上一篇博文讲了Java注解是什么、有什么作用。现在让我们来谈谈Java本身提供的一些注解,包括内置注解跟元注解(后面解释)。
概要
- 系统注解
- 内置注解
- @Deprecated
- @Override
- @SuppressWarnings
- 元注解
- @Retention
- @Target
- @Inherited
- @Documented
内置注解
Java本身提供了一些比较常用的注解,下面就分别介绍一下@Deprecated、@Override、@SuppressWarnings。
-
作用: 标示一个方法、类或属性已经过时,不再推荐使用。
-
-
/** * Annotation type used to mark program elements that should no longer be used * by programmers. Compilers produce a warning if a deprecated program element * is used. * * @since 1.5 */ @Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface Deprecated { }@Documented标明该注解要加入Javadoc文档 ,@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)标明该注解运行时可见(具体文章后面会介绍到)。
@Deprecated部分源码 -
-
-
User.java -
public class User { /** * 测试 @Deprecated 注解 */ @Deprecated public String deprecatedMethod(){ return "I am deprecated Method"; } //省略... } -
Test.java -
-
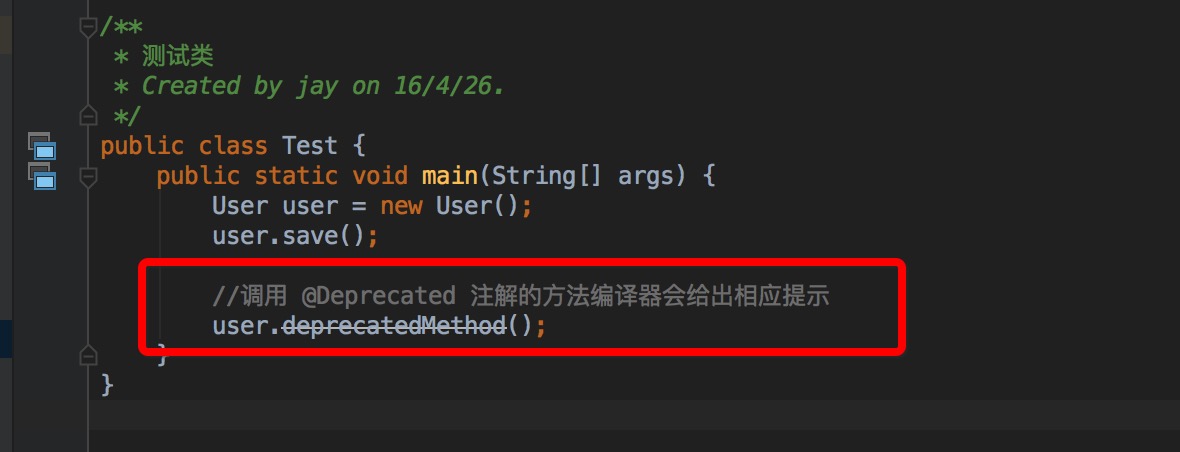
上面的代码中,
deprecatedMethod方法就是被@Deprecated注解的方法。
当调用该方法时,编译器就会检测到deprecatedMethod被@Deprecated注解了,然后就会做一些提示操作(比如画横线)。
@Deprecated使用示例代码: -
-
作用:标示子类的方法重载了父类的方法
-
-
/** * Annotation type used to mark methods that override a method declaration in a * superclass. Compilers produce an error if a method annotated with @Override * does not actually override a method in a superclass. * * @since 1.5 */ @Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) public @interface Override { }@Target(ElementType.METHOD)标明该注解可修饰元素为方法 ,@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)标明该注解为只在源码中可见(具体文章后面会介绍到)。
@Override部分源码 -
-
-
User.javapublic class User{ public String getProfile(){ String profile = "I am a normal user."; return profile; } } -
SpecialUser.javapublic class SpecialUser extends User{ @Override public String getProfile() { String profile = "I am special user, so I had override getProfile method."; return profile; } } -
上述代码中
SpecialUser继承了User并重写了getProfile方法,这里加上了@Override编译器就会知道SpecialUser是重写了User的方法,编译器就会在User类中找getProfile方法(如果User类中找不到就到User的父类去找,如此一直查找到基类),如果找不到就会报错。 -
但重写方法并不强制加上
@Override,但推荐的做法还是加上,因为如果不加上可能会出现下面的问题。 -
由于需求的变更,要把
User类中的getProfile更名为getDetail但忘记修改SpecialUser中的getProfile。 -
假设
SpecialUser中getProfile没有用@Override修饰,编译器就不会报错,编译器会认为你的getProfile是一个SpecialUser中的新方法(但这明显就不符合逻辑)。 -
