愉快地聊一聊PriorityQueue的特点吧~(以下都是基于jdk1.8)
| 一棵树 |
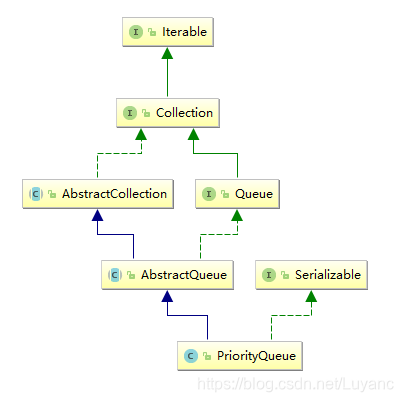
PriorityQueue的继承树如下图:
| 基本特点 |
(1)底层使用可变数组Object[ ] queue,数组容量按需增长
(2)它是一个比较标准的队列,不是绝对标准,因为它不是严格的先进先出,内部按队列元素的大小进行了重新排序(定制排序、自然排序),所以要放入集合中的元素必须实现Comparable接口。
(3)不能存储null
(4)默认数组初始长度是11,也可以指定初始容量(也是实际会分配的容量)
(5)线程不安全。可以使用java.util.concurrent.PriorityBlockingQueue(线程安全)
(6)当遍历一个 PriorityQueue 时,没有任何顺序保证
(7)通过判断如果需要扩容,先扩容,再插入。【数组容量满了之后才会触发扩容】
(8)二叉堆【根元素最小】
(9)默认数组最大长度是MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8
| 源码之旅 |
这里只取部分源码进行分析:扩容,以及二叉堆的调整。
(1)扩容,以offer为例:
//添加元素
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//记录二叉堆被调整的次数
modCount++;
//size是数组元素的个数
int i = size;
//如果当前数组元素个数>=数组容量,则进行扩容
if (i >= queue.length)
//扩容,扩容的最小容量是当前数组元素个数加1
grow(i + 1);
size = i + 1;
if (i == 0)
queue[0] = e;
else
//从下往上调整二叉堆
siftUp(i, e);
return true;
}
再看具体的扩容方法:
/**
* Increases the capacity of the array.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = queue.length;
// Double size if small; else grow by 50%
//数组现有容量小于64时,扩容的容量就是现有容量的2倍,再加2
//否则,扩容的容量就是现有数组容量+现有数组容量/2
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((oldCapacity < 64) ?
(oldCapacity + 2) :
(oldCapacity >> 1));
// overflow-conscious code
//扩容容量是否超过数组默认最大长度
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
//指向扩容后的新数组
queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
再看Arrays类下的静态方法Arrays.copyOf方法:
//Cloning
/**
* Copies the specified array, truncating or padding with nulls (if necessary)
* so the copy has the specified length. For all indices that are
* valid in both the original array and the copy, the two arrays will
* contain identical values. For any indices that are valid in the
* copy but not the original, the copy will contain <tt>null</tt>.
* Such indices will exist if and only if the specified length
* is greater than that of the original array.
* The resulting array is of exactly the same class as the original array.
*
* @param <T> the class of the objects in the array
* @param original the array to be copied
* @param newLength the length of the copy to be returned
* @return a copy of the original array, truncated or padded with nulls
* to obtain the specified length
* @throws NegativeArraySizeException if <tt>newLength</tt> is negative
* @throws NullPointerException if <tt>original</tt> is null
* @since 1.6
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) {
return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass());
}
/**
* Copies the specified array, truncating or padding with nulls (if necessary)
* so the copy has the specified length. For all indices that are
* valid in both the original array and the copy, the two arrays will
* contain identical values. For any indices that are valid in the
* copy but not the original, the copy will contain <tt>null</tt>.
* Such indices will exist if and only if the specified length
* is greater than that of the original array.
* The resulting array is of the class <tt>newType</tt>.
*
* @param <U> the class of the objects in the original array
* @param <T> the class of the objects in the returned array
* @param original the array to be copied
* @param newLength the length of the copy to be returned
* @param newType the class of the copy to be returned
* @return a copy of the original array, truncated or padded with nulls
* to obtain the specified length
* @throws NegativeArraySizeException if <tt>newLength</tt> is negative
* @throws NullPointerException if <tt>original</tt> is null
* @throws ArrayStoreException if an element copied from
* <tt>original</tt> is not of a runtime type that can be stored in
* an array of class <tt>newType</tt>
* @since 1.6
*/
public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
(2)二叉堆的调整:
siftUp:自下往上调整
/**
* Inserts item x at position k, maintaining heap invariant by
* promoting x up the tree until it is greater than or equal to
* its parent, or is the root.
*
* To simplify and speed up coercions and comparisons. the
* Comparable and Comparator versions are separated into different
* methods that are otherwise identical. (Similarly for siftDown.)
*
* @param k the position to fill
* @param x the item to insert
*/
private void siftUp(int k, E x) {
if (comparator != null)
//定制排序
siftUpUsingComparator(k, x);
else
//自然排序
siftUpComparable(k, x);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void siftUpComparable(int k, E x) {
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>) x;
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
Object e = queue[parent];
if (key.compareTo((E) e) >= 0)
break;
queue[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = key;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void siftUpUsingComparator(int k, E x) {
//找到二叉堆中的索引k的父节点,从此处开始,拿待插入元素与其比较,
//如果待插入元素大于父节点元素的值,则在k索引处插入元素。
//否则,父节点值下移,待插入元素继续与上层父节点比较。
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
Object e = queue[parent];
if (comparator.compare(x, (E) e) >= 0)
break;
queue[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = x;
}
siftDown:自上往下调整
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E poll() {
if (size == 0)
return null;
int s = --size;
modCount++;
//取出堆顶元素,为堆中最后一个元素(变为待插入元素)寻找插入位置,进行二叉堆的调整
E result = (E) queue[0];
E x = (E) queue[s];
queue[s] = null;
if (s != 0)
//调整二叉堆
siftDown(0, x);
return result;
}
/**
* Inserts item x at position k, maintaining heap invariant by
* demoting x down the tree repeatedly until it is less than or
* equal to its children or is a leaf.
*
* @param k the position to fill
* @param x the item to insert
*/
private void siftDown(int k, E x) {
if (comparator != null)
//定制排序
siftDownUsingComparator(k, x);
else
//自然排序
siftDownComparable(k, x);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void siftDownComparable(int k, E x) {
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>)x;
int half = size >>> 1; // loop while a non-leaf
while (k < half) {
int child = (k << 1) + 1; // assume left child is least
Object c = queue[child];
int right = child + 1;
if (right < size &&
((Comparable<? super E>) c).compareTo((E) queue[right]) > 0)
c = queue[child = right];
if (key.compareTo((E) c) <= 0)
break;
queue[k] = c;
k = child;
}
queue[k] = key;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void siftDownUsingComparator(int k, E x) {
int half = size >>> 1;
//自上往下调整,找到根节点的左孩子child和右孩子right,
//比较得到左右孩子中较小的一个。
//待插入元素与较小孩子元素进行比较,
//如果待插入元素大于较小的孩子元素,则较小孩子上移,继续循环此过程。
//否则,k处即为待插入位置。
while (k < half) {
int child = (k << 1) + 1;
Object c = queue[child];
int right = child + 1;
if (right < size &&
comparator.compare((E) c, (E) queue[right]) > 0)
c = queue[child = right];
if (comparator.compare(x, (E) c) <= 0)
break;
queue[k] = c;
k = child;
}
queue[k] = x;
}





















 1088
1088











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








