blur
Blurs an image using the normalized box filter.
-
C++:
void
blur
(InputArray
src, OutputArray
dst, Size
ksize, Point
anchor=Point(-1,-1), int
borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT
)
-
Python:
cv2.
blur
(src, ksize
[, dst
[, anchor
[, borderType
]
]
]
) → dst
-
Parameters: - src – input image; it can have any number of channels, which are processed independently, but the depth should be CV_8U, CV_16U, CV_16S, CV_32F or CV_64F.
- dst – output image of the same size and type as src.
- ksize – blurring kernel size.
- anchor – anchor point; default value Point(-1,-1) means that the anchor is at the kernel center.
- borderType – border mode used to extrapolate pixels outside of the image.
- 边界模式用于推断图片以外的像素
- The function smoothes an image using the kernel:

The call blur(src, dst, ksize, anchor, borderType) is equivalent to boxFilter(src, dst, src.type(), anchor, true, borderType) .
See also
boxFilter(), bilateralFilter(), GaussianBlur(), medianBlur()
归一化块滤波器 (Normalized Box Filter)
-
最简单的滤波器, 输出像素值是核窗口内像素值的均值 ( 所有像素加权系数相等)
-
核如下:
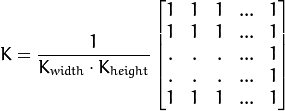
归一化块滤波器:
OpenCV函数 blur 执行了归一化块平滑操作。
我们输入4个实参 (详细的解释请参考 Reference):
- src: 输入图像
- dst: 输出图像
- Size( w,h ): 定义内核大小( w 像素宽度, h 像素高度)
- Point(-1, -1): 指定锚点位置(被平滑点), 如果是负值,取核的中心为锚点。
GaussianBlur
Blurs an image using a Gaussian filter.
-
C++:
void
GaussianBlur
(InputArray
src, OutputArray
dst, Size
ksize, double
sigmaX, double
sigmaY=0, int
borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT
)
-
Python:
cv2.
GaussianBlur
(src, ksize, sigmaX
[, dst
[, sigmaY
[, borderType
]
]
]
) → dst
-
Parameters: - src – input image; the image can have any number of channels, which are processed independently, but the depth should be CV_8U, CV_16U, CV_16S, CV_32F or CV_64F.
- dst – output image of the same size and type as src.
- ksize – Gaussian kernel size. ksize.width and ksize.height can differ but they both must be positive and odd. Or, they can be zero’s and then they are computed from sigma* .
- sigmaX – Gaussian kernel standard deviation in X direction.
- sigmaY – Gaussian kernel standard deviation in Y direction; if sigmaY is zero, it is set to be equal to sigmaX, if both sigmas are zeros, they are computed from ksize.width andksize.height , respectively (see getGaussianKernel() for details); to fully control the result regardless of possible future modifications of all this semantics, it is recommended to specify all of ksize, sigmaX, and sigmaY.
- borderType – pixel extrapolation method (see borderInterpolate() for details).
The function convolves the source image with the specified Gaussian kernel. In-place filtering is supported.
See also
sepFilter2D(), filter2D(), blur(), boxFilter(), bilateralFilter(), medianBlur()
-
高斯滤波器 (Gaussian Filter)
-
最有用的滤波器 (尽管不是最快的)。 高斯滤波是将输入数组的每一个像素点与 高斯内核 卷积将卷积和当作输出像素值。
-
还记得1维高斯函数的样子吗?
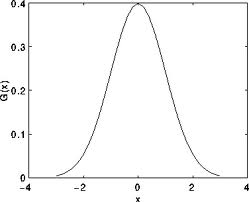
假设图像是1维的,那么观察上图,不难发现中间像素的加权系数是最大的, 周边像素的加权系数随着它们远离中间像素的距离增大而逐渐减小。
Note
2维高斯函数可以表达为 :
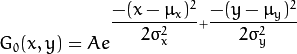
其中
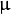 为均值 (峰值对应位置),
为均值 (峰值对应位置), 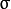 代表标准差 (变量
代表标准差 (变量 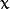 和 变量
和 变量 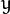 各有一个均值,也各有一个标准差)
各有一个均值,也各有一个标准差)-
高斯滤波器:
OpenCV函数 GaussianBlur 执行高斯平滑 :
我们输入4个实参 (详细的解释请参考 Reference):
- src: 输入图像
- dst: 输出图像
- Size(w, h): 定义内核的大小(需要考虑的邻域范围)。
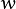 和
和 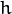 必须是正奇数,否则将使用
必须是正奇数,否则将使用  和
和  参数来计算内核大小。
参数来计算内核大小。  : x 方向标准方差, 如果是
: x 方向标准方差, 如果是  则
则  使用内核大小计算得到。
