DSA签名算法
详情移步ctf.wiki.org,导航如下:
DSA签名算法
题目
from Crypto.Util.number import getPrime, bytes_to_long, inverse, long_to_bytes
from Crypto.PublicKey import DSA
from hashlib import sha256
import random
from secret import flag
def gen(a):
p = getPrime(a)
q = getPrime(a)
r = getPrime(a)
x = getPrime(a)
n = p*q*r*x
phi = (p-1)*(q-1)*(r-1)*(x-1)
return n, phi, [p, q, r, x]
def sign(m, k, x, p, q, g):
hm = bytes_to_long(sha256(m).digest())
r = pow(g, k, p) % q
s = (hm + x*r) * inverse(k, q) % q
return r,s
e = 65537
a = 256
x = bytes_to_long(flag)
# print(x)
n, phi, n_factors = gen(a)
n_factors = sorted(n_factors)
print(f'n = {n}')
print(f'phi = {phi}')
m1 = long_to_bytes(n_factors[0] + n_factors[3])
m2 = long_to_bytes(n_factors[1] + n_factors[2])
# print(f'm1 = {m1}')
# print(f'm2 = {m2}')
key = DSA.generate(int(2048))
q = key.q
p = key.p
g = key.g
assert q > x
k = random.randint(1, q-1)
r1, s1 = sign(m1, k, x, p, q, g)
r2, s2 = sign(m2, k, x, p, q, g)
# print(f'k = {k}')
print(f'q = {q}')
print(f's1 = {s1}')
print(f'r1 = {r1}')
print(f's1 = {s1}')
print(f'r2 = {r2}')
print(f's2 = {s2}')
'''
n = 104228256293611313959676852310116852553951496121352860038971098657350022997841589403091722735802150153734050783858816709247647536393314564077002364012463220999962114186339228164032217361145009468516448617173972835797623658266515762201804936729547278758839604969469770650218191574897316410254695420895895051693
phi = 104228256293611313959676852310116852553951496121352860038971098657350022997837434645707418205268240995284026522165519145773852565112344453740579163420312890001524537570675468046604347184376661743552799809753709321949095844960227307733389258381950812717245522599433727311919405966404418872873961877021696812800
q = 24513014442114004234202354110477737650785387286781126308169912007819
s1 = 764450933738974696530033347966845551587903750431946039815672438603
r1 = 8881880595434882344509893789458546908449907797285477983407324325035
s1 = 764450933738974696530033347966845551587903750431946039815672438603
r2 = 8881880595434882344509893789458546908449907797285477983407324325035
s2 = 22099482232399385060035569388467035727015978742301259782677969649659
'''
分析以及脚本
过程分析
已知n和phi,如何分解n是一个问题
在谷歌找到一个已知n和phi分解n的脚本
脚本如下:
from math import gcd
from math import isqrt
from random import randrange
def factorize_multi_prime(N, phi):
"""
Recovers the prime factors from a modulus if Euler's totient is known.
This method works for a modulus consisting of any number of primes, but is considerably be slower than factorize.
More information: Hinek M. J., Low M. K., Teske E., "On Some Attacks on Multi-prime RSA" (Section 3)
:param N: the modulus
:param phi: Euler's totient, the order of the multiplicative group modulo N
:return: a tuple containing the prime factors
"""
prime_factors = set()
factors = [N]
while len(factors) > 0:
# Element to factorize.
N = factors[0]
w = randrange(2, N - 1)
i = 1
while phi % (2 ** i) == 0:
sqrt_1 = pow(w, phi // (2 ** i), N)
if sqrt_1 > 1 and sqrt_1 != N - 1:
# We can remove the element to factorize now, because we have a factorization.
factors = factors[1:]
p = gcd(N, sqrt_1 + 1)
q = N // p
if is_prime(p):
prime_factors.add(p)
elif p > 1:
factors.append(p)
if is_prime(q):
prime_factors.add(q)
elif q > 1:
factors.append(q)
# Continue in the outer loop
break
i += 1
return tuple(prime_factors)
分解n得到n_factors,由于
n_factors = sorted(n_factors)
m1 = long_to_bytes(n_factors[0] + n_factors[3])
m2 = long_to_bytes(n_factors[1] + n_factors[2])
所以解得m1和m2
此题采用了同一个随机密钥k签名了两次
假设签名的消息为 m1,m2,显然,两者的 r 的值一样,此外

