今天来简单讲讲HashSet,因为HashSet实际上是基于HashMap来实现的,底层使用HashMap来保存集合元素,关于HashMap会在接下来的博客中加以介绍,所以这次HashSet就简单写一写了。(以下都是基于jdk1.8)
| 继承树 |
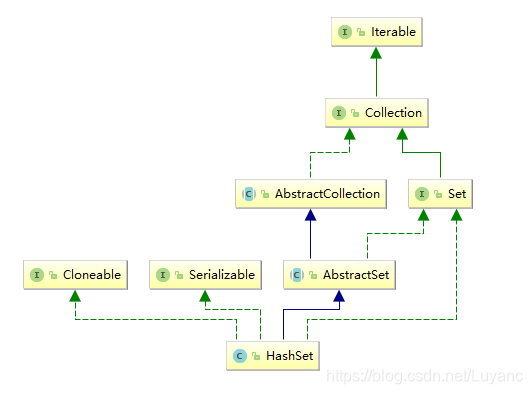
HashSet的继承树如下图:
| 类注释解析 |
(1)基于HashMap实现,不能保证集合的迭代顺序;特别是它不能保证元素的顺序不随时间而改变。且允许null值。
This class implements the <tt>Set</tt> interface, backed by a hash table
(actually a <tt>HashMap</tt> instance). It makes no guarantees as to the
iteration order of the set; in particular, it does not guarantee that the
order will remain constant over time. This class permits the <tt>null</tt>
element.
(2)线程不安全。
Note that this implementation is not synchronized.
可通过如下方式使用线程安全的操作:
Set s = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet(...));
(3)通过集合的iterator方法返回的迭代器实现了快速失败机制,如果迭代器被创建之后,集合被修改(除了迭代器自己的remove方法修改),迭代器将会抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。因此,在并发修改的情况下,迭代器会快速失败,而不会等待。
需要注意的是,它不能保证在非并发修改的情况下,快速报错不会被触发,迭代器只能尽力而为。因此,不应该编写一段依赖ConcurrentModificationException异常的程序。迭代器的快速报错应该只用于检测Bug.
* <p>The iterators returned by this class's <tt>iterator</tt> method are
* <i>fail-fast</i>: if the set is modified at any time after the iterator is
* created, in any way except through the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt>
* method, the Iterator throws a {@link ConcurrentModificationException}.
* Thus, in the face of concurrent modification, the iterator fails quickly
* and cleanly, rather than risking arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at
* an undetermined time in the future.
*
* <p>Note that the fail-fast behavior of an iterator cannot be guaranteed
* as it is, generally speaking, impossible to make any hard guarantees in the
* presence of unsynchronized concurrent modification. Fail-fast iterators
* throw <tt>ConcurrentModificationException</tt> on a best-effort basis.
* Therefore, it would be wrong to write a program that depended on this
* exception for its correctness: <i>the fail-fast behavior of iterators
* should be used only to detect bugs.</i>
| 源码之旅 |
(1)使用不需要序列化的HashMap类型的对象来保存集合元素
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;
(2)默认initial capacity是16,load factor 是0.75
/**
* Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has
* default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
(3)指定初始容量大小和加载因子的构造函数。
public HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
(4)指定初始容量大小的构造函数。
public HashSet(int initialCapacity) {
map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity);
}
(5)常用方法:
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return map.keySet().iterator();
}
public int size() {
return map.size();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return map.isEmpty();
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return map.containsKey(o);
}
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return map.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
public void clear() {
map.clear();
}
可以看到这些方法都是用的HashMap的方法,留待后面讲HashMap的时候再详细总结。





















 1645
1645











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








