首先下载eclipse和cdt,我的版本号依次是:Version: Indigo Service Release 2和Version: 1.0.0.201202111925,再下载windows的ndk,我使用的是android-ndk-r9d
什么cygwin这等东西,太恶心了,下载慢,大的要命!复杂,今天给一个最爽的编译教程。
前面的cdt插件怎么这里pass,网上教程很多的。直接配置。。。
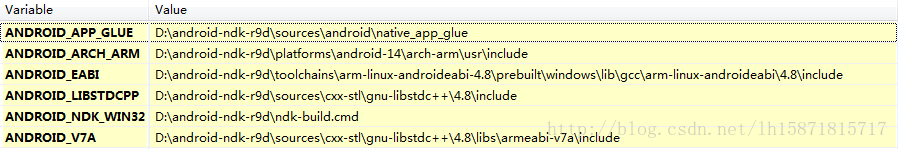
启动eclipse,然后点Windows-Prefrences-C/C++-Build-Envionment,添加以下路径
然后创建一个android工程,把代码全部删除,资源全部删除,AndroidManifest.xml内容如下
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
- package="com.example.native_activity"
- android:versionCode="1"
- android:versionName="1.0" >
- <uses-sdk
- android:minSdkVersion="9"
- tools:ignore="UsesMinSdkAttributes" />
- <application
- android:hasCode="false"
- android:label="纯CPP应用"
- tools:ignore="AllowBackup,MissingApplicationIcon" >
- <activity
- android:name="android.app.NativeActivity"
- android:configChanges="orientation|keyboardHidden" >
- <!-- Tell NativeActivity the name of or .so -->
- <meta-data
- android:name="android.app.lib_name"
- android:value="native-activity" />
- <intent-filter>
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
- </intent-filter>
- </activity>
- </application>
- </manifest>
然后创建jni目录,里面放三个文件,依次是Android.mk
- LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir)
- include $(CLEAR_VARS)
- LOCAL_MODULE := native-activity
- LOCAL_SRC_FILES := main.cpp
- LOCAL_LDLIBS := -llog -landroid -lEGL -lGLESv1_CM
- LOCAL_STATIC_LIBRARIES := android_native_app_glue
- include $(BUILD_SHARED_LIBRARY)
- $(call import-module,android/native_app_glue)
Application.mk
- APP_PLATFORM := android-14
main.cpp
- #include <jni.h>
- #include <errno.h>
- #include <EGL/egl.h>
- #include <GLES/gl.h>
- #include <string.h>
- #include <android/sensor.h>
- #include <android/log.h>
- #include <android_native_app_glue.h>
- #define LOGI(...) ((void)__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO, "native-activity", __VA_ARGS__))
- #define LOGW(...) ((void)__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_WARN, "native-activity", __VA_ARGS__))
- /**
- * Our saved state data.
- */
- struct saved_state {
- float angle;
- int32_t x;
- int32_t y;
- };
- /**
- * Shared state for our app.
- */
- struct engine {
- struct android_app* app;
- ASensorManager* sensorManager;
- const ASensor* accelerometerSensor;
- ASensorEventQueue* sensorEventQueue;
- int animating;
- EGLDisplay display;
- EGLSurface surface;
- EGLContext context;
- int32_t width;
- int32_t height;
- struct saved_state state;
- };
- /**
- * Initialize an EGL context for the current display.
- */
- static int engine_init_display(struct engine* engine) {
- // initialize OpenGL ES and EGL
- /*
- * Here specify the attributes of the desired configuration.
- * Below, we select an EGLConfig with at least 8 bits per color
- * component compatible with on-screen windows
- */
- const EGLint attribs[] = { EGL_SURFACE_TYPE, EGL_WINDOW_BIT, EGL_BLUE_SIZE,
- 8, EGL_GREEN_SIZE, 8, EGL_RED_SIZE, 8, EGL_NONE };
- EGLint w, h, dummy, format;
- EGLint numConfigs;
- EGLConfig config;
- EGLSurface surface;
- EGLContext context;
- EGLDisplay display = eglGetDisplay(EGL_DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
- eglInitialize(display, 0, 0);
- /* Here, the application chooses the configuration it desires. In this
- * sample, we have a very simplified selection process, where we pick
- * the first EGLConfig that matches our criteria */
- eglChooseConfig(display, attribs, &config, 1, &numConfigs);
- /* EGL_NATIVE_VISUAL_ID is an attribute of the EGLConfig that is
- * guaranteed to be accepted by ANativeWindow_setBuffersGeometry().