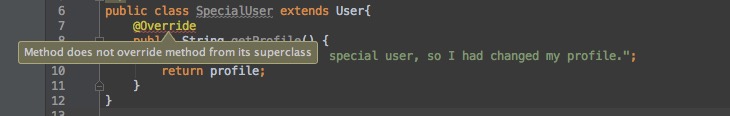
但如果你在
SpecialUser的getProfile前加上了@Override,编译的时候就会报错(提醒你复写的方法不存在,你就知道你忘记改SpecialUser中的getProfile为getDetail了),IDE工具中你也可以得到如下提示:
@Override用法示例代码 -
-
作用:让编译器忽略一些提醒(比如使用了过时的API)
-
-
/** * Annotation type used to indicate that the compiler should not issue the * specified warnings for the marked program element. Warnings are not only * suppressed for the annotated element but also for all program elements * contained in that element. * <p> * It is recommended that programmers always use this annotation on the most * deeply nested element where it is actually needed. * * @since 1.5 */ @Target( { ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) public @interface SuppressWarnings { /** * The list of warnings a compiler should not issue. */ public String[] value(); }@Target标明该注解可以注解的元素为 类、接口、枚举变量、成员变量、 方法、 参数、 构造器、 局部变量,@Retention标明该注解为只在源码中可见(后面具体介绍),它有一个 value 标明它需要传入一个 String[] 的参数(这里先不做具体讲解,后续文章会有介绍)。
@SuppressWarnings部分源码 -
-
-
属性值 作用 deprecation使用了不赞成使用的类或方法时的警告 path在类路径、源文件路径等中有不存在的路径时的警告 serial当在可序列化的类上缺少 serialVersionUID 定义时的警告 finally任何 finally 子句不能正常完成时的警告 fallthrough当 Switch 程序块直接通往下一种情况而没有 Break 时的警告 unchecked执行了未检查的转换时的警告,例如当使用集合时没有用泛型 (Generics) 来指定集合保存的类型 all关于以上所有情况的警告
value的可选值 -
-
-
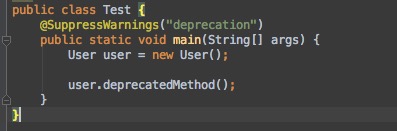
开发过程中难免会用到一些不推荐使用的方法,但又不希望IDE一直给出划线的提示(强迫症。。。),这里就可以用到这个注解。
上面我们在讲@Deprecated注解的时候把deprecatedMethod注解了,所以使用的时候会被划横线,但是加上@SuppressWarnings注解之后就可以去除掉相应的提示。
@SuppressWarnings用法示例代码 -
开发过程中难免会用到一些不推荐使用的方法,但又不希望IDE一直给出划线的提示(强迫症。。。),这里就可以用到这个注解。
@Deprecated
@Override
@SuppressWarnings
元注解
-
在上一篇文章中就提到注解是有可见范围的(运行时可见、构建时可见、编译时可见),控制注解什么时候可见的就是
@Retention。 -
作用:标示注解在什么时候可见(运行时可见、仅在.class文件及源代码中可见、仅在源代码中可见)
-
-
/** * Defines a meta-annotation for determining the scope of retention for an * annotation. If the retention annotation is not set {@code * RetentionPolicy.CLASS} is used as default retention. * * @since 1.5 */ @Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) public @interface Retention { RetentionPolicy value(); }@Document标明该注解需要加到Javadoc文档中,@Retention标明该注解为运行时可见,@Target标明该注解可注解元素类型为注解类型,同样它也需要传入一个value属性(用于标明什么时候可见)。
@Retention部分源码 -
-
-
