一.最长公共子串问题集(Longest Common Substring/LCS)
最长公共子串问题的基本表述为:
给定两个字符串,求出它们之间最长的相同子字符串的长度。
最直接的解法自然是找出两个字符串的所有子字符串进行比较看他们是否相同,然后取得相同最长的那个。对于一个长度为n的字符串,它有n(n+1)/2 个非空子串。所 以假如两个字符串的长度同为n,通过比较各个子串其算法复杂度大致为O(n4)。这还没有考虑字符串比较所需的时间。简单想想其实并不需要取出所有的子串,而只要考虑每个子串的开始位置就可以,这样可以把复杂度减到O(n3)。
但这个问题最好的解决办法是动态规划法,在后边会更加详细介绍这个问题使用动态规划法的契机:有重叠的子问题。进而可以通过空间换时间,让复杂度优化到O(n2),代价是空间复杂度从O(1)一下子提到了O(n2)。
- #include<string.h>
- #define M 100
-
-
- char* LCS(char left[],char right[])
- {
-
- int lenLeft=strlen(left),lenRight=strlen(right),k;
-
-
- char*c=malloc(lenRight),*p;
-
- int start,end,len,i,j;
- end=len=0;
-
- for(i=0; i<lenLeft; i++)
- {
-
-
-
- for(j=lenRight-1; j>=0; j--)
- {
- if(left[i] == right[j])
- {
- if(i==0||j==0)
- c[j]=1;
- else
- {
- c[j]=c[j-1]+1;
- }
- }
- else
- c[j] = 0;
- if(c[j] > len)
- {
- len=c[j];
- end=j;
- }
- }
- }
- start=end-len+1;
-
-
- p =(char*)malloc(len+1);
- for(i=start; i<=end; i++)
- {
- p[i-start] = right[i];
- }
- p[len]='\0';
- return p;
- }
-
- void main()
- {
- char str1[M],str2[M];
- printf("请输入字符串1:");
-
- gets(str1)
- printf("请输入字符串2:");
-
- gets(str2);
- printf("最长子串为:");
-
- printf("%s\n",LCS(str1,str2));
-
- }
字符串1:21232523311324
字符串2:312123223445
数组c的变化情况为:
0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 2 0 3 0 1 1 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 4 0 0 2 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 1 0 5 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 2 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0
0 2 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 1 0 2 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0
长:14(串1的长度),宽:12(串2的长度)
最长子串为:21232
评论:该算法只能打印出最长公共子串中的一个,而不是全部解.
或者如下代码:
-
-
- #include "stdafx.h"
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- using namespace std;
-
- string getLCSLength(string &s, string &t);
-
- int main()
- {
- string s,t;
- cout<<"请输入字符串s:"<<endl;
- cin>>s;
- cout<<"请输入字符串t:"<<endl;
- cin>>t;
- cout<<"最长公共子串为:"<<endl;
- cout<<getLCSLength(s,t)<<endl;
- return 0;
- }
-
- string getLCSLength(string &s, string &t)
- {
- int p = s.length();
- int q = t.length();
-
- string **num = new string *[p];
- for(int i=0;i<p;i++)
- {
- num[i] = new string[q];