- * As soon as we picked a EGLConfig, we can safely reconfigure the
- * ANativeWindow buffers to match, using EGL_NATIVE_VISUAL_ID. */
- eglGetConfigAttrib(display, config, EGL_NATIVE_VISUAL_ID, &format);
- ANativeWindow_setBuffersGeometry(engine->app->window, 0, 0, format);
- surface = eglCreateWindowSurface(display, config, engine->app->window,
- NULL);
- context = eglCreateContext(display, config, NULL, NULL);
- if (eglMakeCurrent(display, surface, surface, context) == EGL_FALSE) {
- LOGW("Unable to eglMakeCurrent");
- return -1;
- }
- eglQuerySurface(display, surface, EGL_WIDTH, &w);
- eglQuerySurface(display, surface, EGL_HEIGHT, &h);
- engine->display = display;
- engine->context = context;
- engine->surface = surface;
- engine->width = w;
- engine->height = h;
- engine->state.angle = 0;
- // Initialize GL state.
- glHint(GL_PERSPECTIVE_CORRECTION_HINT, GL_FASTEST);
- glEnable(GL_CULL_FACE);
- glShadeModel(GL_SMOOTH);
- glDisable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
- return 0;
- }
- /**
- * Just the current frame in the display.
- */
- static void engine_draw_frame(struct engine* engine) {
- if (engine->display == NULL) {
- // No display.
- return;
- }
- // Just fill the screen with a color.
- glClearColor(((float) engine->state.x) / engine->width, engine->state.angle,
- ((float) engine->state.y) / engine->height, 1);
- glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
- eglSwapBuffers(engine->display, engine->surface);
- }
- /**
- * Tear down the EGL context currently associated with the display.
- */
- static void engine_term_display(struct engine* engine) {
- if (engine->display != EGL_NO_DISPLAY) {
- eglMakeCurrent(engine->display, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_SURFACE,
- EGL_NO_CONTEXT);
- if (engine->context != EGL_NO_CONTEXT) {
- eglDestroyContext(engine->display, engine->context);
- }
- if (engine->surface != EGL_NO_SURFACE) {
- eglDestroySurface(engine->display, engine->surface);
- }
- eglTerminate(engine->display);
- }
- engine->animating = 0;
- engine->display = EGL_NO_DISPLAY;
- engine->context = EGL_NO_CONTEXT;
- engine->surface = EGL_NO_SURFACE;
- }
- /**
- * Process the next input event.
- */
- static int32_t engine_handle_input(struct android_app* app,
- AInputEvent* event) {
- struct engine* engine = (struct engine*) app->userData;
- if (AInputEvent_getType(event) == AINPUT_EVENT_TYPE_MOTION) {
- engine->animating = 1;
- engine->state.x = AMotionEvent_getX(event, 0);
- engine->state.y = AMotionEvent_getY(event, 0);
- return 1;
- }
- return 0;
- }
- /**
- * Process the next main command.
- */
- static void engine_handle_cmd(struct android_app* app, int32_t cmd) {
- struct engine* engine = (struct engine*) app->userData;
- switch (cmd) {
- case APP_CMD_SAVE_STATE:
- // The system has asked us to save our current state. Do so.
- engine->app->savedState = malloc((size_t)sizeof(struct saved_state));
- *((struct saved_state*) engine->app->savedState) = engine->state;
- engine->app->savedStateSize = sizeof(struct saved_state);
- break;
- case APP_CMD_INIT_WINDOW:
- // The window is being shown, get it ready.
- if (engine->app->window != NULL) {
- engine_init_display(engine);
- engine_draw_frame(engine);
- }
- break;
- case APP_CMD_TERM_WINDOW:
- // The window is being hidden or closed, clean it up.
- engine_term_display(engine);
- break;
- case APP_CMD_GAINED_FOCUS:
- // When our app gains focus, we start monitoring the accelerometer.
- if (engine->accelerometerSensor != NULL) {
- ASensorEventQueue_enableSensor(engine->sensorEventQueue,
- engine->accelerometerSensor);
- // We'd like to get 60 events per second (in us).
- ASensorEventQueue_setEventRate(engine->sensorEventQueue,
- engine->accelerometerSensor, (1000L / 60) * 1000);
- }
- break;
- case APP_CMD_LOST_FOCUS:
- // When our app loses focus, we stop monitoring the accelerometer.
- // This is to avoid consuming battery while not being used.
- if (engine->accelerometerSensor != NULL) {
- ASensorEventQueue_disableSensor(engine->sensorEventQueue,
- engine->accelerometerSensor);
- }
- // Also stop animating.
- engine->animating = 0;
- engine_draw_frame(engine);
- break;
- }
- }
- /**
- * This is the main entry point of a native application that is using
- * android_native_app_glue. It runs in its own thread, with its own
- * event loop for receiving input events and doing other things.
- */
- void android_main(struct android_app* state) {
- struct engine engine = {0};
- // Make sure glue isn't stripped.
