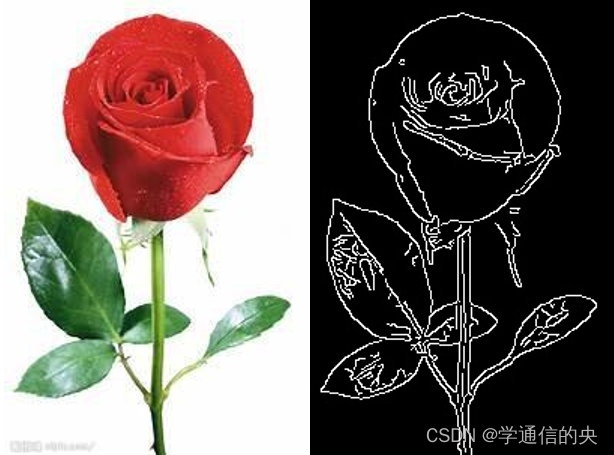
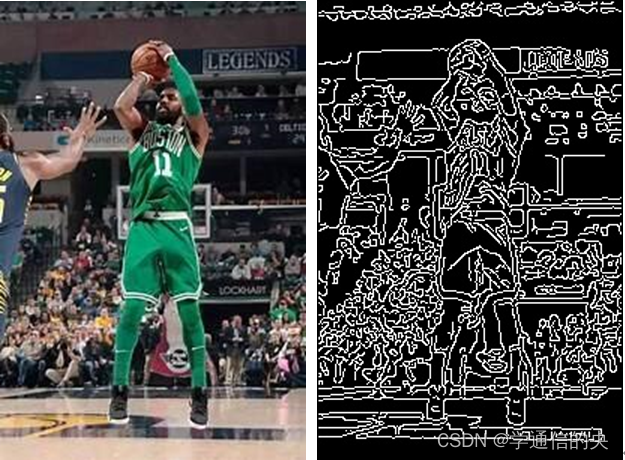


4 完整代码
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
/*
* 边缘连接:从确定边缘点出发,延长边缘
* @param x
* @param y 当前像素坐标
* @param magnitude 梯度幅值.CV_32FC1
* @param tUpper
* @param tLower 双阈值
* @param edges 边缘图 CV_8UC1
*/
void followEdges(int x, int y, const cv::Mat& magnitude, int TU,
int TL, cv::Mat& edges);
/*
* 边缘检测.通过滞后阈值,进行伪边缘去除和边缘连接
* @param magnitude 梯度幅值 CV_32FC1
* @param tUpper
* @param tLower 双阈值
* @param edges 边缘图 CV_8UC1
*/
void edgeDetect(const Mat& magnitude, int TU, int TL, Mat& edges);
/*
*非极大值抑制
* @param magnitudeImage CV_32FC1 各点的梯度幅值
* @param directionImage CV_32FC1 存储各点的梯度方向0-360°
*/
void nonMaximumSuppression(Mat& magnitudeImage, const Mat& directionImage);
/*
* 自定义Canny算法实现
* @param src
* @param edges
* @param upperThresh
* @param lowerThresh
*/
void myCanny(const Mat& src, Mat& edges, int TU, int TL)
{
//Step1. 高斯滤波 Remove noise (apply gaussian)
Mat image;
GaussianBlur(src, image, Size(3, 3), 1.5);
//Step2. 使用sobel计算相应的梯度幅值及方向. Calculate gradient (apply sobel operator)
Mat magX, magY;//X,Y方向的梯度
Sobel(image, magX, CV_32FC1, 1, 0, 3);
Sobel(image, magY, CV_32FC1, 0, 1, 3);
Mat Mag, Ori;//梯度幅值,幅角
cartToPolar(magX, magY, Mag, Ori, true);//幅角0~360
//Step3.Non-maximum supression 非极大值抑制
nonMaximumSuppression(Mag, Ori);
//Step4. 双阈值检测和边缘连接 Double thresholding
edgeDetect(Mag, TU, TL, edges);
}
void nonMaximumSuppression(Mat& magnitudeImage, const Mat& directionImage)
{
Mat edgeMag_noMaxsup = Mat::zeros(magnitudeImage.size(), CV_32FC1);
//根据输入的角度,判断该点梯度方向位于位于那个区间
//[0,45,90,135]
auto judgeDir = [](float angle)->int {
if ((0 <= angle && angle < 22.5) || (157.5 <= angle && angle < 202.5) || (337.5 <= angle && angle < 360))//梯度方向为水平方向
return 0;
else if ((22.5 <= angle && angle < 67.5) || (202.5 <= angle && angle < 247.5))//45°方向
return 45;
else if ((67.5 <= angle && angle < 112.5) || ((247.5 <= angle && angle < 292.5)))
return 90;
else /*if( (112.5<=angle&&angle<157.5) || ((292.5<=angle&&angle<337.5)) )*/
return 135;
};
for (int r = 1; r < magnitudeImage.rows - 1; ++r)
{
for (int c = 1; c < magnitudeImage.cols - 1; ++c)
{
const float mag = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r, c);//当前位置梯度幅值
//将其量化到4个方向中进行计算
const float angle = directionImage.at<float>(r, c);
const int nDir = judgeDir(angle);
//非极大值抑制,8邻域的点进行比较,但只比较梯度方向
//或者采用线性插值的方式,在亚像素层面进行比较
//由于图像的y轴向下,x轴向右,因此注意这里的45°和135°
switch (nDir)
{
case 0://梯度方向为水平方向-邻域内左右比较
{
float left = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r, c - 1);
