FileInputStream、FileOutputStream和FileReader、FileWriter用法
前言
按读写方法,对文件的读写操作方法有以下几种类型:
1、以字节方式读写,适合所有文件类型;
2、以字符方式单个或按行读写,适合文本文件。
这里仅介绍使用2种常用的文件读写方法:字节方式读写和按行读写:FileInputStream、FileOutputStream和FileReader、FileWriter用法
一、FileInputStream和FileOutputStream用法
1、新建工程:FileOperation

2、新建包:

3、创建文件读写的工具类:FileOperation
代码如下:
package com.my.file;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 文件读写操作类
*/
public class FileOperation {
/**
* 根据输入的文件路径读取文件内容,仅支持读取文本文件。
* @param filePath
* @return
*/
public static String readFromFile(String filePath){
//输入检查:如果输入的文件不存在则返回空字符串
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.isFile()){
return "";
}
//开始读取文件
String result = "";
//读文件的缓存
byte[] temp = new byte[1024];
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
// 使用 循环读取, FileInputStream的read方法,会一次读取内容放到temp。
// 读取内容的多少根据temp定义的大小而定。如果没有数据可读了,read方法会返回-1.
while(fis.read(temp) != -1){
result = result + new String(temp);
}
fis.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(filePath + " 文件没有找到。");
return "";
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(filePath + " 读文件时发生异常。");
return "";
}
return result;
}
/**
* 将字节数组的内容写入文件
* @param filePath
* @param bytes
* @return
*/
public static boolean writeToFile(String filePath, byte[] bytes){
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()){ //文件若不存在则创建一个
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);
out.write(bytes);
out.flush();
out.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(filePath + " 文件没有找到。");
return false;
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(filePath + " 写文件时发生异常。");
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 使用FileReader读文本文件
* @param filePath
* @return
*/
public static String readFileByLine(String filePath){
//输入检查:如果输入的文件不存在则返回空字符串
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.isFile()){
return "";
}
//开始读取文件
String result = "";
String temp = "";
try {
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
while ((temp = br.readLine()) != null){
result = result + br;
}
br.close();
fr.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
/**
* 将字符串内容写入文件,使用FileWriter
* @param filePath
* @param bytes
* @return
*/
public static boolean writeToFileByFileWriter(String filePath,String content){
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()){ //文件若不存在则创建一个
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
bw.write(content);
bw.close();
fw.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(filePath + " 文件没有找到。");
return false;
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(filePath + " 写文件时发生异常。");
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
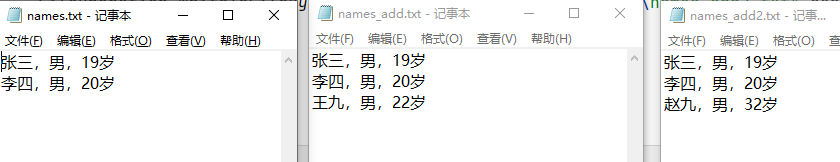
张三,男,19岁
李四,男,20岁
4、创建测试类(main函数入口类):FileOperationTest
代码如下:
package com.my.file;
public class FileOperationTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、按字节方式读取
//从文件读取内容并打印
String filePath="E:\\new\\1.11\\names.txt";
String content = FileOperation.readFromFile(filePath);
System.out.println(filePath+"文件里的内容为:\n"+content);
//将读取的文件内容,增加数据并写入另一个文件
content = content.trim();//去掉字符串首尾的空格
content = content + "\n" + "王九,男,22岁";
FileOperation.writeToFile("E:\\new\\1.11\\names_add.txt",content.getBytes());
//检查E:\new\1.11\names_add.txt的内容,应该为:
//张三,男,19岁
//李四,男,20岁
//王九,男,22岁
//2、按字符方式,按行读取
//从文件读取内容并打印
filePath="E:\\new\\1.11\\names.txt";
content = FileOperation.readFileByLine(filePath);
content = content.trim();
System.out.println(filePath+"文件里的内容为:\n"+content);
content = content + "\n" + "赵九,男,32岁";
FileOperation.writeToFileByFileWriter("E:\\new\\1.11\\names_add2.txt",content);
}
}
<font color=#999AAA >5、运行查看结果:

























 394
394

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