- }
-
- char char1 = '\0';
- char char2 = '\0';
-
- int len = 0;
- string lcs = "" ;
-
- for(int i=0; i<p; i++)
- {
- for (int j=0; j<t.length(); j++)
- {
- char1 = s.at(i);
- char2 = t.at(j);
- if(char1!=char2)
- {
- num[i][j] = "" ;
- }
- else
- {
- if (i==0||j==0)
- {
- num[i][j]=char1;
- }
- else
- {
- num[i][j]=num[i-1][j-1]+char1;
- }
- if(num[i][j].length()>len)
- {
- len = num[i][j].length() ;
- lcs = num[i][j];
- }
- else if(num[i][j].length()==len)
- {
- lcs = lcs + "," + num[i][j];
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- for(int i=0;i<p;i++)
- {
- delete[] num[i];
- }
- delete[] num;
-
- return lcs;
- }
这个代码在len相等时保存了已经计算完毕的最大公共字串,从而使多个字串的保存得以实现。
二.最长公共子序列问题集(
Longest Common Subsequence/LCS
)
最长公共子序列问题的基本表述为:
字符序列的子序列是指从给定字符序列中随意地(不一定连续)去掉若干个字符(可能一个也不去掉)后所形成的字符序列。令给定的字符序列X=“x0,x1,…,xm-1”,序列Y=“y0,y1,…,yk-1”是X的子序列,存在X的一个严格递增下标序列<i0,i1,…,ik-1>,使得对所有的j=0,1,…,k-1,有xij=yj。例如,X=“ABCBDAB”,Y=“BCDB”是X的一个子序列。
最长公共子串(Longest Common Substirng)和最长公共子序列(Longest Common Subsequence,LCS)的区别为:子串是串的一个连续的部分,子序列则是从不改变序列的顺序,而从序列中去掉任意的元素而获得新的序列;也就是说,子串中字符的位置必须是连续的,子序列则可以不必连续。
LCS问题即最长公共子序列问题,它
不
要求所求得的字符在所给的字符串中是连续的
动态规划算法分以下4个步骤:
- 描述最优解的结构
- 递归定义最优解的值
- 按自底向上的方式计算最优解的值 //此3步构成动态规划解的基础。
- 由计算出的结果构造一个最优解。 //此步如果只要求计算最优解的值时,可省略。
例如,设所给的两个序列为X=A B C B D A B 和Y= B D C A B A。由算法LCS_LENGTH和LCS计算出的结果如下图所示:
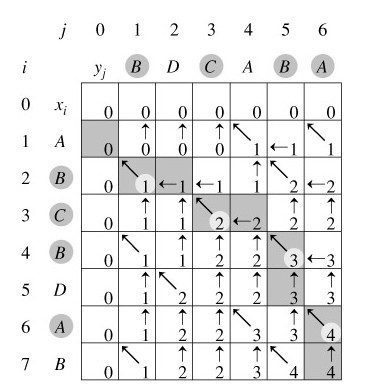
我来说明下此图(参考算法导论)。在序列X={A,B,C,B,D,A,B}和 Y={B,D,C,A,B,A}上,由LCS_LENGTH计算出的表c和b。第i行和第j列中的方块包含了c[i,j]的值以及指向b[i,j]的箭头。在c[7,6]的项4,表的右下角为X和Y的一个LCS的长度。对于i,j>0,项c[i,j]仅依赖于是否有xi=yi,及项c[i-1,j]和c[i,j-1]的值,这几个项都在c[i,j]之前计算。为了重构一个LCS的元素,从右下角开始跟踪b[i,j]的箭头即可,这条路径标示为阴影,这条路径上的每一个“↖”对应于一个使xi=yi为一个LCS的成员的项(高亮标示)。
所以根据上述图所示的结果,程序将最终输出:“B C B A”,或“B D A B”。
可能还是有读者对上面的图看的不是很清楚,下面,我再通过对最大子序列,最长公共子串与最长公共子序列的比较来阐述相关问题@Orisun:
- 最大子序列:最大子序列是要找出由数组成的一维数组中和最大的连续子序列。比如{5,-3,4,2}的最大子序列就是{5,-3,4,2},它的和是8,达到最大;而{5,-6,4,2}的最大子序列是{4,2},它的和是6。你已经看出来了,找最大子序列的方法很简单,只要前i项的和还没有小于0那么子序列就一直向后扩展,否则丢弃之前的子序列开始新的子序列,同时我们要记下各个子序列的和,最后找到和最大的子序列。更多请参看:程序员编程艺术第七章、求连续子数组的最大和。
- 最长公共子串:找两个字符串的最长公共子串,这个子串要求在原字符串中是连续的。其实这又是一个序贯决策问题,可以用动态规划来求解。我们采用一个二维矩阵来记录中间的结果。这个二维矩阵怎么构造呢?直接举个例子吧:"bab"和"caba"(当然我们现在一眼就可以看出来最长公共子串是"ba"或"ab")
b a b
c 0 0 0
a 0 1 0
b 1 0 1
a 0 1 0