这里我们除了 x 和 k 不知道剩下的均知道,那么

两式相减
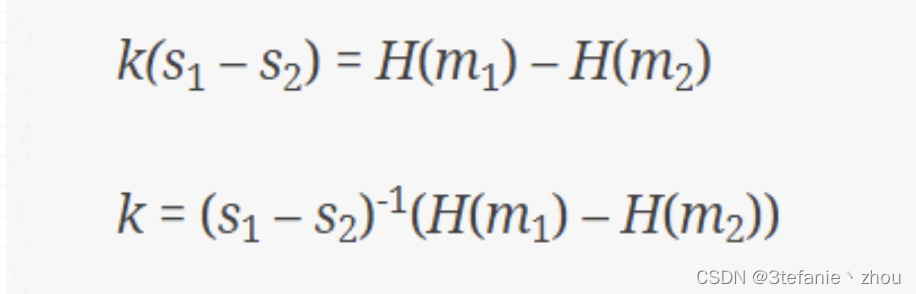
此时 即可解出 k
当我们知道随机密钥k,q,hm,r,s时候,并且那么我们就可以根据签名算法
def sign(m, k, x, p, q, g):
hm = bytes_to_long(sha256(m).digest())
r = pow(g, k, p) % q
s = (hm + x*r) * inverse(k, q) % q
return r,s
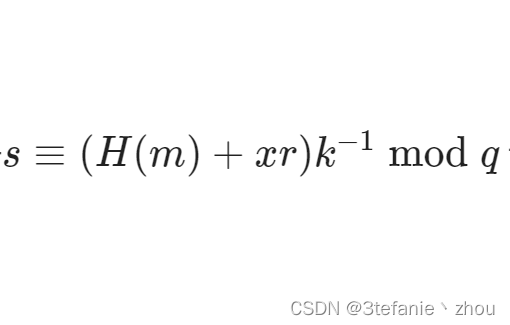
计算私钥出 x,即flag

sage解密脚本
import libnum
from hashlib import sha256
from math import gcd
from random import randrange
import gmpy2
def factorize_multi_prime(N, phi):
"""
Recovers the prime factors from a modulus if Euler's totient is known.
This method works for a modulus consisting of any number of primes, but is considerably be slower than factorize.
More information: Hinek M. J., Low M. K., Teske E., "On Some Attacks on Multi-prime RSA" (Section 3)
:param N: the modulus
:param phi: Euler's totient, the order of the multiplicative group modulo N
:return: a tuple containing the prime factors
"""
prime_factors = set()
factors = [N]
while len(factors) > 0:
# Element to factorize.
N = factors[0]
w = randrange(2, N - 1)
i = 1
while phi % (2 ** i) == 0:
sqrt_1 = pow(w, phi // (2 ** i), N)
if sqrt_1 > 1 and sqrt_1 != N - 1:
# We can remove the element to factorize now, because we have a factorization.
factors = factors[1:]
p = gcd(N, sqrt_1 + 1)
q = N // p
if is_prime(p):
prime_factors.add(p)
elif p > 1:
factors.append(p)
if is_prime(q):
prime_factors.add(q)
elif q > 1:
factors.append(q)
# Continue in the outer loop
break
i += 1
return tuple(prime_factors)
n = 104228256293611313959676852310116852553951496121352860038971098657350022997841589403091722735802150153734050783858816709247647536393314564077002364012463220999962114186339228164032217361145009468516448617173972835797623658266515762201804936729547278758839604969469770650218191574897316410254695420895895051693
phi = 104228256293611313959676852310116852553951496121352860038971098657350022997837434645707418205268240995284026522165519145773852565112344453740579163420312890001524537570675468046604347184376661743552799809753709321949095844960227307733389258381950812717245522599433727311919405966404418872873961877021696812800
q = 24513014442114004234202354110477737650785387286781126308169912007819
s1 = 764450933738974696530033347966845551587903750431946039815672438603
r1 = 8881880595434882344509893789458546908449907797285477983407324325035
s2 = 22099482232399385060035569388467035727015978742301259782677969649659
r2 = 8881880595434882344509893789458546908449907797285477983407324325035
n_factors = factorize_multi_prime(n, phi)
n_factors = sorted(n_factors)
m1 = libnum.n2s(int(n_factors[0]) + int(n_factors[3]))
m2 = libnum.n2s(int(n_factors[1]) + int(n_factors[2]))
hm1 = libnum.s2n(sha256(m1).digest())
hm2 = libnum.s2n(sha256(m2).digest())
k = gmpy2.invert((s1-s2),q)*(hm1-hm2) % q
x = (s1*k-hm1)*gmpy2.invert(r1,q) % q
print(libnum.n2s(int(x)))
flag:
flag{ea16de7-1981-11ed-b58f}
【世间唯有痴情,不容他人取笑,也唯有痴情最可笑。】






















 2228
2228











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








