time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Denis, who managed to buy flowers and sweets (you will learn about this story in the next task), went to a meeting with Nastya to invite her to become a couple. And so, they sit together in a cafe, chatting. Denis finally offers to be them together, but ... Nastya doesn't give any answer.
The poor boy was very upset due to that. He was so sad that he kicked some kind of scoreboard with numbers. The numbers are displayed in the same way as on an electronic clock: each digit position consists of 77 segments, which can be turned on or off to display different numbers. The picture shows how all 1010 decimal digits are displayed:
After the kick, some sticks stopped working, that is, some sticks might stop glowing if they glowed earlier. But Denis remembered how many sticks were glowing and how many are glowing now. Let exactly kk sticks break and we know which sticks are working now. Denis came up with the question: what is the maximum number that can burn on the board if you turn on exactly kk sticks (which are off now)?
It is allowed that the number includes leading zeros.
Input
The first line contains integer nn (1≤n≤2000)(1≤n≤2000) — the number of digits on scoreboard and kk (0≤k≤2000)(0≤k≤2000) — the number of sticks that stopped working.
The next nn lines contain one binary string of length 77, the ii-th of which encodes the ii-th digit of the scoreboard.
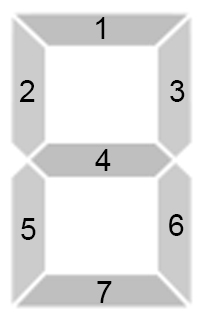
Each digit on the scoreboard consists of 77 sticks. We number them, as in the picture below, and let the ii-th place of the binary string be 00 if the ii-th stick is not glowing and 11 if it is glowing. Then a binary string of length 77 will specify which sticks glowing.
Thus, the sequences "1110111", "0010010", "1011101", "1011011", "0111010", "1101011", "1101111", "1010010", "1111111", "1111011" encode in sequence all digits from 00 to 99 inclusive.
Output
Print a single number consisting of nn digits — the maximum number that can be obtained if you turn on exactly kk sticks or −1−1, if it is impossible to turn on exactly kk sticks so that some sort of sequence appears on the scoreboard digits.
Examples
input
Copy
1 7 0000000
output
Copy
8
input
Copy
2 5 0010010 0010010
output
Copy
97
input
Copy
3 5 0100001 1001001 1010011
output
Copy
-1
Note
In the first test, we are obliged to include all 77 sticks and get one 88 digit on the scoreboard.
In the second test, we have sticks turned on so that units are formed. For 55 of additionally included sticks, you can get the numbers 0707, 1818, 3434, 4343, 7070, 7979, 8181 and 9797, of which we choose the maximum — 9797.
In the third test, it is impossible to turn on exactly 55 sticks so that a sequence of numbers appears on the scoreboard.
题意:给你从0~9的数字编码(只包含0或1,长度均为7)。现在有n(n<=2000)个长度为7的编码。本来全是数字的编码,但是其中某些编码中,1变成了0。
你需要将正好k(k<=2000)个0变回1,求原来的数字最大是多少。
思路:出题人出这种难度的题目刚好就是给我这种程度的菜鸡练的。。。
首先,很容易想到dp[i][j]表示前i个编码,用了j个1,能得到的最大数字。预处理一下每个7位01编码分别变成题目所给0~9需要变回1的数目。然后直接枚举j进行状态转移就可以。
由于数字长度过大(最高2000位,前导零不能去掉),我用dp数组使用string类型,荣获MLE一发。
发现i可以改为滚动数组,荣获TLE一发。
冷静了一会儿,发现我们其实没有必要记录最大的数字。假设到dp[i][j]时我们已经获得了最大数字,那么下一个dp[i+1][j']就直接优先从这个dp[i][j]转移即可(第dp[i+1][]优先从dp[i][j]转移,用一个vector记录优先获得的j'),并且对于相同的j',我们只取首先转移过来的状态的数字即可。这样第一个转移到dp[n][m]的一定是(字典序)最大的数。
其实本质就是,我们贪心按照字典序来进行状态转移。每次优先把上一个先转移的、数字最大的进行状态转移。再用一个pre[i][j]数组记录一下上一次的状态即可(因为最后还要输出高达2000位的答案)
细品,一定要细品。
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define rep(i,a,b) for(register int i=(a);i<=(b);i++)
#define dep(i,a,b) for(register int i=(a);i>=(b);i--)
using namespace std;
const int maxn=2e3+5;
//const double pi=acos(-1.0);
//const double eps=1e-9;
//const ll mo=1e9+7;
int n,m,k;
char s[maxn];
int dp[maxn][maxn],pre[maxn][maxn];
int count(int x){
int sum=0;
while(x){
sum++;
x&=(x-1);
}
return sum;
}
int a[]={119,18,93,91,58,107,111,82,127,123};
int zt[maxn][maxn];
vector<int>vc[maxn];
void print(int i,int zt){
if(i==1) printf("%d",dp[i][zt]);
else {
print(i-1,pre[i][zt]);
printf("%d",dp[i][zt]);
}
}
int main(){
rep(i,0,127)
{
dep(j,9,0)
if((a[j]|i)==a[j])
{
zt[i][a[j]]=count(a[j])-count(i);
vc[i].push_back(j);
}
else zt[i][a[j]]=-inf;
}
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
rep(i,0,n)
rep(j,0,m)
dp[i][j]=-1;
dp[0][0]=0;
int ct=0;
vector<int>vj,vv;
vv.push_back(0);
rep(i,1,n){
scanf("%s",s);
int ans=0,sum=1;
dep(k,6,0) {
if(s[k]&1) ans+=sum;
sum<<=1;
}
vj=vv;
vv.clear();
for(int jj=0;jj<vj.size();jj++) {
int j=vj[jj];
for(int k=0;k<vc[ans].size();k++){
int nk=vc[ans][k];
if(j+zt[ans][a[nk]]>m) continue;
if(dp[i-1][j]==-1) continue;
if(dp[i][j+zt[ans][a[nk]]]!=-1) continue;
dp[i][j+zt[ans][a[nk]]]=nk;
vv.push_back(j+zt[ans][a[nk]]);
//cout<<i<<" "<<j+zt[ans][a[nk]]<<" "<<ans<<" "<<zt[ans][a[nk]]<<" "<<nk<<endl;
pre[i][j+zt[ans][a[nk]]]=j;
//cout<<i<<" "<<j<<" "<<zt[ans][a[nk]]<<" "<<dp[i][j]<<endl;
}
}
}
if(dp[n][m]==-1) puts("-1");
else {
print(n,m);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
























 345
345











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