我们看矩阵的斜对角线最长的那个就能找出最长公共子串。
不过在二维矩阵上找最长的由1组成的斜对角线也是件麻烦费时的事,下面改进:当要在矩阵是填1时让它等于其左上角元素加1。
b a b
c 0 0 0
a 0 1 0
b 1 0 2
a 0 2 0
这样矩阵中的最大元素就是最长公共子串的长度。
在构造这个二维矩阵的过程中由于得出矩阵的某一行后其上一行就没用了,所以实际上在程序中可以用一维数组来代替这个矩阵。
- 最长公共子序列LCS问题:最长公共子序列与最长公共子串的区别在于最长公共子序列不要求在原字符串中是连续的,比如ADE和ABCDE的最长公共子序列是ADE。
我们用动态规划的方法来思考这个问题如是求解。首先要找到状态转移方程:
等号约定,C1是S1的最右侧字符,C2是S2的最右侧字符,S1‘是从S1中去除C1的部分,S2'是从S2中去除C2的部分。
LCS(S1,S2)等于:
(1)LCS(S1,S2’)
(2)LCS(S1’,S2)
(3)如果C1不等于C2:LCS(S1’,S2’);如果C1等于C2:LCS(S1',S2')+C1;
边界终止条件:如果S1和S2都是空串,则结果也是空串。
下面我们同样要构建一个矩阵来存储动态规划过程中子问题的解。这个矩阵中的每个数字代表了该行和该列之前的LCS的长度。与上面刚刚分析出的状态转移议程相对应,矩阵中每个格子里的数字应该这么填,它等于以下3项的最大值:
(1)上面一个格子里的数字
(2)左边一个格子里的数字
(3)左上角那个格子里的数字(如果C1不等于C2);左上角那个格子里的数字+1(如果C1等于C2)
举个例子:
G C T A
0 0 0 0 0
G 0 1 1 1 1
B 0 1 1 1 1
T 0 1 1 2 2
A 0 1 1 2 3
填写最后一个数字时,它应该是下面三个的最大者:
(1)上边的数字2
(2)左边的数字2
(3)左上角的数字2+1=3,因为此时C1==C2
所以最终结果是3。
在填写过程中我们还是记录下当前单元格的数字来自于哪个单元格,以方便最后我们回溯找出最长公共子串。有时候左上、左、上三者中有多个同时达到最大,那么任取其中之一,但是在整个过程中你必须遵循固定的优先标准。在我的代码中优先级别是左上>左>上。
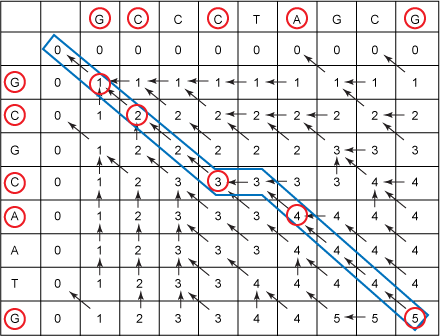
下图给出了回溯法找出LCS的过程:
-
-
-
-
- #include "stdafx.h"
- #include "string.h"
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
-
-
- enum decreaseDir {kInit = 0, kLeft, kUp, kLeftUp};
-
- void LCS_Print(int **LCS_direction, char* pStr1, char* pStr2, size_t row, size_t col);
-
-
-
-
-
- int LCS(char* pStr1, char* pStr2)
- {
- if(!pStr1 || !pStr2)
- return 0;
-
- size_t length1 = strlen(pStr1);
- size_t length2 = strlen(pStr2);
- if(!length1 || !length2)
- return 0;
-
- size_t i, j;
-
-
- int **LCS_length;
- LCS_length = (int**)(new int[length1]);
- for(i = 0; i < length1; ++ i)
- LCS_length[i] = (int*)new int[length2];
-
- for(i = 0; i < length1; ++ i)
- for(j = 0; j < length2; ++ j)
- LCS_length[i][j] = 0;
-
-
- int **LCS_direction;
- LCS_direction = (int**)(new int[length1]);
- for( i = 0; i < length1; ++ i)
- LCS_direction[i] = (int*)new int[length2];
-
- for(i = 0; i < length1; ++ i)
- for(j = 0; j < length2; ++ j)
- LCS_direction[i][j] = kInit;
-
- for(i = 0; i < length1; ++ i)
- {
- for(j = 0; j < length2; ++ j)
- {
-
- if(i == 0 || j == 0)
- {
- if(pStr1[i] == pStr2[j])
- {
- LCS_length[i][j] = 1;
- LCS_direction[i][j] = kLeftUp;
- }
- else
- {
- if(i > 0)
- {