float right = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r, c + 1);
if (mag > left && mag >= right)
edgeMag_noMaxsup.at<float>(r, c) = mag;
break;
}
case 135://即我们平常认为的45°.邻域内右上 左下比较.
{
float right_top = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r - 1, c + 1);
float left_down = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r + 1, c - 1);
if (mag > right_top && mag >= left_down)
edgeMag_noMaxsup.at<float>(r, c) = mag;
break;
}
case 90://梯度方向为垂直方向-邻域内上下比较
{
float top = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r - 1, c);
float down = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r + 1, c);
if (mag > top && mag >= down)
edgeMag_noMaxsup.at<float>(r, c) = mag;
break;
}
case 45://邻域内右下 左上比较
{
float left_top = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r - 1, c - 1);
float right_down = magnitudeImage.at<float>(r + 1, c + 1);
if (mag > left_top && mag >= right_down)
edgeMag_noMaxsup.at<float>(r, c) = mag;
break;
}
default:
break;
}
}//每列
}//每行
edgeMag_noMaxsup.copyTo(magnitudeImage);
}
void edgeDetect(const Mat& magnitude, int TU, int TL, Mat& edges)
{
int rows = magnitude.rows;
int cols = magnitude.cols;
edges = Mat(magnitude.size(), CV_8UC1, Scalar(0));
for (int y = 0; y < rows; y++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < cols; x++)
{
// 梯度幅值判断.//大于高阈值,为确定边缘点
if (magnitude.at<float>(y, x) >= TU)
{
followEdges(x, y, magnitude, TU, TL, edges);
}
}
}
}
void followEdges(int x, int y, const Mat& magnitude, int TU,
int TL, Mat& edges)
{
edges.at<uchar>(y, x) = 255;//该点与强边缘点邻接,故确定其为边缘点
for (int i = -1; i < 2; i++)//8邻域: (i,j) ∈ [-1 0 1].一共8个点,要去掉自身
{
for (int j = -1; j < 2; j++)
{
if (i == 0 && j == 0)//去除自身点
continue;
// 边界限制
if ((x + i >= 0) && (y + j >= 0) &&
(x + i < magnitude.cols) && (y + j < magnitude.rows))
{
// 梯度幅值边缘判断及连接
if ((magnitude.at<float>(y + j, x + i) > TL)
&& (edges.at<uchar>(y + j, x + i) != 255))//大于低阈值,且该点尚未被确定为边缘点
{
followEdges(x + i, y + j, magnitude, TU, TL, edges);
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
Mat srcImage = imread("E:\\visualC++\\my_Canny\\Irving.jpg", IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
int TU = 100;
int TL = 40;
Mat cannyEdges;
Mat cvcannyEdges;
myCanny(srcImage, cannyEdges, TU, TL);
imshow("original", srcImage);
imshow("myedges", cannyEdges);
imwrite("E:visualC++\\my_Canny\\canny.jpg", cannyEdges);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}






















 2万+
2万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