属性值 作用 RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME标示该注解可以再运行时通过反射找到(ORM框架许多注解使用了该参数) RetentionPolicy.CLASS标示该注解保存在.class文件中,但在运行时不能通过反射找到 RetentionPolicy.SOURSE标示该注解只在源码中可见
value可用参数 -
-
-
自定义了两个注解(如何自定义后面文章会介绍),RuntimeAnnotation(运行时可见注解)、SourceAnnotation(源码中可见注解)
-
RuntimeAnnotation.java@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface RuntimeAnnotation { } -
SourceAnnotation.java@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) public @interface SourceAnnotation { } -
User.javapublic class User { @RuntimeAnnotation private String name = ""; @SourceAnnotation private String age = ""; public void testRetentionAnnotation() { /** * 通过反射获取运行时注解 */ Class thisClass = this.getClass(); Field[] fields = thisClass.getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field : fields) { if (field.isAnnotationPresent(RuntimeAnnotation.class)) { System.out.println("Get Runtime Annotation Success in run time!"); } else if (field.isAnnotationPresent(SourceAnnotation.class)) { System.out.println("Get Source Annotation Success in run time!"); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { new User().testRetentionAnnotation(); } } -
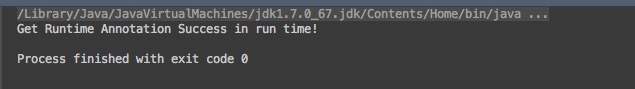
上面利用了简单的反射知识(运行时),运行
User的main方法,我们看到输出了“Get Runtime Annotation Success in run time!“,所以@Retention确实标示了注解的可见范围。 -
运行结果:
@Retention用法示例代码 -
-
-
/** * Defines a meta-annotation for determining what {@link ElementType}s an * annotation can be applied to. * * @since 1.5 */ @Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) public @interface Target { ElementType[] value(); }@Documented标明该注解要加入Javadoc文档中、@Retention标明该注解运行时可见、@Target标明该注解可注解元素为为注解类型,同时它也有一个value参数(下面会有该参数的取值跟意义介绍)。
@Retention部分源码 -
-
-
属性值 作用 ElementType.PACKAGE标示该注解用于注解包声明 ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE标示该注解用于注解其他注解 ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR标示该注解用于注解构造函数 ElementType.FIELD标示该注解用于注解成员变量 ElementType.METHOD标示该注解用于注解方法 ElementType.TYPE标示该注解用于注解类,接口,枚举类型 ElementType.PARAMETER标示该注解用于注解参数 ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE标示该注解用于注解局部变量
value可用参数 -
-
-
自定义了两个注解,MethodAnnotation(注解方法类型元素)、FieldAnnotation(注解成员变量)
-
MethodAnnotation.java@Target(ElementType.METHOD) public @interface MethodAnnotation { } -