- LCS_length[i][j] = LCS_length[i - 1][j];
- LCS_direction[i][j] = kUp;
- }
- if(j > 0)
- {
- LCS_length[i][j] = LCS_length[i][j - 1];
- LCS_direction[i][j] = kLeft;
- }
- }
- }
-
-
- else if(pStr1[i] == pStr2[j])
- {
- LCS_length[i][j] = LCS_length[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
- LCS_direction[i][j] = kLeftUp;
- }
-
- else if(LCS_length[i - 1][j] > LCS_length[i][j - 1])
- {
- LCS_length[i][j] = LCS_length[i - 1][j];
- LCS_direction[i][j] = kUp;
- }
-
- else
- {
- LCS_length[i][j] = LCS_length[i][j - 1];
- LCS_direction[i][j] = kLeft;
- }
- }
- }
- LCS_Print(LCS_direction, pStr1, pStr2, length1 - 1, length2 - 1);
- return LCS_length[length1 - 1][length2 - 1];
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- void LCS_Print(int **LCS_direction, char* pStr1, char* pStr2, size_t row, size_t col)
- {
- if(pStr1 == NULL || pStr2 == NULL)
- return;
-
- size_t length1 = strlen(pStr1);
- size_t length2 = strlen(pStr2);
-
- if(length1 == 0 || length2 == 0 || !(row < length1 && col < length2))
- return;
-
-
- if(LCS_direction[row][col] == kLeftUp)
- {
- if(row > 0 && col > 0)
- LCS_Print(LCS_direction, pStr1, pStr2, row - 1, col - 1);
-
-
- printf("%c", pStr1[row]);
- }
- else if(LCS_direction[row][col] == kLeft)
- {
-
- if(col > 0)
- LCS_Print(LCS_direction, pStr1, pStr2, row, col - 1);
- }
- else if(LCS_direction[row][col] == kUp)
- {
-
- if(row > 0)
- LCS_Print(LCS_direction, pStr1, pStr2, row - 1, col);
- }
- }
-
- int main(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
- {
- char* pStr1="abcde";
- char* pStr2="acde";
- LCS(pStr1,pStr2);
- printf("\n");
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
比较一下简化版本:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <string.h>
- #define MAXLEN 100
-
- void LCSLength(char *x, char *y, int m, int n, int c[][MAXLEN], int b[][MAXLEN])
- {
- int i, j;
-
- for(i = 0; i <= m; i++)
- c[i][0] = 0;
- for(j = 1; j <= n; j++)
- c[0][j] = 0;
- for(i = 1; i<= m; i++)
- {
- for(j = 1; j <= n; j++)
- {
- if(x[i-1] == y[j-1])
- {
- c[i][j] = c[i-1][j-1] + 1;
- b[i][j] = 0;
- }
- else if(c[i-1][j] >= c[i][j-1])
- {
- c[i][j] = c[i-1][j];
- b[i][j] = 1;
- }
- else
- {
- c[i][j] = c[i][j-1];
