

温馨提示:
本篇幅较长,非战斗人员请撤退。。。
一、包
包是什么?

包的本质
包的本质 实际上就是创建不同的文件夹来保存类文件
java常用的包

包的使用


二、访问修饰符
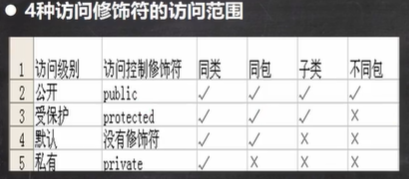
访问修饰符是什么?

访问范围(重点)
三、封装
封装是什么?
封装就是把抽象的属性和方法封装在一起,数据被保护在内部,程序的其他部分只能通过被授权的方法才能访问。
封装的好处:
1)隐藏实现细节
2)可以对数据进行验证,保证合理安全
封装步骤

四、继承
继承是是什么?

继承的使用
1)继承使代码的复用性提高了
2)代码的可扩张性和可维护性提高了
使用细节:
1)子类继承了所有的属性和方法,但是私有属性和方法不能在子类中直接方法,要通过父类提供的公共方法访问
2)子类必须调用父类的构造器完成父类的初始化
3)当创建子类对象时,不管使用子类的哪个构造器,默认情况下总会调用父类的无参构造器,如果父类没有提供无参构造器,则必须在子类的构造器中用super去指定使用父类的哪个构造完成对父类的初始化工作,否则编译不通过。
4)如果希望指定调用父类的哪个构造器,则显式的调用一下
5)super在使用时需放在构造器的第一行
6)super()和this()都只能放在构造器的第一行,因此这两个方法不能共存在一个构造器
7)java中所有类都是Object类的子类
8)父类构造器的调用不限于直接父类,将一直往上追溯到顶级父类(Object 类)
9)子类最多只能继承一个父类
10)不能滥用继承,必须满足is-a的关系
如:Person is a Music ×
Cat is a Anaimal √
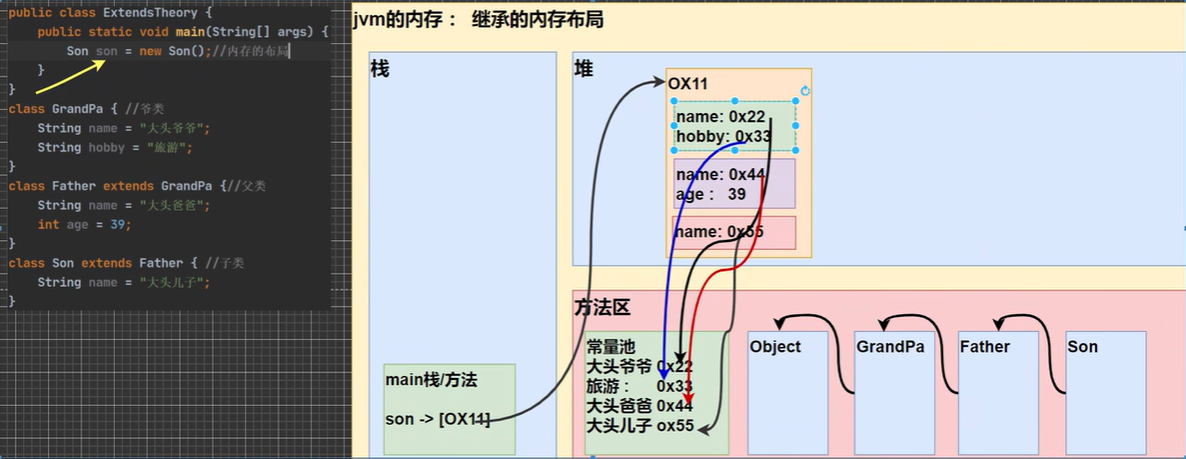
继承的本质
练习一:
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:
*/
public class A {
A(){
System.out.println("a");
}
A(String name){
System.out.println("a+name");
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:
*/
public class B extends A{
B(){
this("abc");
System.out.println("b");
}
B(String name){
System.out.println("b+name");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
B b = new B();
}
}输出:
a
b+name
b
五、super关键字
1.super关键字是什么?
super代表父类的引用,用于访问父类的属性,方法和构造器
2.基本语法