FieldAnnotation.java@Target(ElementType.FIELD) public @interface FieldAnnotation { } -
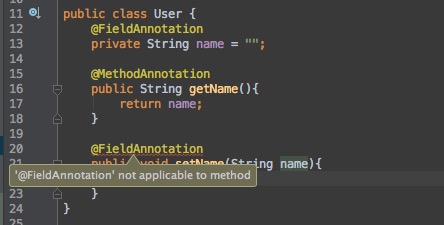
User.javapublic class User { @FieldAnnotation private String name = ""; @MethodAnnotation public String getName(){ return name; } public void setName(String name){ this.name = name; } } -
上面的代码我们就可以知道拥有不同Target的注解可以用来注解不同的元素。
-
当我们把只可用于方法变量的注解用到函数上就会出错(比如使用@FieldAnnotation去注解setName方法)。
@Target使用示例代码 -
-
-
/** * Defines a meta-annotation for indicating that an annotation is automatically * inherited. * * @since 1.5 */ @Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) public @interface Inherited { }@Documented标明该注解要加入Javadoc文档中、@Retention标明该注解运行时可见、@Target标明该注解可注解元素为为注解类型
@Inherited部分源码 -
-
InheritedAnnotation.java@Inherited @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface InheritedAnnotation { } -
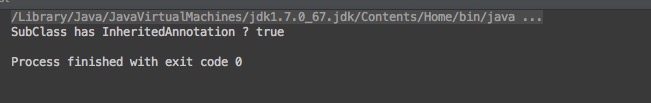
Test.javapublic class Test { @InheritedAnnotation public class BaseClass { } public class SubClass extends BaseClass { } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("SubClass has InheritedAnnotation ? " + SubClass.class.isAnnotationPresent(InheritedAnnotation.class)); } }运行结果:
上面运行结果可以看出
SubClass确实也有拥有InheritedAnnotation注解。 -
-
/** * Defines a meta-annotation for indicating that an annotation is documented and * considered part of the public API. * * @since 1.5 */ @Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) public @interface Documented { }@Documented标明该注解要加入Javadoc文档中、@Retention标明该注解运行时可见、@Target标明该注解可注解元素为为注解类型
@Documented部分源码 -
-
- 直接在需要加入到JavaDoc的地方加上该注解即可。
@Documented使用
作用:负责注解其他注解(可用于自定义注解)
@Retention
@Target
作用:标示该注解用于注解什么元素(类、方法、变量等)
@Inherited
作用:指定被它修饰的注解具有继承性(比如InheritedAnnotation注解了BaseClass,SubClass继承了BaseClass,这时SubClass也会具有InheritedAnnotation注解,但方法跟参数等的注解不会被继承)
@Inherited使用示例代码
@Documented
作用:表明被注解元素应该加入到JavaDoc(文档)
总结
本文主要介绍了Java提供的常用注解(@Deprecated、@Override、@SuppressWarnings)以及自定义注解时需要用到的元注解(@Retetion、@Target、@Inherited、@Documented),全文篇幅较长但讲的内容整体比较简单,主要还是靠自己动手打代码实践。
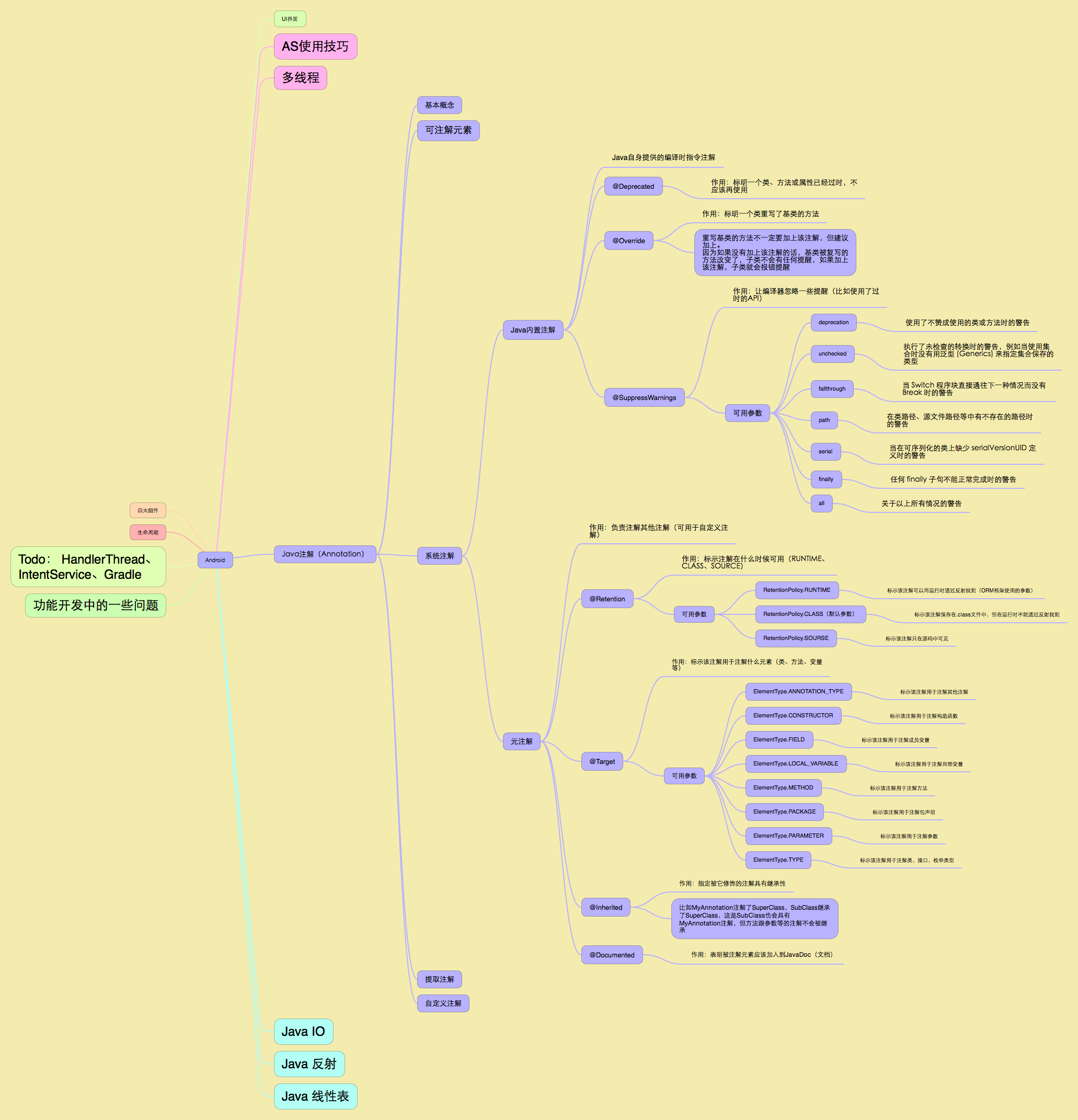
思路脑图
完整的思维导图可以在我的github上面查找,地址为https://github.com/liujiescut/AndroidKnowledge
下一篇文章将介绍 如何提取注解。






















 27万+
27万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