- b[i][j] = -1;
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- void PrintLCS(int b[][MAXLEN], char *x, int i, int j)
- {
- if(i == 0 || j == 0)
- return;
- if(b[i][j] == 0)
- {
- PrintLCS(b, x, i-1, j-1);
- printf("%c ", x[i-1]);
- }
- else if(b[i][j] == 1)
- PrintLCS(b, x, i-1, j);
- else
- PrintLCS(b, x, i, j-1);
- }
-
- int main(int argc, char **argv)
- {
- char x[MAXLEN] = {"ABCBDAB"};
- char y[MAXLEN] = {"BDCABA"};
- int b[MAXLEN][MAXLEN];
- int c[MAXLEN][MAXLEN];
- int m, n;
-
- m = strlen(x);
- n = strlen(y);
-
- LCSLength(x, y, m, n, c, b);
- PrintLCS(b, x, m, n);
-
- return 0;
- }
三.最长回文子串
(
Longest Palindromic Substring/ LPS
)
最长回文子串问题的基本表述为:
所谓回文子串就是S的某个子串Ai...Aj为回文。例如,对字符串S=abcdcbeba,它的回文子串有:bcdcb,cdc,beb,满足题目要求的最长回文子串为bcdcb。
最长
算法基本要点:首先用一个非常巧妙的方式,将所有可能的奇数/偶数长度的回文子串都转换成了奇数长度:在每个字符的两边都插入一个特殊的符号。比如 abba 变成 #a#b#b#a#, aba变成 #a#b#a#。 为了进一步减少编码的复杂度,可以在字符串的开始加入另一个特殊字符,这样就不用特殊处理越界问题,比如$#a#b#a#。
下面以字符串12212321为例,经过上一步,变成了 S[] = "$#1#2#2#1#2#3#2#1#";
然后用一个数组 P[i] 来记录以字符S[i]为中心的最长回文子串向左/右扩张的长度(包括S[i]),比如S和P的对应关系:
S # 1 # 2 # 2 # 1 # 2 # 3 # 2 # 1 #
P 1 2 1 2 5 2 1 4 1 2 1 6 1 2 1 2 1
(p.s. 可以看出,P[i]-1正好是原字符串中回文串的总长度)
下面计算P[i],该算法增加两个辅助变量id和mx,其中id表示最大回文子串中心的位置,mx则为id+P[id],也就是最大回文子串的边界。
这个算法的关键点就在这里了:如果mx > i,那么P[i] >= MIN(P[2 * id - i], mx - i)。
具体代码如下:
- if(mx > i)
- {
- p[i] = (p[2*id - i] < (mx - i) ? p[2*id - i] : (mx - i));
- }
- else
- {
- p[i] = 1;
- }
当 mx - i > P[j] 的时候,以S[j]为中心的回文子串包含在以S[id]为中心的回文子串中,由于 i 和 j 对称,以S[i]为中心的回文子串必然包含在以S[id]为中心的回文子串中,所以必有 P[i] = P[j],见下图。

当 P[j] > mx - i 的时候,以S[j]为中心的回文子串不完全包含于以S[id]为中心的回文子串中,但是基于对称性可知,下图中两个绿框所包围的部分是相同的,也就是说以S[i]为中心的回文子串,其向右至少会扩张到mx的位置,也就是说 P[i] >= mx - i。至于mx之后的部分是否对称,就只能一个一个匹配了。

对于 mx <= i 的情况,无法对 P[i]做更多的假设,只能P[i] = 1,然后再去匹配了
下面给出原文,进一步解释算法为线性的原因

源代码:
- #include "stdio.h"
- #include <iostream>
- #include <cstring>
- using namespace std;
- #define GetMin(x, y) ((x)<(y)?(x):(y))
- const int N=50;
-
- int MaxSub(char InterQuantityChar[],int iInterLength)
- {
- int SubLength[N];
- int MaxID = 0, MaxAsist = 0;
- int i = 1;
- for(i=1; i<iInterLength; i++)
- {
- if( MaxAsist > i )
- SubLength[i] = GetMin( SubLength[2*MaxID-i], SubLength[MaxID]+MaxID-i );
- else
- SubLength[i] = 1;
