main.c/*
*2013-11-7
*双向链表的基本操作,类似于单向链表,只不过多出了一个前节点指针
*基本操作详见代码中
*/
#include "D_List.h"
int main(void)
{
pDLIST pHead = creat_dlist();
traverse(pHead);
en_dlist(pHead, 3, 8);
traverse(pHead);
search(pHead, 8);
search(pHead, 65);
out_dlist(pHead, 5);
traverse(pHead);
clear(pHead);
traverse(pHead);
return 0;
}
以下是D_List.h
#ifndef D_LIST_H
#define D_LIST_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct DList //定义链表结构体
{
ElemType data;
struct DList * prior;
struct DList * next;
}DLIST, *pDLIST;
pDLIST creat_dlist();
void en_dlist(pDLIST, int pos, ElemType val);
void out_dlist(pDLIST, int pos);
bool is_empty(pDLIST);
void traverse(pDLIST);
int len_dlist(pDLIST);
void clear(pDLIST);
void search(pDLIST, int);
#endif
D_List.cpp
//功能实现
#include "D_List.h"
pDLIST creat_dlist()
{
pDLIST head = (pDLIST)malloc(sizeof(DLIST));//创建头节点
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("分配内存失败!!!\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
head->prior = head->next = NULL;
int n, i;
printf("请输入你要创建的节点个数 :n = ");
scanf("%d", &n);
srand(time(NULL));
pDLIST pNext = NULL;
for ( i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
pDLIST pNew = (pDLIST)malloc(sizeof(DLIST));
if (NULL == pNew)
{
printf("内存分配失败!!!\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
pNext = head->next; //保存下一个节点
pNew->data = rand()%100; //放入数据
head->next = pNew;
pNew->prior = head;
pNew->next = pNext;
if(pNext != NULL)
{
pNext->prior = pNew;
}
}
}
return head;
}
}
//插入第pos个节点,其中p是移动到了pos-1的位置,这种用法比较好!!
void en_dlist(pDLIST pL, int pos, ElemType val)
{
int i = 0;
pDLIST p = pL;
while (NULL != p && i < pos-1) //将p指到pos-1所在的位置
{
i++;
p = p->next;
}
if (i > pos-1 || NULL == p)
{
printf("你插入的节点位置有问题!位置为:pos = %d !!\n", pos);
return;
}
else
{
pDLIST q = p->next;
pDLIST pNew = (pDLIST)malloc(sizeof(DLIST));
pNew->data = val;
p->next = pNew;
pNew->prior = p;
pNew->next = q;
if (q != NULL)
{
q->prior = pNew;
}
printf("第 %d 个节点 %d 插入成功!!\n", pos, val);
return;
}
}
void out_dlist(pDLIST pL, int pos)
{
int i = 0;
pDLIST p = pL;
while (NULL != p->next && i < pos-1)
{
i++;
p = p->next;
}
if (i > pos-1 || NULL == p->next)
{
printf("你删除的节点不存在!!你要删除的位置为pos = %d \n", pos);
return;
}
else
{
pDLIST temp = p->next;
pDLIST q = temp->next;
p->next = q;
printf("第 %d 个节点 %d 删除成功!!\n", pos, temp->data);
if (q != NULL)
{
q->prior = q;
}
free(temp);
temp = NULL;
}
}
void traverse(pDLIST pL)
{
if (is_empty(pL))
{
printf("链表为空,不能遍历!!!!!\n");
return;
}
pDLIST p = pL->next;
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("%d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void search(pDLIST pL, int val)
{
int i = 0 ;
int j = 0;
pDLIST p = pL->next;
while (p != NULL)
{
i++;
if (p->data == val)
{
j++;
printf("%d 是第 %d 个节点!! \n",val , i);
}
p = p->next;
}
if (j == 0)
{
printf("%d不在这个链表中!!\n", val);
}
}
void clear(pDLIST pL)
{
pDLIST p = pL->next;
pL->next = NULL;
printf("清空链表………\n");
while (p != NULL)
{
pDLIST q = p->next;
free(p);
p = q;
}
}
int len_dlist(pDLIST pL)
{
int len=0;
pDLIST p = pL->next;
while (NULL != p)
{
len++;
p = p->next;
}
return len;
}
bool is_empty(pDLIST pL)
{
if (pL->next == NULL && pL->prior == NULL)
{
return true;
}
else return false;
}
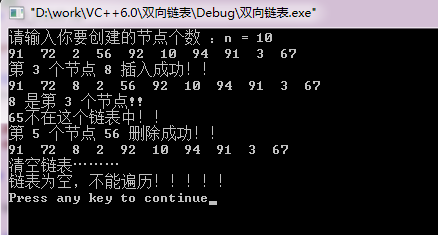
测试结果为:






















 4064
4064











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