使用


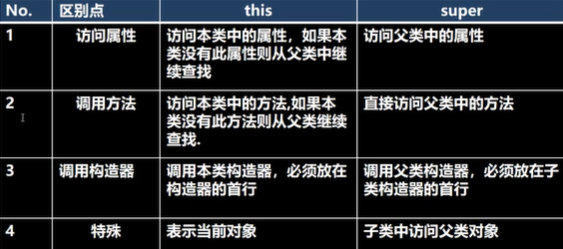
super和this的比较
六、方法的重写
重写是什么?
子类拥有和父类一样(返回值类型,方法名,参数)的方法称为重写。
方法重写细节

七、多态
方法和对象具有多种形态是面向对象的第三大特征,多态是建立在封装和继承的基础之上的。
方法的多态
重载和重写就体现了方法的多态
对象的多态(重点,难点)

1)对象多态案例:

/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:主人类
*/
public class Master {
private String name;
public Master(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void feed(Animal animal,Food food){
System.out.println("主人" + name + "给" + animal.getName() + "喂食" + food.getName());
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:动物父类
*/
public class Animal {
private String name;
public Animal(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:狗子类
*/
public class Dog extends Animal{
public Dog(String name) {
super(name);
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:猫子类
*/
public class Cat extends Animal{
public Cat(String name) {
super(name);
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:食物父类
*/
public class Food {
private String name;
public Food(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:鱼子类
*/
public class Fish extends Food{
public Fish(String name) {
super(name);
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:骨头子类
*/
public class Bone extends Food{
public Bone(String name) {
super(name);
}
}测试:
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:对象多态测试
*/
public class Poly01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Master master = new Master("小王");
Animal animal = new Dog("二哈");
Food food = new Bone("骨头");
master.feed(animal,food);
Master master2 = new Master("小王");
Animal animal2 = new Cat("喵喵");
Food food2 = new Bone("黄花鱼");
master2.feed(animal2,food2);
}
}输出:
主人小王给二哈喂食骨头
主人小王给喵喵喂食黄花鱼
2)多态的使用注意事项

向上转型:

/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:动物父类
*/
public class Animal {
String name="动物";
int age = 10;
public void eat(){
System.out.println("吃");
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:猫子类
*/
public class Cat extends Animal{
public void eat(){
System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
}
public void catchMouse(){
System.out.println("猫抓老鼠");
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:多态注意事项:向上转型
*/
public class PolyDetail {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//向上转型
Animal animal = new Cat();
animal.eat();
System.out.println("ok...");
}
}输出:
猫吃鱼
ok...
向下转型:
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:多态注意事项:向下转型
*/
public class PolyDetail {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//向下转型
Animal animal = new Cat();
Cat cat = (Cat)animal;
cat.catchMouse();
//Dog dog = (Dog)animal;//运行时会抛异常:ClassCastException
}
}输出:
猫抓老鼠
属性重写
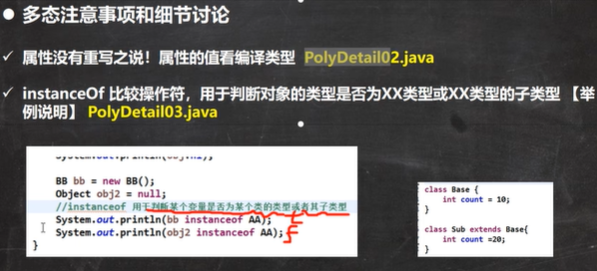
多态练习一:

多态练习二:
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:
*/
public class Base {
int count = 20;
public void display(){
System.out.println(this.count);
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:
*/
public class Sub extends Base{
int count = 10;
public void display(){
System.out.println(this.count);
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:
*/
public class PolyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sub s = new Sub();
System.out.println(s.count);//10
s.display();//10
Base b = s;
System.out.println(b == s);//true
System.out.println(b.count);//20
b.display();//10
}
}动态绑定机制

多态数组
应用案例:

多态数组一:
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:
*/
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String say(){
return name + "\t" +age;
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:
*/
public class Teacher extends Person{
private double salay;
public Teacher(String name, int age,double salay) {
super(name, age);
this.salay = salay;
}
public double getSalay() {
return salay;
}
public void setSalay(double salay) {
this.salay = salay;
}
@Override
public String say() {
return super.say() + "\t" + "salay:" + salay;
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:
*/
public class Student extends Person{
private double score;
public Student(String name, int age,double score) {
super(name, age);
this.score = score;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String say() {
return super.say() + "\t" + "score:" + score;
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:动态数组测试
*/
public class PolyArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person[] person = new Person[3];
person[0] = new Person("Jone",99);
person[1] = new Teacher("Smith",35,20000);
person[2] = new Student("Jack",18,98);
for (int i = 0; i < person.length; i++) {
String say = person[i].say();//动态绑定
System.out.println(say);
}
}
}输出
Jone 99
Smith 35 salay:20000.0
Jack 18 score:98.0
多态数组二:

/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:
*/
public class Teacher extends Person{
private double salay;
public Teacher(String name, int age,double salay) {
super(name, age);
this.salay = salay;
}
public double getSalay() {
return salay;
}
public void setSalay(double salay) {
this.salay = salay;
}
@Override
public String say() {
return super.say() + "\t" + "salay:" + salay;
}
public void teach(){
System.out.println("老师" + getName() + "正在授课");
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:
*/
public class Student extends Person{
private double score;
public Student(String name, int age,double score) {
super(name, age);
this.score = score;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String say() {
return super.say() + "\t" + "score:" + score;
}
public void study(){
System.out.println("学生" + getName() + "正在学习");
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:动态数组升级测试
*/
public class PolyArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person[] person = new Person[3];
person[0] = new Person("Jone",99);
person[1] = new Teacher("Smith",35,20000);
person[2] = new Student("Jack",18,98);
/*for (int i = 0; i < person.length; i++) {
String say = person[i].say();//动态绑定
System.out.println(say);
}*/
for (int i = 0; i < person.length; i++) {
String say = person[i].say();//动态绑定
System.out.println(say);
if(person[i] instanceof Teacher){
Teacher teacher = (Teacher) person[i];
teacher.teach();
}else if(person[i] instanceof Student){
Student student = (Student)person[i];
student.study();
}else{
}
}
}
}输出:
Jone 99
Smith 35 salay:20000.0
老师Smith正在授课
Jack 18 score:98.0
学生Jack正在学习
多态参数

应用案例:

代码示例
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:
*/
public class Employee {
private String name;
private double salary;
public Employee(String name, double salary) {
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
}
public Double getAnnual(){
return this.salary * 12;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:
*/
public class Worker extends Employee{
public Worker(String name, double salary) {
super(name, salary);
}
public void work(){
System.out.println("员工" + getName() + "在工作。。。");
}
@Override
public Double getAnnual() {
return super.getAnnual();
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:
*/
public class Manager extends Employee{
private Double bonus;
public Manager(String name, double salary,double bonus) {
super(name, salary);
this.bonus = bonus;
}
public void manage(){
System.out.println("经理"+ getName() + "在管理。。。");
}
@Override
public Double getAnnual() {
return super.getAnnual() + bonus;
}
}
/**
* @author: 程序员飞扬
* @description:
*/
public class PolyParameterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee employee = new Employee("张三", 12000);
Worker worker = new Worker("小王",10000);
Manager manager = new Manager("老李",12000,50000);
PolyParameterTest polyParameterTest = new PolyParameterTest();
polyParameterTest.showEmpAnnal(worker);
polyParameterTest.showEmpAnnal(manager);
polyParameterTest.testWork(worker);
polyParameterTest.testWork(manager);
}
public void showEmpAnnal(Employee e){
System.out.println(e.getAnnual());
}
public void testWork(Employee e){
if(e instanceof Worker){
((Worker) e).work();
}else if(e instanceof Manager){
((Manager) e).manage();
}
}
}输出:
120000.0
194000.0
员工小王在工作。。。
经理老李在管理。。。























 184
184











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