- for(; InterQuantityChar[i+SubLength[i]] == InterQuantityChar[i-SubLength[i]]; SubLength[i]++)
- ;
- if( SubLength[i] + i > MaxAsist )
- {
- MaxAsist = SubLength[i] + i;
- MaxID = i;
- }
- }
- MaxID = 0;
- for (i = 0; i < iInterLength; ++i)
- {
- if ( MaxID < SubLength[i] )
- {
- MaxID = SubLength[i];
- }
- }
- return MaxID;
- }
-
- int GetMax(int InterChar[],int iInterLength)
- {
- int i = 0;
- int iMax = 0;
- for (i = 0; i < iInterLength; ++i)
- {
- if ( iMax < InterChar[i] )
- {
- iMax = InterChar[i];
- }
- }
- return iMax;
- }
-
- int InitChar(char InterQuantityChar[],char OriginQuantityChar[])
- {
- int iOriginalLength = strlen( OriginQuantityChar );
-
- int iInterLength = 0;
- InterQuantityChar[0] = '$';
- InterQuantityChar[1] = '#';
- for (iInterLength = 0; iInterLength < iOriginalLength; iInterLength++)
- {
- InterQuantityChar[ 2*iInterLength + 2 ] = OriginQuantityChar[ iInterLength ];
- InterQuantityChar[ 2*iInterLength + 3 ] = '#';
- }
- iInterLength = iOriginalLength * 2 + 2;
- return iInterLength;
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- int iOriginalLength = 0, iInterLength = 0, MaxID = 0;
-
- char OriginChar[N], InterChar[N];
- int* SubLength;
- while(scanf("%s", OriginChar)!=EOF)
- {
- iOriginalLength = strlen( OriginChar );
- iInterLength = InitChar( InterChar , OriginChar );
- MaxID = MaxSub( InterChar, iInterLength );
- printf("%d\n", MaxID-1);
- }
- return 0;
- }
四.字符串匹配
(string match)
字符串匹配问题的基本表述为:
其输入是原字符串(String)和子串(又称模式,Pattern)组成,输出为子串在原字符串中的首次出现的位置。通常精确的字符串搜索算法包括暴力搜索(Brute force),KMP, BM(Boyer Moore), sunday, robin-karp 以及 bitap。
在朴素的字符串模式匹配算法上,当遇到主串和模式串的字符不能匹配成功时,不论已经匹配了多少字符都要进行指针回溯,再开始下一轮的匹配。
这样效率是十分的低下的。KMP算法,是在朴素的模式匹配算法的基础上,实现了匹配不成功时,不对主串指针进行回溯,使模式匹配的时间复杂度
降低为:O(n + m)。
对KMP算法的理解,在网上查找了不少资料,也看了算法导论上的描述,一直是一知半解。有次闲暇之余,想像着将模式串、主串都看着是条直线,进行了下推导,才恍然大悟。
KMP算法的核心思想是,在s[i] 和 p[j]不匹配时,不对主串进行指针回溯,而是在模式串中p中寻找k,用s[i] 和 p[k]进行下一轮的匹配。
在这里,将主串 S 和模式串 P 都看成是一条直线,故而在S[i] 和 P[j] 匹配不成共时,有如下情形:

图1 s[i] 和 p[j] 匹配不成功
即是:p[1…j-1] == s[i-j+1,…,i-1].
p[j] 和 s[i] 不匹配,现在要在模式串p[1,…,j-1]确定一个位置k(1<= k < j-1),用p[k]和s[i]进行下一轮匹配,那么k必须要满足以下条件:
p[1,..,k-1] == s[i-k+1, … , i-1] .
将模式串和主串都看着一条直线,那么就有下图:

图2 使用p[k]和s[i]进行下一轮匹配
由于 1<= k < j-1,那么将两图合并起来会有什么效果呢?