使用内核大小计算得到。 : y 方向标准方差, 如果是
: y 方向标准方差, 如果是  则
则  使用内核大小计算得到。.
使用内核大小计算得到。.
medianBlur
Blurs an image using the median filter.
-
C++:
void
medianBlur
(InputArray
src, OutputArray
dst, int
ksize
)
¶
-
Python:
cv2.
medianBlur
(src, ksize
[, dst
]
) → dst
-
Parameters: - src – input 1-, 3-, or 4-channel image; when ksize is 3 or 5, the image depth should be CV_8U, CV_16U, or CV_32F, for larger aperture sizes, it can only be CV_8U.
- dst – destination array of the same size and type as src.
- ksize – aperture linear size; it must be odd and greater than 1, for example: 3, 5, 7 ...
The function smoothes an image using the median filter with the
 aperture. Each channel of a multi-channel image is processed independently. In-place operation is supported.
aperture. Each channel of a multi-channel image is processed independently. In-place operation is supported.See also
中值滤波器 (Median Filter)¶
中值滤波将图像的每个像素用邻域 (以当前像素为中心的正方形区域)像素的 中值 代替
中值滤波器:
OpenCV函数 medianBlur 执行中值滤波操作:
我们用了3个参数:
- src: 输入图像
- dst: 输出图像, 必须与 src 相同类型
- i: 内核大小 (只需一个值,因为我们使用正方形窗口),必须为奇数。
bilateralFilter
Applies the bilateral filter to an image.
-
C++:
void
bilateralFilter
(InputArray
src, OutputArray
dst, int
d, double
sigmaColor, double
sigmaSpace, int
borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT
)
-
Python:
cv2.
bilateralFilter
(src, d, sigmaColor, sigmaSpace
[, dst
[, borderType
]
]
) → dst
-
Parameters: - src – Source 8-bit or floating-point, 1-channel or 3-channel image.
- dst – Destination image of the same size and type as src .
- d – Diameter of each pixel neighborhood that is used during filtering. If it is non-positive, it is computed from sigmaSpace .
- sigmaColor – Filter sigma in the color space. A larger value of the parameter means that farther colors within the pixel neighborhood (see sigmaSpace ) will be mixed together, resulting in larger areas of semi-equal color.
- sigmaSpace – Filter sigma in the coordinate space. A larger value of the parameter means that farther pixels will influence each other as long as their colors are close enough (see sigmaColor ). When d>0 , it specifies the neighborhood size regardless of sigmaSpace . Otherwise, d is proportional to sigmaSpace .
The function applies bilateral filtering to the input image, as described in http://www.dai.ed.ac.uk/CVonline/LOCAL_COPIES/MANDUCHI1/Bilateral_Filtering.html bilateralFilter can reduce unwanted noise very well while keeping edges fairly sharp. However, it is very slow compared to most filters.
Sigma values: For simplicity, you can set the 2 sigma values to be the same. If they are small (< 10), the filter will not have much effect, whereas if they are large (> 150), they will have a very strong effect, making the image look “cartoonish”.
Filter size: Large filters (d > 5) are very slow, so it is recommended to use d=5 for real-time applications, and perhaps d=9 for offline applications that need heavy noise filtering.
This filter does not work inplace.
双边滤波 (Bilateral Filter)
- 目前我们了解的滤波器都是为了 平滑 图像, 问题是有些时候这些滤波器不仅仅削弱了噪声, 连带着把边缘也给磨掉了。 为避免这样的情形 (至少在一定程度上 ), 我们可以使用双边滤波。
- 类似于高斯滤波器,双边滤波器也给每一个邻域像素分配一个加权系数。 这些加权系数包含两个部分, 第一部分加权方式与高斯滤波一样,第二部分的权重则取决于该邻域像素与当前像素的灰度差值。
- 详细的解释可以查看
双边滤波器
OpenCV函数 bilateralFilter 执行双边滤波操作:
我们使用了5个参数:
- src: 输入图像
- dst: 输出图像
- d: 像素的邻域直径
 : 颜色空间的标准方差
: 颜色空间的标准方差 : 坐标空间的标准方差(像素单位)
: 坐标空间的标准方差(像素单位)
-
-
转自:http://www.opencv.org.cn/opencvdoc/2.3.2/html/doc/tutorials/imgproc/gausian_median_blur_bilateral_filter/gausian_median_blur_bilateral_filter.html#smoothing






















 2527
2527

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