- app_dummy();
- state->userData = &engine;
- state->onAppCmd = engine_handle_cmd;
- state->onInputEvent = engine_handle_input;
- engine.app = state;
- // Prepare to monitor accelerometer
- engine.sensorManager = ASensorManager_getInstance();
- engine.accelerometerSensor = ASensorManager_getDefaultSensor(
- engine.sensorManager, ASENSOR_TYPE_ACCELEROMETER);
- engine.sensorEventQueue = ASensorManager_createEventQueue(
- engine.sensorManager, state->looper, LOOPER_ID_USER, NULL, NULL);
- if (state->savedState != NULL) {
- // We are starting with a previous saved state; restore from it.
- engine.state = *(struct saved_state*) state->savedState;
- }
- // loop waiting for stuff to do.
- while (true) {
- // Read all pending events.
- int ident;
- int events;
- struct android_poll_source* source;
- // If not animating, we will block forever waiting for events.
- // If animating, we loop until all events are read, then continue
- // to draw the next frame of animation.
- while ((ident = ALooper_pollAll(engine.animating ? 0 : -1, NULL,
- &events, (void**) &source)) >= 0) {
- // Process this event.
- if (source != NULL) {
- source->process(state, source);
- }
- // If a sensor has data, process it now.
- if (ident == LOOPER_ID_USER) {
- if (engine.accelerometerSensor != NULL) {
- ASensorEvent event;
- while (ASensorEventQueue_getEvents(engine.sensorEventQueue,
- &event, 1) > 0) {
- LOGI("accelerometer: x=%f y=%f z=%f", event.acceleration.x, event.acceleration.y, event.acceleration.z);
- }
- }
- }
- // Check if we are exiting.
- if (state->destroyRequested != 0) {
- engine_term_display(&engine);
- return;
- }
- }
- if (engine.animating) {
- // Done with events; draw next animation frame.
- engine.state.angle += .01f;
- if (engine.state.angle > 1) {
- engine.state.angle = 0;
- }
- engine_draw_frame(&engine);
- }
- }
- }
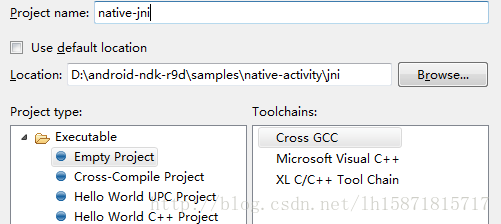
创建完成收工,然后创建另外一个工程。路径必须是刚才创建工程的jni目录,名字随便,重点看图
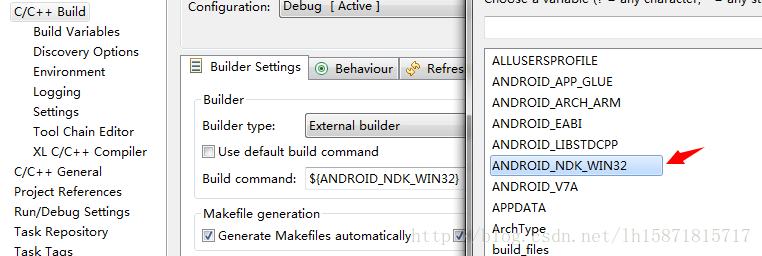
好了点完成,然后打开main.cpp发现N多错误,直接下设置一下环境变量,右键工程,属性(是刚创建的C++工程)
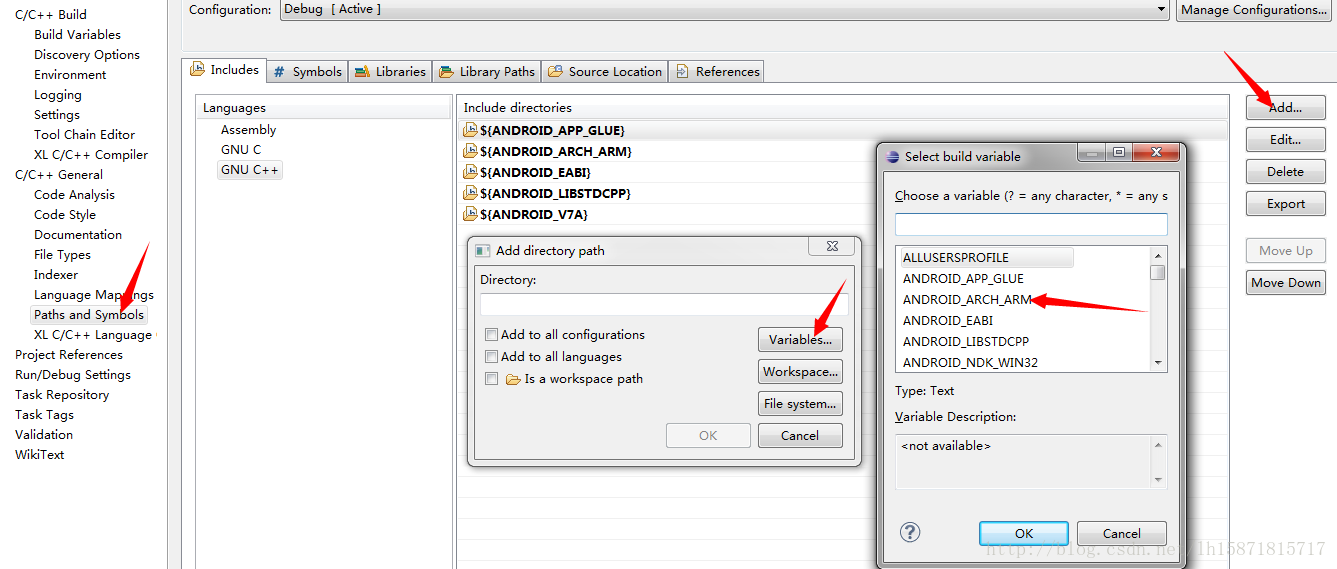
接下来看图,把所有的库加进去。
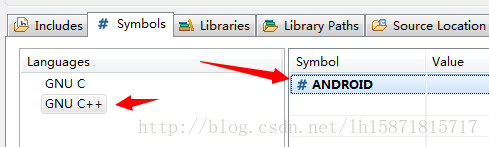
最后加一个Symbol,其实就是定义一个宏,告诉编译器我现在的平台是Android,add
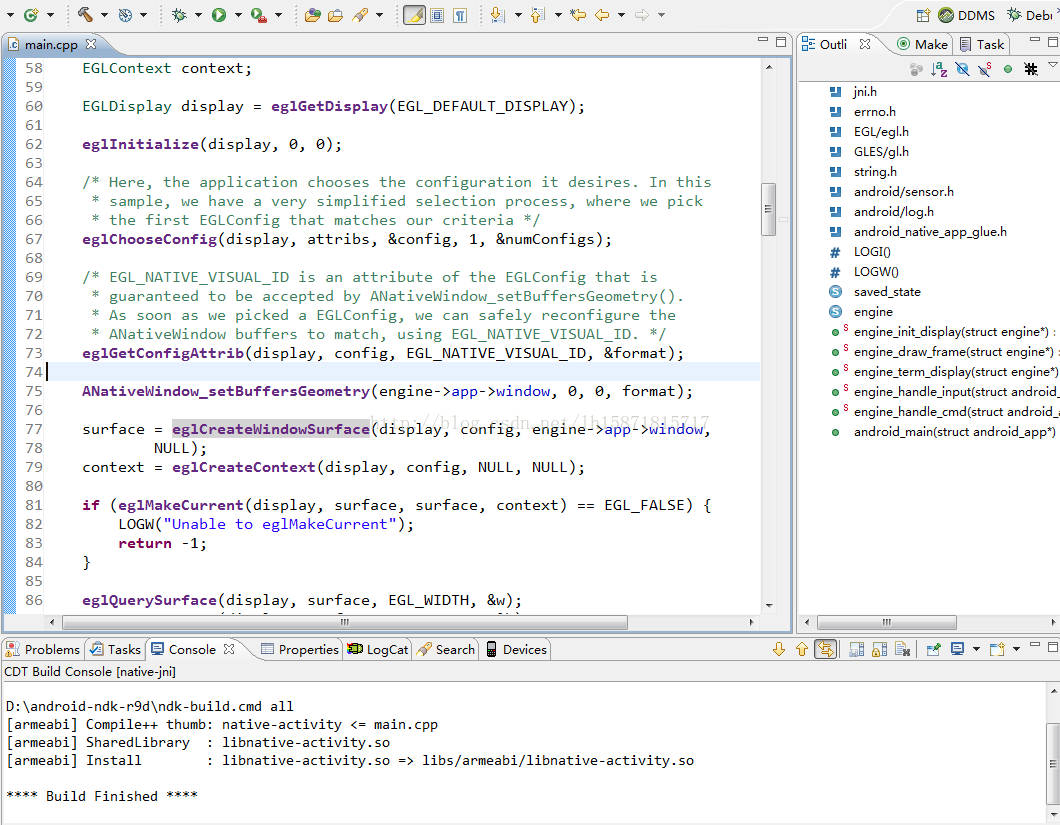
最后点OK,所有的函数都能正常识别,提示功能也可以用了。开发效率高多了。编译直接点锤子就行了。
然后在原来的工程运行安装就行了!






















 3158
3158











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