从上图可以看出,当s[i]和p[j]匹配不成功时,假如能用p[k]和s[i]进行下一轮匹配,则有:
s[i-k+1], … , i-1] == p[j-k+1,…,j-1] == p[1,…,k-1] 。
就是说,当s[i] 和 p[j] 匹配不成功时,最对主串不进行指针回溯,而是用p[k]和s[i]进行匹配时,k必须满足以下条件:
p[1,…,k-1] == p[j-k+1, … , j-1]。
- /代码4-1
-
- void get_nextval(char const* ptrn, int plen, int* nextval)
- {
- int i = 0;
- nextval[i] = -1;
- int j = -1;
- while( i < plen-1 )
- {
- if( j == -1 || ptrn[i] == ptrn[j] )
- {
- ++i;
- ++j;
-
- if( ptrn[i] != ptrn[j] )
- nextval[i] = j;
- else
- nextval[i] = nextval[j];
- }
- else
- j = nextval[j];
- }
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
- int kmp_search(char const* src, int slen, char const* patn, int plen, int const* nextval, int pos)
- {
- int i = pos;
- int j = 0;
- while ( i < slen && j < plen )
- {
- if( j == -1 || src[i] == patn[j] )
- {
- ++i;
- ++j;
- }
- else
- {
- j = nextval[j];
-
-
- }
- }
- if( j >= plen )
- return i-plen;
- else
- return -1;
- }
-
- void print_progress(char const* src, int src_index, char const* pstr, int pstr_index)
- {
- cout<<src_index<<"\t"<<src<<endl;
- cout<<pstr_index<<"\t";
- for( int i = 0; i < src_index-pstr_index; ++i )
- cout<<" ";
- cout<<pstr<<endl;
- cout<<endl;
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- std::string src = "aabcabcebafabcabceabcaefabcacdabcab";
- std::string prn = "abac";
-
- int* nextval = new int[prn.size()];
-
- get_nextval(prn.data(), prn.size(), nextval);
-
-
- for( int i = 0; i < prn.size(); ++i )
- cout<<nextval[i]<<"\t";
- cout<<endl;
-
- cout<<"result sub str: "<<src.substr( kmp_search(src.data(), src.size(), prn.data(), prn.size(), nextval, 0) )<<endl;
- system("pause");
-
- delete[] nextval;
- return 0;
- }
五.
最大子序列和
(string match)
最大子序列和问题的基本表述为:
给定一整数序列A1, A2,... An (可能有负数),求A1~An的一个子序列Ai~Aj,使得Ai到Aj的和最大。
例如:整数序列-2, 11, -4, 13, -5, 2, -5, -3, 12, -9的最大子序列的和为21。
- #include "stdafx.h"
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include<string.h>
- #include<stdlib.h>
- void get_max(int a[], int n)
- {
- int temp_start, temp_end, final_start, final_end;
- int temp_max, final_max;
- temp_start = temp_end = 0;
- final_start = final_end = 0;
- temp_max = final_max = a[0];
- int i;
- for (i = 1; i<n; i++)
- {
- if (temp_max + a[i]>a[i])
- {
- temp_max += a[i];
- temp_end++;
- }
- else
- {
- temp_max = a[i];
- temp_start = i;
- temp_end = i;
- }
- if (temp_max > final_max)
- {
- final_max = temp_max;
- final_start = temp_start;
- final_end = temp_end;
- }
- }
- printf("%d-%d:%d\n", final_start, final_end, final_max);
- }
-
- int main(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
- {
- int num[] = { 1, -3 ,2, 4, -1, 5, -6, 3 };
- int len = sizeof(num) / sizeof(int);
- get_max(num, len);
- return 0;
- }
如果只需要求最大子序列和,不需要记录起止点,则代码简化为:
- int max_sum(int a[],int size)
- {
- int max=0,temp=0;
- for (int i=0;i!=size;i++)
- {
- temp+=a[i];
- if(temp>max)
- max=temp;
- else if(temp<=0)
- temp=0;
- }
- return max;
- }





























 1645
1645

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








